
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Main Page}} | ||
<onlyinclude> | <onlyinclude> | ||
{{H2 | |||
{{ | |L=Joseph Smith/Polygamy/Marriages to young women | ||
|H=Joseph Smith's marriages to young women | |||
|S= | |||
|L1=Question: Why was Joseph Smith sealed to young women? | |||
|L2=Question: Was Joseph Smith a "serial practitioner of statutory rape?" | |||
}} | |||
</onlyinclude> | |||
{{:Question: Why was Joseph Smith sealed to young women?}} | |||
{{ | {{:Question: Was Joseph Smith a "serial practitioner of statutory rape?"}} | ||
Joseph Smith | |||
{{SeeAlso|Polygamy_book/Age_of_wives|l1=Polygamy book: Age of wives}} | {{SeeAlso|Polygamy_book/Age_of_wives|l1=Polygamy book: Age of wives}} | ||
{{HalesSite | {{HalesSite | ||
|subject1=Joseph Smith’s Sealings to Young Wives: FAQ | |subject1=Joseph Smith’s Sealings to Young Wives: FAQ | ||
|link1=http://josephsmithspolygamy.org/ | |link1=http://josephsmithspolygamy.org/common-questions/14-year-old-wives-teenage-brides/ | ||
|summary1= | |summary1=Hales deals with this sometimes-controversial aspect of Joseph's plural marriages. | ||
|subject4=The Faith of the Nauvoo Polygamists | |||
== == | |link4=http://josephsmithspolygamy.org/stories-faith-polygamists/ | ||
|summary4=Why did early members of the Church practice polygamy? Were they all dupes? Easily manipulated? Religious fanatics who believed Joseph could do no wrong? This article explores the initial reactions and eventual decisions made by the first generation of polygamists in Nauvoo. | |||
|subject2=Joseph Smith’s Personal Polygamy | |||
|link2=http://josephsmithspolygamy.org/beginnings-mormon-polygamy/#AReluctantPolygamist | |||
|summary2=Many are quick to declare that Joseph's polygamy sprang from religious extremism and/or sexual desire. This article explores the difficulties that Joseph had with plural marriage, and evidence for what truly motivated his acts. | |||
}} | |||
[[de: | {{Critical sources box:Joseph Smith/Polygamy/Marriages to young women/CriticalSources}} | ||
[[ | {{endnotes sources}} | ||
<!-- PLEASE DO NOT REMOVE ANYTHING BELOW THIS LINE --> | |||
[[fi:Joseph Smith/Moniavioisuus/Joseph Smithin nuoret vaimot]] | |||
[[de:Joseph Smith/Polygamie/Eheschließung mit jungen Frauen]] | |||
[[es:José Smith/Poligamia/Esposas plurales/Matrimonios con mujeres jóvenes]] | |||
Jump to details:
Some of Joseph Smith's polygamous marriages were to young women.
Joseph Smith's polygamous marriages to young women may seem difficult to understand or explain today, but in his own time such age differences were not typically an obstacle to marriage. The plural marriages were unusual, to say the least; the younger ages of the brides were much less so. Critics do not provide this perspective because they wish to shock the audience and have them judge Joseph by the standards of the modern era, rather than his own time.
The information we have on Joseph Smith's plural marriages is sketchy, simply because there were few official records kept at the time because of the fear of misunderstanding and persecution. What we do know is culled from journals and reminiscences of those who were involved.
The most conservative estimates indicate that Joseph entered into plural marriages with 29–33 women, 7 of whom were under the age of 18. The youngest was Helen Mar Kimball, daughter of LDS apostle Heber C. Kimball, who was 14. The rest were 16 (two) or 17 (three). One wife (Maria Winchester) about which virtually nothing is known, was either 14 or 15.
Some people have concluded that Helen did have sexual relations with Joseph, which would have been proper considering that they were married with her consent and the consent of her parents. However, historian Todd Compton does not hold this view; he criticized the anti-Mormons Jerald and Sandra Tanner for using his book to argue for sexual relations, and wrote:
The Tanners made great mileage out of Joseph Smith's marriage to his youngest wife, Helen Mar Kimball. However, they failed to mention that I wrote that there is absolutely no evidence that there was any sexuality in the marriage, and I suggest that, following later practice in Utah, there may have been no sexuality. (p. 638) All the evidence points to this marriage as a primarily dynastic marriage. [2]
In other words, polygamous marriages often had other purposes than procreation—one such purpose was likely to tie faithful families together, and this seems to have been a purpose of Joseph's marriage to the daughter of a faithful Apostle. (See: Law of Adoption.)
Critics who assume plural marriage "is all about sex" may be basing their opinion on their own cultural biases and assumptions, rather than upon the actual motives of Church members who participated in the practice.
Hales has identified a further line of evidence which suggests that Helen's marriage was not consummated. In 1892, the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (RLDS, now Community of Christ) brought suit against the Hendrickite, or "Temple Lot" break-off group. They claimed that the Independence, Missouri temple site was rightfully RLDS property, since they were the direct heirs of Joseph Smith's original religious group.
Although not embracing plural marriage themselves, the Temple Lot group was anxious to demonstrate that Joseph Smith had taught plural marriage--for, if this was so, then the RLDS (who denied that Joseph had practiced it, and certainly did not embrace the doctrine) would have difficulty proving that they were the direct successors to the church founded by Joseph.
Hales reports:
Nine of Joseph Smith's plural wives were still living when depositions started at Salt Lake City on March 14, 1892. Three were polyandrous wives (Zina Huntington Jacobs Young, Mary Elizabeth Rollins Lightner, and Patty Bartlett Sessions) and six were nonpolyandrous (Helen Mar Kimball, Martha McBride, Almera Johnson, Emily Partridge, Malissa Lott, and Lucy Walker.) Factors evidently affecting the choice of witnesses involved the health and travel distances for the women, and importantly, whether their polygamous marriages to the Prophet included conjugality. Non-sexual sealings would have been treated as spiritual marriages of little importance and would have played right into the hands of RLDS attorneys....
Among nonpolyandrous wives who were not summoned was Martha McBride who lived in Hooper, Utah (thirty-seven miles to the north). McBride's relationship with Joseph Smith is poorly documented, with no evidence of sexual relations....Also passed by was Salt Lake resident Helen Mar Kimball who had written two books defending the practice of plural marriage. Her sealing to the Prophet ocurred when she was only fourteen and the presence or absence of sexual relations in her plural marriage is debated by historians.
Throughout the length question-and-answer sessions with Malissa Lott, Emily Partridge, and Lucy Walker, the details of their polygamous marriages with Joseph Smith were paramount; the physical aspect of sexuality was a core issue. If [Helen or others] could not testify to such relations, their testimonies as the Prophet's polygamous wives could hurt the Church of Christ (Temple Lot) cause. [3]
Helen "took pen and paper in hand before she died to describe vividly her ties as a member of the Latter-day Saint Church during its first two decades of existence in a series of articles published in the Woman's Exponent" in the 1880s. [4]:ix Some of her articles dealt with plural marriage: "Her personal remembrances of those days constitute an important source that, taken together with other first-hand accounts by participants, provides a more complete view of the introduction of one of the most distinctive features of nineteenth-century Mormonism." [4]:xvHelen Mar's writings, an important source of LDS history, were published by BYU's Religious Studies Center in 1997 in a book entitled A Woman's View: Helen Mar Whitney's Reminiscences of Early Church History. The book also includes her 1881 autobiography to her children wherein, concerning her marriage to the Prophet Joseph Smith, she wrote:
I have long since learned to leave all with [God], who knoweth better than ourselves what will make us happy. I am thankful that He has brought me through the furnace of affliction & that He has condesended to show me that the promises made to me the morning that I was sealed to the Prophet of God will not fail & I would not have the chain broken for I have had a view of the principle of eternal salvation & the perfect union which this sealing power will bring to the human family & with the help of our Heavenly Father I am determined to so live that I can claim those promises.[4]:487
One of the wives about whom we know relatively little is Fanny Alger, Joseph's first plural wife, whom he came to know in early 1833 when she stayed at the Smith home as a house-assistant of sorts to Emma (such work was common for young women at the time). There are no first-hand accounts of their relationship (from Joseph or Fanny), nor are there second-hand accounts (from Emma or Fanny's family). All that we do have is third hand accounts, most of them recorded many years after the events.
Unfortunately, this lack of reliable and extensive historical detail leaves much room for critics to claim that Joseph Smith had an affair with Fanny and then later invented plural marriage as way to justify his actions. The problem is we don't know the details of the relationship or exactly of what it consisted, and so are left to assume that Joseph acted honorably (as believers) or dishonorably (as critics).
There is some historical evidence that Joseph Smith knew as early as 1831 that plural marriage would be restored, so it is perfectly legitimate to argue that Joseph's relationship with Fanny Alger was such a case. Mosiah Hancock (a Mormon) reported a wedding ceremony; and apostate Mormons Ann Eliza Webb Young and her father Chauncery both referred to Fanny's relationship as a "sealing." Ann Eliza also reported that Fanny's family was very proud of Fanny's relationship with Joseph, which makes little sense if it was simply a tawdry affair. Those closest to them saw the marriage as exactly that—a marriage.
Plural marriage was certainly not in keeping with the values of "mainstream America" in Joseph Smith's day. However, modern readers also judge the age of the marriage partners by modern standards, rather than the standards of the nineteenth century.
Within Todd Compton's book on Joseph Smith's marriages, he also mentions the following monogamous marriages:
| Wife | Wife's Age | Husband | Husband's Age | Difference in age |
| Lucinda Pendleton | 18 | William Morgan | 44 | 26 |
| Marinda Johnson | 19 | Orson Hyde | 29 | 10 |
| Almira McBride | 17 | Sylvester Stoddard | 40s | >23 |
| Fanny Young | 44 | Roswell Murray | 62 | 18 |
And, a variety of Mormon and non-Mormon historical figures had similar wide differences in age:
| Husband | Husband's Age | Wife | Wife's Age | Difference |
| Johann Sebastian Bach | 36 | Anna Magdalena Wilcke | 19 | 17 |
| Lord Baden-Powell (Founder of Scouting) | 55 | Olave Soames | 23 | 32 [5] |
| William Clark (of the Lewis and Clark Expedition) | 37 | Julia Hancock | 16 | 21 [6] |
| Grover Cleveland (22nd, 24th US President) | 49 | Frances Cleveland | 21 | 28 |
| Thomas A. Edison | 24 | Mary Stillwell | 16 | 8 |
| Thomas A. Edison | 39 | Mina Miller | 20 | 19 |
| Martin Harris (1808) | 24 | Lucy Harris (1st cousin) | 15 | 9 [7] |
| Levi Ward Hancock (7 April 1803) | 30 | Clarissa Reed | 17 | 13 [8] |
| Andrew Mellon | 45 | Nora Mary McMullen | 20 | 25 |
| John Milton (Paradise Lost) | 34 | Mary Powell (1st wife) | 17 | 17 |
| John Milton | 55 | Elizabeth Minshull (3rd wife) | 24 | 31 |
| Edgar Allen Poe | 26 | Virginia Clemn (his cousin) | 13 | 13 |
| Alexander Smith | 23 | Elizabeth Kendall | 16 | 7 [9] |
| David Hyrum Smith | 26 | Clara Hartshorn | 18 | 8 [10] |
| Frederick Granger Williams Smith | 21 | Annie Maria Jones | 16 | 5 [11] |
| Joseph Smith, III | 66 | Ada Rachel Clark | 29 | 37 [12] |
| John Tyler (US President, 1844) | 56 | Julia Gardiner | 24 | 32[13] |
| Almonzo Wilder | 28 | Laura Ingalls (Little House) | 18 | 10 |
Statistical information for marital ages is available from the 1850 census. [14] Using a 1% random sample of individuals, 989 men and 962 women indicated they had been married within the last year. The plot below breaks these individuals down by census age.
Of note is that 41.7% of women married as teenagers compared to only 4.1% of men. The mean age for men was more than five years older than that for women (27.6 vs. 22.5). For young women, marriage in the early to mid teens was rare, but not unheard of as both the anecdotal and statistical evidence above show. Teenage brides married a husband that averaged 6.6 +/- 4.7 (std) years older. To put that in perspective, 13% of the time the husband was over 10 years older than his teenage wife.
The 21st century reader is likely to see marriages of young women to much older men as inappropriate, though it is still not uncommon. In the U.S. today, in most states, the "age of consent" is set by statute to be 18. This is the age at which a person can consent to sexual activity or to marriage. However, even today, the "marriageable age," the minimum age at which a person may marry with parental permission or with a judge's permission, is 16 in most states. In California, there is no minimum marriageable age; a child of any age may marry with parental consent. [15] So Joseph Smith's marriage to Helen Mar Kimball, having been done with her parents' permission, would be legal in California even today, except for the polygamous aspect of it.
But the modern age limits in most states represent only the modern attitude. The age of consent under English common law was ten. United States law did not raise the age of consent until the late nineteenth century. In Joseph Smith's day, most states still had the declared age of consent to be ten. Some had raised it to twelve, and Delaware had lowered it to seven! [16]
It is significant that none of Joseph's contemporaries complained about the age differences between polygamous or monogamous marriage partners. This was simply part of their environment and culture; it is unfair to judge nineteenth century members by twenty-first century social standards. As one non-LDS scholar of teenage life in American history noted:
Until the twentieth century, adult expectations of young people were determined not by age but by size. If a fourteen-year-old looked big and strong enough to do a man's work on a farm or in a factory or mine, most people viewed him as a man. And if a sixteen-year-old was slower to develop and couldn't perform as a man, he wasn't one. For, young women, the issue was much the same. To be marriageable was the same as being ready for motherhood, which was determined by physical development, not age....
The important thing, though, was that the maturity of each young person was judged individually. [17]
In past centuries, women would often die in childbirth, and men often remarried younger women afterwards. Women often married older men, because these were more financially established and able to support them than men their own age.
Critics of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints have accused Joseph Smith and other early Latter-day Saint men of pedophilia because they married teenaged women. Indeed, they have emphatically declared that such marriages were against 19th-century societal norms. However, historians and other experts have repeatedly stated that young people married throughout the 19th-century, and such marriages have been relatively common throughout all of US history. This article examines some of the accusations of early Latter-day Saint pedophilia and places such marriages within the greater historical and social context, illustrating that such marriages were normal and acceptable for their time and place.
Summary: This page collects responses to questions surrounding the marriage of Joseph Smith to his youngest wife, Helen Mar Kimball.
Some points regarding the circumstances surrounding the sealing of Helen Mar Kimball to Joseph Smith[19]:
During the winter of 1843, there were plenty of parties and balls. … Some of the young gentlemen got up a series of dancing parties, to be held at the Mansion once a week. … I had to stay home, as my father had been warned by the Prophet to keep his daughter away from there, because of the blacklegs and certain ones of questionable character who attended there. … I felt quite sore over it, and thought it a very unkind act in father to allow [my brother] to go and enjoy the dance unrestrained with others of my companions, and fetter me down, for no girl loved dancing better than I did, and I really felt that it was too much to bear. It made the dull school still more dull, and like a wild bird I longer for the freedom that was denied me; and thought myself a much abused child, and that it was pardonable if I did murmur.[25]
Brian Hales observes:
In 1892, the RLDS Church led by Joseph Smith III sued the Church of Christ (Temple Lot),[26] disputing its claim to own the temple lot in Independence, Missouri. The Church of Christ (Temple Lot) held physical possession, and the RLDS Church took the official position that since it was the true successor of the church originally founded by Joseph Smith, it owned the property outright.[27]
Although the LDS Church was not a party to the suit, it provided support to the Church of Christ (Temple Lot). The issue was parsed this way: If the Church of Christ (Temple Lot) could prove that plural marriage was part of the original Church, then the RLDS Church was obviously not the true successor since it failed to practice such a key doctrine.[28]During the proceedings, three plural wives of Joseph Smith (Lucy Walker, Emily Partridge, and Malissa Lott) were deposed.[29]
Why was Helen Kimball Whitney not also called to testify in the Temple Lot trial regarding her marriage relations with Joseph Smith? She lived in Salt Lake City, geographically much closer than two of the three witnesses: Malissa Lott live thirty miles south in Lehi, and Lucy Walker lived eighty-two miles north in Logan.
A likely reason is that Helen could not provide the needed testimony. All three of Joseph Smith’s wives who did testify affirmed that sexual relations were part of their plural marriages to the Prophet.[30] Testifying of either an unconsummated time-and-eternity sealing or an eternity-only marriage would have hurt the Temple Lot case. Such marriages would have been easily dismissed as unimportant.
If Helen’s plural union did not include conjugality, her testimony would not have been helpful. If it did, the reason for not inviting her to testify is not obvious. Not only was Helen passed over, but Mary Elizabeth Lightner, Zina Huntington, and Patty Sessions, who were sealed to Joseph in eternity-only marriages, were similarly not deposed.
The lack of evidence does not prove the lack of sexual relations, but these observations are consistent with an unconsummated union.
I am thankful that He [Heavenly Father] has brought me through the furnace of affliction and that He has condescended to show me that the promises made to me the morning that I was sealed to the Prophet of God will not fail and I would not have the chain broken for I have had a view of the principle of eternal salvation and the perfect union which this sealing power will bring to the human family and with the help of our Heavenly Father I am determined to so live that I can claim those promises.[31]
Later in life, Helen wrote a poem entitled "Reminiscences." It is often cited for the critics' claims:
The first portion of the poem expresses the youthful Helen's attitude. She is distressed mostly because of the loss of socialization and youthful ideas about romance. But, as Helen was later to explain more clearly in prose, she would soon realize that her youthful pout was uncalled for—she saw that her plural marriage had, in fact, protected her. "I have long since learned to leave all with Him, who knoweth better than ourselves what will make us happy," she noted after the poem.[33]
Thus, she would later write of her youthful disappointment in not being permitted to attend a party or dance:
During the winter of 1843, there were plenty of parties and balls. … Some of the young gentlemen got up a series of dancing parties, to be held at the Mansion once a week. … I had to stay home, as my father had been warned by the Prophet to keep his daughter away from there, because of the blacklegs and certain ones of questionable character who attended there. … I felt quite sore over it, and thought it a very unkind act in father to allow [my brother] to go and enjoy the dance unrestrained with others of my companions, and fetter me down, for no girl loved dancing better than I did, and I really felt that it was too much to bear. It made the dull school still more dull, and like a wild bird I longed for the freedom that was denied me; and thought myself a much abused child, and that it was pardonable if I did murmur.
I imagined that my happiness was all over and brooded over the sad memories of sweet departed joys and all manner of future woes, which (by the by) were of short duration, my bump of hope being too large to admit of my remaining long under the clouds. Besides my father was very kind and indulgent in other ways, and always took me with him when mother could not go, and it was not a very long time before I became satisfied that I was blessed in being under the control of so good and wise a parent who had taken counsel and thus saved me from evils, which some others in their youth and inexperience were exposed to though they thought no evil. Yet the busy tongue of scandal did not spare them. A moral may be drawn from this truthful story. "Children obey thy parents," etc. And also, "Have regard to thy name, for that shall continue with you above a thousand great treasures of gold." "A good life hath but few days; but a good name endureth forever.[34]
So, despite her youthful reaction, Helen uses this as an illustration of how she was being a bit immature and upset, and how she ought to have trusted her parents, and that she was actually protected from problems that arose from the parties she missed.
Critics of the Church provide a supposed "confession" from Helen, in which she reportedly said:
I would never have been sealed to Joseph had I known it was anything more than ceremony. I was young, and they deceived me, by saying the salvation of our whole family depended on it.[35]
Author Todd Compton properly characterizes this source, noting that it is an anti-Mormon work, and calls its extreme language "suspect."[36]
Author George D. Smith tells his readers only that this is Helen "confiding," while doing nothing to reveal the statement's provenance from a hostile source.[37] Newell and Avery tell us nothing of the nature of this source and call it only a "statement" in the Stanley Ivins Collection;[38] Van Wagoner mirrors G. D. Smith by disingenuously writing that "Helen confided [this information] to a close Nauvoo friend," without revealing its anti-Mormon origins.[39]
To credit this story at face value, one must also admit that Helen told others in Nauvoo about the marriage (something she repeatedly emphasized she was not to do) and that she told a story at variance with all the others from her pen during a lifetime of staunch defense of plural marriage.[40]
As Brian Hales writes:
It is clear that Helen’s sealing to Joseph Smith prevented her from socializing as an unmarried lady. The primary document referring to the relationship is an 1881 poem penned by Helen that has been interpreted in different ways ...
After leaving the church, dissenter Catherine Lewis reported Helen saying: "I would never have been sealed to Joseph had I known it was anything more than a ceremony."
Assuming this statement was accurate, which is not certain, the question arises regarding her meaning of "more than a ceremony"? While sexuality is a possibility, a more likely interpretation is that the ceremony prevented her from associating with her friends as an unmarried teenager, causing her dramatic distress after the sealing.[41]
Critics generally do not reveal that their sources have concluded that Helen's marriage to Joseph Smith was unconsummated, preferring instead to point out that mere fact of the marriage of a 14-year-old girl to a 37-year-old man ought to be evidence enough to imply sexual relations and "pedophilia." For example, George D. Smith quotes Compton without disclosing his view,[42] cites Compton, but ignores that Compton argues that " there is absolutely no evidence that there was any sexuality in the marriage, and I suggest that, following later practice in Utah, there may have been no sexuality. All the evidence points to this marriage as a primarily dynastic marriage." [43] and Stanley Kimball without disclosing that he believed the marriage to be "unconsummated." [44]
Helen made clear what she disliked about plural marriage in Nauvoo, and it was not physical relations with an older man:
I had, in hours of temptation, when seeing the trials of my mother, felt to rebel. I hated polygamy in my heart, I had loved my baby more than my God, and mourned for it unreasonably….[45]
Helen is describing a period during the westward migration when (married monogamously) her first child died. Helen was upset by polygamy only because she saw the difficulties it placed on her mother. She is not complaining about her own experience with it.
Helen Mar Kimball:
All my sins and shortcomings were magnified before my eyes till I believed I had sinned beyond redemption. Some may call it the fruits of a diseased brain. There is nothing without a cause, be that as it may, it was a keen reality to me. During that season I lost my speech, forgot the names of everybody and everything, and was living in another sphere, learning lessons that would serve me in future times to keep me in the narrow way. I was left a poor wreck of what I had been, but the Devil with all his cunning, little thought that he was fitting and preparing my heart to fulfill its destiny….
[A]fter spending one of the happiest days of my life I was moved upon to talk to my mother. I knew her heart was weighed down in sorrow and I was full of the holy Ghost. I talked as I never did before, I was too weak to talk with such a voice (of my own strength), beside, I never before spoke with such eloquence, and she knew that it was not myself. She was so affected that she sobbed till I ceased. I assured her that father loved her, but he had a work to do, she must rise above her feelings and seek for the Holy Comforter, and though it rent her heart she must uphold him, for he in taking other wives had done it only in obedience to a holy principle. Much more I said, and when I ceased, she wiped her eyes and told me to rest. I had not felt tired till she said this, but commenced then to feel myself sinking away. I silently prayed to be renewed, when my strength returned that instant…
I have encouraged and sustained my husband in the celestial order of marriage because I knew it was right. At various times I have been healed by the washing and annointing, administered by the mothers in Israel. I am still spared to testify to the truth and Godliness of this work; and though my happiness once consisted in laboring for those I love, the Lord has seen fit to deprive me of bodily strength, and taught me to 'cast my bread upon the waters' and after many days my longing spirit was cheered with the knowledge that He had a work for me to do, and with Him, I know that all things are possible…[46]
Imagine a school-child who asks why French knights didn't resist the English during the Battle of Agincourt (in 1415) using Sherman battle tanks. We might gently reply that there were no such tanks available. The child, a precocious sort, retorts that the French generals must have been incompetent, because everyone knows that tanks are necessary. The child has fallen into the trap of presentism—he has presumed that situations and circumstances in the past are always the same as the present. Clearly, there were no Sherman tanks available in 1415; we cannot in fairness criticize the French for not using something which was unavailable and unimagined.
Spotting such anachronistic examples of presentism is relatively simple. The more difficult problems involve issues of culture, behavior, and attitude. For example, it seems perfectly obvious to most twenty-first century North Americans that discrimination on the basis of race is wrong. We might judge a modern, racist politician quite harshly. We risk presentism, however, if we presume that all past politicians and citizens should have recognized racism, and fought it. In fact, for the vast majority of history, racism has almost always been present. Virtually all historical figures are, by modern standards, racists. To identify George Washington or Thomas Jefferson as racists, and to judge them as moral failures, is to be guilty of presentism.
A caution against presentism is not to claim that no moral judgments are possible about historical events, or that it does not matter whether we are racists or not. Washington and Jefferson were born into a culture where society, law, and practice had institutionalized racism. For them even to perceive racism as a problem would have required that they lift themselves out of their historical time and place. Like fish surrounded by water, racism was so prevalent and pervasive that to even imagine a world without it would have been extraordinarily difficult. We will not properly understand Washington and Jefferson, and their choices, if we simply condemn them for violating modern standards of which no one in their era was aware.
Condemning Joseph Smith for "statutory rape" is a textbook example of presentist history. "Rape," of course, is a crime in which the victim is forced into sexual behavior against her (or his) will. Such behavior has been widely condemned in ancient and modern societies. Like murder or theft, it arguably violates the moral conscience of any normal individual. It was certainly a crime in Joseph Smith's day, and if Joseph was guilty of forced sexual intercourse, it would be appropriate to condemn him.
(Despite what some claim, not all marriages or sealings were consummated, as in Helen's case discussed above.)
"Statutory rape," however, is a completely different matter. Statutory rape is sexual intercourse with a victim that is deemed too young to provide legal consent--it is rape under the "statute," or criminal laws of the nation. Thus, a twenty-year-old woman who chooses to have sex has not been raped. Our society has concluded, however, that a ten-year-old child does not have the physical, sexual, or emotional maturity to truly understand the decision to become sexually active. Even if a ten-year-old agrees to sexual intercourse with a twenty-year-old male, the male is guilty of "statutory rape." The child's consent does not excuse the adult's behavior, because the adult should have known that sex with a minor child is illegal.
Even in the modern United States, statutory rape laws vary by state. A twenty-year-old who has consensual sex with a sixteen-year-old in Alabama would have nothing to fear; moving to California would make him guilty of statutory rape even if his partner was seventeen.
By analogy, Joseph Smith likely owned a firearm for which he did not have a license--this is hardly surprising, since no law required guns to be registered on the frontier in 1840. It would be ridiculous for Hitchens to complain that Joseph "carried an unregistered firearm." While it is certainly true that Joseph's gun was unregistered, this tells us very little about whether Joseph was a good or bad man. The key question, then, is not "Would Joseph Smith's actions be illegal today?" Only a bigot would condemn someone for violating a law that had not been made.
Rather, the question should be, "Did Joseph violate the laws of the society in which he lived?" If Joseph did not break the law, then we might go on to ask, "Did his behavior, despite not being illegal, violate the common norms of conscience or humanity?" For example, even if murder was not illegal in Illinois, if Joseph repeatedly murdered, we might well question his morality.
"Pedophilia" applies to children; Helen was regarded as a mature young woman
Helen specifically mentioned that she was regarded as mature.[47] 'Pedophilia' is an inflammatory charge that refers to a sexual attraction to pre-pubertal children. It simply does not apply in the present case, even if the relationship had been consummated.
Critics of Mormonism claim that Helen Mar Kimball was prepubescent at the time that she was sealed to Joseph Smith, and that this is therefore evidence that Joseph was a pedophile. Pedophila describes a sexual attraction to prepubescent children. However, there is no evidence that Helen ever cohabited with or had sexual relations with Joseph. In fact, she continued to live with her parents after the sealing.
The use of the term "pedophilia" by critics in this situation is intended to generate a negative emotional response in the reader. Pedophiles don't advertise their obsession and they certainly don't discuss marriages with the parents of their intended victims. It was Heber C. Kimball that requested that this sealing be performed, not Joseph. There is no evidence that Joseph was a pedophile.
European data indicates a long term linear drop, while US data is much more sparse. Using post-1910 data, Wyshak (1983) determined that the average age at menarche was dropping linearly at 3.2 month/decade with a value of 13.1 in 1920. This trend projects to 15.2 in 1840 and 16.3 in 1800. The onset of menarche follows a normal distribution that had a larger spread in the 19th century (σ≈1.7 to 2.0) in Brown (1966) and Laslett (1977).[48]
Helen Mar Kimball was likely married near the end of the month of May in 1843 and was thus approximately 14.8 years old when she was sealed to Joseph Smith. With only the statistics cited above we can conclude that 40% of the young women her age would have already matured and thus in their society be considered marriage eligible. If 40% is taken as an a priori probability, additional information puts maturity at her first marriage beyond a reasonable doubt using Bayesian methodology.
Helen remembered transitioning from childhood to adulthood over a year before her first marriage as she attended social functions with older teens. Here is quote on the abruptness of this transition in the past from a graduate course's textbook on child development:
In industrial societies, as we have mentioned, the concept of adolescence as a period of development is quite recent. Until the early twentieth century, young people were considered children until they left school (often well before age 13), married or got a job, and entered the adult world. By the 1920s, with the establishment of comprehensive high schools to meet the needs of a growing economy and with more families able to support extended formal education for their children, the teenage years had become a distinct period of development (Keller, 1999). In some preindustrial societies, the concept of adolescence still does not exist. The Chippewa, for example, have only two periods of childhood: from birth until the child walks, and from walking to puberty. What we call adolescence is, for them, part of adulthood (Broude, 1995), as was true in societies before industrialization.[49]
Helen recalls that by March 1842, she "had grown up very fast and my father often took me out with him and for this reason was taken to be older than I was." At these social gatherings, she developed a crush on her future husband Horace Whitney. She later married him after Joseph Smith's martyrdom and her 16th birthday and had 12 children with him.
According to Helen:
Sarah Ann's brother, Horace, who was twenty months her senior, made one of the party but had never dreamed of such a thing as matrimony with me, whom he only remembered in the earliest school days in Kirtland as occupying one of the lowest seats. He becoming enough advanced, soon left the one taught in the red schoolhouse on the flat and attended a higher one on the hill, and through our moving to Missouri and Illinois we lost sight of each other. After the party was over I stopped the rest of the night with Sarah, and as her room and his were adjoining, being only separated by a partition, our talk seemed to disturb him, and he was impolite enough to tell us of it, and request us to stop and let him go to sleep, which was proof enough that he had never thought of me only as the green school girl that I was, or he would certainly have submitted gracefully (as lovers always should) to be made a martyr of.[50]
Scholars that study fertility often divide large samples into cohorts which are 5 years wide based on birth year or marriage age . In contrast to what some critics claim, the marriage cohort of 15-19 year olds has been shown at times to be more fertile than the 20-24 cohort. The authors of one study found that "Unlike most other reported natural-fertility populations, period fertility rates for married Mormon women aged 15-19 are higher between 1870 and 1894 than those for married women in their 20s. Women aged 15-19 in 1870-74 would have been born in the 1850s when 55.8 percent were married before their 20th birthday; thus, this cannot be treated as an insignificant group." And also "In addition, the median interval between marriage and birth of the first child is consistently about one year for all age-at-marriage groups."[51] Another study disproved that younger marital age (15-19) resulted in a higher infant mortality rate due to the mother not being fully mature (termed the "biological-insufficiency hypothesis.").[52]
Helen continued to live with her parents after the sealing. After Joseph's death, Helen was married and had children.
Unlike today, it was acceptable to be sealed to one person for eternity while being married for time to another person. It is not known if this was the case with Helen, however.
We must, then, address four questions:
Even LDS authors are not immune from presentist fallacies: Todd Compton, convinced that plural marriage was a tragic mistake, "strongly disapprove[s] of polygamous marriages involving teenage women." [53] This would include, presumably, those marriages which Joseph insisted were commanded by God. Compton notes, with some disapproval, that a third of Joseph's wives were under twenty years of age. The modern reader may be shocked. We must beware, however, of presentism—is it that unusual that a third of Joseph's wives would have been teenagers?
When we study others in Joseph's environment, we find that it was not. A sample of 201 Nauvoo-era civil marriages found that 33.3% were under twenty, with one bride as young as twelve. [54] Another sample of 127 Kirtland marriages found that nearly half (49.6%) were under twenty. [55] And, a computer-aided study of LDS marriages found that from 1835–1845, 42.3% of women were married before age twenty. [56] The only surprising thing about Joseph's one third is that more of his marriage partners were not younger.
Furthermore, this pattern does not seem to be confined to the Mormons (see Chart 12 1). A 1% sample from the 1850 U.S. census found 989 men and 962 who had been married in the last year. Teens made up 36.0% of married women, and only 2.3% of men; the average age of marriage was 22.5 for women and 27.8 for men. [57] Even when the men in Joseph's age range (34–38 years) in the U.S. Census are extracted, Joseph still has a lower percentage of younger wives and more older wives than non-members half a decade later. [58]
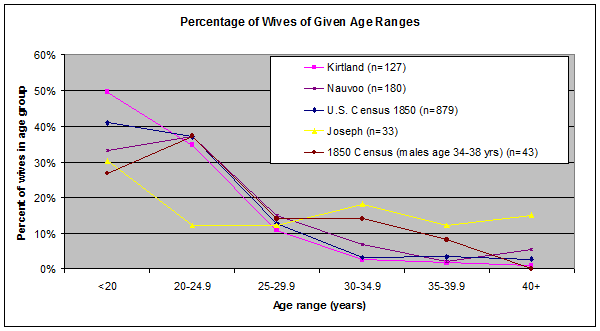
I suspect that Compton goes out of his way to inflate the number of young wives, since he lumps everyone between "14 to 20 years old" together. [59] It is not clear why this age range should be chosen—women eighteen or older are adults even by modern standards.
A more useful breakdown by age is found in Table 12-1. Rather than lumping all wives younger than twenty-one together (a third of all the wives), our analysis shows that only a fifth of the wives would be under eighteen. These are the only women at risk of statutory rape issues even in the modern era.
{
Helen Mar Kimball wrote of her parents:
My mother had noticed a change in his [Heber's] looks and appearance [since the command to practice plural marriage], and when she enquired the cause, he tried to evade her question, saying it was only her imagination, or that he was not feeling well, etc. But it so worked upon his mind that his anxious and haggard looks betrayed him daily and hourly, and finally his misery became so unbearable that it was impossible to control his feelings. He became sick in body, but his mental wretchedness was too great to allow of his retiring at night, and instead of going to bed he would walk the floor; and the agony of his mind was so terrible that he would wring his hands and weep, beseeching the Lord with his whole soul to be merciful and reveal to his wife the cause of his great sorrow, for he himself could not break his vow of secrecy. His anguish and my mother's, were indescribable and when unable to endure it longer, she retired to her room, where with a broken and contrite heart, she poured out her grief to [God]. . . .
My father's heart was raised at the same time in supplication, and while pleading as one would plead for life, the vision of her mind was opened, and she saw the principle of Celestial Marriage illustrated in all its beauty and glory, together with the great exaltation and honor it would confer upon her in that immortal and celestial sphere if she would but accept it and stand in her place by her husband's side. She was also shown the woman he had taken to wife, and contemplated with joy the vast and boundless love and union which this order would bring about, as well as the increase of kingdoms, power, and glory extending throughout the eternities, worlds without end.
Her soul was satisfied and filled with the Spirit of God. With a countenance beaming with joy she returned to my father, saying, "Heber, what you have kept from me the Lord has shown me."
She related the scene to me and to many others, and told me she never saw so happy a man as father was, when she described the vision and told him she was satisfied and knew that it was from God. She covenanted to stand by him and honor the principle, which covenant she faithfully kept, and though her trials were often heavy and grievous to bear, her integrity was unflinching to the end.[61]
| See also: | Circumstances of the marriage of the Kimball's daughter, Helen Mar, to Joseph Smith. |
Hales deals with this sometimes-controversial aspect of Joseph's plural marriages. |
|
Many are quick to declare that Joseph's polygamy sprang from religious extremism and/or sexual desire. This article explores the difficulties that Joseph had with plural marriage, and evidence for what truly motivated his acts. |
|
Why did early members of the Church practice polygamy? Were they all dupes? Easily manipulated? Religious fanatics who believed Joseph could do no wrong? This article explores the initial reactions and eventual decisions made by the first generation of polygamists in Nauvoo. |
Critical sources |
|

FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
We are a volunteer organization. We invite you to give back.
Donate Now