
FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
(→35) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 293: | Line 293: | ||
|authorsources=Joseph Smith, ‘’History of the Church’’, vol. 2 (Salt Lake Cithy: Deseret Book Co., 1978), 182. | |authorsources=Joseph Smith, ‘’History of the Church’’, vol. 2 (Salt Lake Cithy: Deseret Book Co., 1978), 182. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{:Question: Did Joseph Smith prophesy | {{:Question: Did Joseph Smith prophesy that Jesus Christ would return in 1890?}} | ||
====35==== | ====35==== | ||
| Chapter 2: The Marketing of an Image | A FAIR Analysis of: Mormonism Unmasked A work by author: R. Philip Roberts
|
Chapter 4: Polytheism Reborn |
A quote from Joseph Smith is provided:
I have more to boast of than ever any man had. I am the only man that has ever been able to keep a whole church together since the days of Adam. A large majority of the whole have stood by me. Neither Paul, John, Peter, nor Jesus ever did it. I boast that no man ever did such a work as I. The followers of Jesus ran away from Him; but the Latter-day Saints never ran away from me yet.
Author's sources: History of the Church
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |
Joseph Smith is quoted as saying such things as:
These quotes are used to portray Joseph as ego-maniacal, proud, and narcissistic.
To paraphrase G. D. Smith, small wonder, then, that this Joseph—the one revealed by the documents—decided to run for the presidency. The decision was natural since the Saints felt no candidate was worthy of their support—though they knew that a vote for Joseph could well be "throw[ing] away our votes."[1] Joseph’s campaign was "a gesture," though one he took seriously.[2] Experienced students of Mormon history will know this; G. D. Smith evidently counts on his audience not knowing.
G. D. Smith writes that "in defending his theology [during the King Follett discourse], Smith proclaimed, ‘I am learned, and know more than all the world put together.’" The period ending the sentence would imply that this completed his thought—and so it appears in the History of the Church.[3] If the three published versions of the original talk are consulted,[4] However, they each demonstrate that the sentiment may have been quite different:
Now, I ask all the learned men who hear me, why the learned doctors who are preaching salvation say that God created the heavens and the earth out of nothing. They account it blasphemy to contradict the idea. If you tell them that God made the world out of something, they will call you a fool. The reason is that they are unlearned but I am learned and know more than all the world put together—the Holy Ghost does, anyhow. If the Holy Ghost in me comprehends more than all the world, I will associate myself with it.[5]
In the History of the Church version, the statement about the Holy Ghost is placed in its own sentence. This allows G. D. Smith to exclude it with no ellipsis and portray Joseph as decidedly more arrogant than he was. Daniel C. Peterson’s remark is telling: "Amusing, isn’t it, . . . that the very same people who vehemently reject the . . . History of the Church as an unreliable source when it seems to support the Latter-day Saint position clutch it to their bosoms as an unparalleled historical treasure when they think they can use it as a weapon against the alleged errors of Mormonism."[6]:54–55
Critics fail, then, to provide the context for these remarks, some of which are taken from an exchange which Joseph had with newspaperman James Arlington Bennet.[7] For example, G.D. Smith quotes the phrases above and then editorializes: "With such a self-image, it is not surprising that he also aspired to the highest office in the land: the presidency of the United States."[8] Here again, he serves his readers poorly. He neglects to tell us that Joseph’s remark comes from a somewhat tongue-in-cheek exchange with James Bennet, who had been baptized in the East but immediately wrote Joseph to disclaim his "glorious frolic in the clear blue ocean; for most assuredly a frolic it was, without a moment’s reflection or consideration."[9]:71
Bennet went on to praise Joseph in an exaggerated, humorous style: "As you have proved yourself to be a philosophical divine . . . [it] point[s] you out as the most extraordinary man of the present age." "But," cautioned Bennet,
my mind is of so mathematical and philosophical a cast, that the divinity of Moses makes no impression on me, and you will not be offended when I say that I rate you higher as a legislator than I do Moses. . . . I cannot, however, say but you are both right, it being out of the power of man to prove you wrong. It is no mathematical problem, and can therefore get no mathematical solution (italics added)[9]:72
Joseph’s claim that his religious witness can "solve mathematical problems of universities" is thus a playful return shot at Bennet,[10] who has claimed a "so mathematical" mind that cannot decide about Joseph’s truth claims since they admit of "no mathematical solution."[11] G. D. Smith may not get the joke, but he ought to at least let us know that there is one being told.
Bennet continued by suggesting that he need not have religious convictions to support Joseph, adding slyly that "you know Mahomet had his ‘right hand man.’" Joseph’s reply that God is his right-hand man is again a riposte to Bennet and follows Joseph’s half-serious gibe that "your good wishes to go ahead, coupled with Mahomet and a right hand man, are rather more vain than virtuous. Why, sir, Cæsar had his right hand Brutus, who was his left hand assassin." Joseph here pauses, and we can almost see him grin before adding: "Not, however, applying the allusion to you."[9]:77
Bennet had also offered Joseph a carving of "your head on a beautiful cornelian stone, as your private seal, which will be set in gold to your order, and sent to you. It will be a gem, and just what you want. . . . The expense of this seal, set in gold, will be about $40; and [the maker] assures me that if he were not so poor a man, he would present it to you free. You can, however, accept it or not."[9]:72
Joseph does not let this rhetorical opportunity go by, telling Bennet that "facts, like diamonds, not only cut glass, but they are the most precious jewels on earth. . . . As to the private seal you mention, if sent to me, I shall receive it with the gratitude of a servant of God, and pray that the donor may receive a reward in the resurrection of the just."[9]:77, (emphasis added) Joseph’s concluding remark about the necessity of "truth—diamond-hard truth" plays on this same association with the proffered precious stone.
The key point of Bennet’s letter, after the sardonic preliminaries, was an invitation to use untruth for political gain—hence Joseph’s insistence on "diamond-hard truth." Bennet closed his letter by asking to be privately relieved of his honorary commission with the Nauvoo Legion, noting that
I may yet run for a high office in your state, when you would be sure of my best services in your behalf; therefore, a known connection with you would be against our mutual interest. It can be shown that a commission in the Legion was a Herald hoax, coined for the fun of it by me, as it is not believed even now by the public. In short, I expect to be yet, through your influence, governor of the State of Illinois.[9]:72, (emphasis added)
Bennet hoped to use Joseph without embracing his religious pretensions and was bold enough to say so.[12] However, Joseph was not as cynical and malleable as the Easterner hoped, for the Prophet then insisted at length on the impropriety of using "the dignity and honor I received from heaven, to boost a man into [political] power," since "the wicked and unprincipled . . . would seize the opportunity to [harden] the hearts of the nation against me for dabbling at a sly game in politics."
Joseph’s fear in relation to politics is that to support the unworthy would be to corrupt the mission he has been given. "Shall I," continued Joseph rhetorically, ". . . turn to be a Judas? Shall I, who have heard the voice of God, and communed with angels, and spake as moved by the Holy Ghost for the renewal of the everlasting covenant, and for the gathering of Israel in the last days,—shall I worm myself into a political hypocrite?" Rather, Joseph hoped that "the whole earth shall bear me witness that I, like the towering rock in the midst of the ocean, which has withstood the mighty surges of the warring waves for centuries, am impregnable, and am a faithful friend to virtue, and a fearless foe to vice."[9]:77–78
It is at this point that he makes the statement quoted by G. D. Smith—a nice rhetorical summation of the word games he and Bennet were playing and a jovial but direct rejection of Bennet’s politically cynical offer—but hardly evidence of someone with a grandiose self-image.[13]
Joseph Smith is reported as saying:
I have more to boast of than ever any man had. I am the only man that has ever been able to keep a whole church together since the days of Adam... Neither Paul, John, Peter, nor Jesus ever did it. I boast that no man ever did such work as I. The followers of Jesus ran away from Him; but the Latter-day Saints never ran away from me yet." (History of the Church, 6:408–409. Volume 6 link
Assuming that the quote is accurate in History of the Church, it is evident that Joseph's quote is taken out of context. What was Joseph's intent, and why did he use this approach? As it turns out, he was drawing from the Bible and applying its lessons to his own situation. In the original context, Joseph was facing intense persecution by many people, including some he had previously considered to be his friends. The statement about "boasting" was supposedly made about a month before he was killed. He made it after reading 2 Corinthians 11: to the congregation. Note the following statement by Paul, in this scripture:
Paul said:
Again I say, let no one think me foolish; but if you do, receive me even as foolish, that I also may boast a little. That which I am speaking, I am not speaking it as the Lord would, but as in foolishness, in this confidence of boasting. Since many boast according to the flesh, I will boast also. For you, being so wise, bear the foolish gladly. (2 Corinthians 11:16-19, NASB)
Paul then launches into a literary tirade where he claims many things to make himself look the fool, to contrast himself with those who the Corinthians were listening to for their words of salvation, instead of to him. His words were meant to compare and contrast what the Saints at Corinth were doing against what he was offering.
Do the critics dismiss the words of Paul and deny his calling as an Apostle because he used such a literary approach that included boasting? No, they do not. Yet, they dismiss Joseph Smith when it is clear by his own statements, in context, that he engaged in the exact same literary approach. Consider the words of Joseph right after reading this chapter of Paul's to the congregation:
My object is to let you know that I am right here on the spot where I intend to stay. I, like Paul, have been in perils, and oftener than anyone in this generation. As Paul boasted, I have suffered more than Paul did, I should be like a fish out of water, if I were out of persecutions. Perhaps my brethren think it requires all this to keep me humble. The Lord has constituted me curiously that I glory in persecution. I am not nearly so humble as if I were not persecuted. If oppression will make a wise man mad, much more a fool. If they want a beardless boy to whip all the world, I will get on the top of a mountain and crow like a rooster: I shall always beat them. When facts are proved, truth and innocence will prevail at last. My enemies are no philosophers: they think that when they have my spoke under, they will keep me down; but for the fools, I will hold on and fly over them.[14]
Joseph then makes the statements that the critics attack, in the same way that Paul made outrageous "boasts" to contrast his position with the position of those who the Corinthians were starting to listen to. Paul starts the next chapter of 2 Corinthians with the statement "boasting is necessary, though it is not profitable." So, it would appear that Paul recognizes the necessity of boasting at times against the wicked and hard-hearted (though it may do little good, being unprofitable), yet the critics do not allow Joseph to follow Paul's advice and, of necessity, boast at times.
Perhaps the critics are unaware of Paul's advice? Or perhaps they apply a double standard where Paul is allowed such literary and rhetorical license, but Joseph is not?
Such double standards are, sadly, the stock-in-trade of sectarian anti-Mormonism.
Critical sources |
|
Consider the following excerpt from a letter Joseph wrote to his wife Emma:
I will try to be contented with my lot, knowing that God is my friend. In him I shall find comfort. I have given my life into his hands. I am prepared to go at his call. I desire to be with Christ. I count not my life dear to me [except] to do his will.[15]
These are not the words of a man who believed himself to be better than Christ. Joseph loved Christ and throughout his life strove to follow him. These words written in private to his wife demonstrate that Joseph was not so prideful as to think himself better than Christ. Consider also the following statement, made in public, by Joseph Smith:
I do not think there have been many good men on the earth since the days of Adam; but there was one good man and his name was Jesus. Many persons think a prophet must be a great deal better than anybody else....I do not want you to think that I am very righteous, for I am not.[16]
Both in private and in public Joseph Smith demonstrated his humility before the Lord.
Critical sources |
|
Some have argued that Joseph may have said something like this, but was doing so for rhetorical effect to frighten the Missourians into leaving the Saints alone. But, it is by no means certain that he said it at all. Some who made the claims returned to the Church, and other sources were motivated by hostility and a desire to portray the Saints as a military and religious threat.
The source of this claim is from Thomas B. Marsh, an apostate former president of the Quorum of the Twelve. In 1838, Marsh swore an affidavit in which he claimed to have heard Joseph Smith say:
he would yet tread down his enemies, and walk over their dead bodies; and if he was not let alone, he would be a second Mohammed to this generation, and that it would be one gore of blood from the Rocky Mountains to the Atlantic Ocean; that like Mohammed, whose motto in treating for peace was, 'the Alcoran or the Sword,' so should it be eventually with us, 'Joseph Smith or the Sword.' [17]
Arnold Green and Lawrence Goldrup noted in 1971 that "this threat was quite probably a mere fabrication by the disgruntled Marsh," [18] and pointed out Orson Hyde (who was also disaffected at the time) later repented and returned, indicating that parts of the affidavit had been invented by Marsh. Marsh himself was later to repent and return to the Church, which casts further doubt on his story.
The tale was also repeated by George M. Hinkle, John Corrill, George Walter, and partially by Abner Scovil. [19] Joseph Smith's journal for the period notes:
some excitement was raised in the adjoining Counties, that is Ray & Clay, against us, in consequence of the suden departure of these wicked character[s], of the apostates from this Church, into that vicinity reporting false stories, and statements, but when they [the Missourians] come to hear the other side of the question their feeling[s] were all allayed upon that subject especially. [20]
Joseph was under enormous pressure to defend the Saints against the repeated actions of mobbers. As historian Marvin Hill notes,
the actual response to belligerence when it occurred was much more restrained. Although the elders did confiscate property and burn houses, their attacks were generally aimed at specific enemies. Mormons had neither the inclination nor means to wage a general war of extermination against all mobbers, despite menacing talk. The only fatalities occurred in the skirmish with Bogart, where the elders got the worst of the fight. Had the prophet been intent on waging total war, it is unlikely he would have allowed Rigdon to issue his 4th of July warning, which only put the Missourians on guard. [21]
Critical sources |
|
Author's source(s)
Fawn M. Brodie, ‘’No Man Knows My History: The Life of Joseph Smith, the Mormon Prophet’’ (New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1971), 6-33. See also Jerald and Sandra Tanner, ‘’Mormonism-Shadow and Reality?’’ (Salt Lake City: Utah Lighthouse Ministry, 1987) 32-49.
Response
Author's source(s)
Not provided
Response
Author's source(s)
Not provided
Response
Author's source(s)
Not provided.
Response
Critics have also claimed that there were no religious revivals in the Palmyra, New York, area in 1820, as Joseph Smith reported in his history. With today’s greater access to original sources, including the Palmyra Register newspaper, there is ample evidence of religious revivals in the area during 1820 and some years prior. It appears that the Methodists had a regularly used camp meeting ground, and that revivals were common enough that often they garnered no coverage in the newspapers unless something out of the ordinary occurred such as a death. (Footnote 12)
The author states that “as of 1820, Joseph Smith was teaching that the Father and the Son both had physical bodies...”
Author's sources: Not provided.
The author states that the “early documents of Mormonism show that during the 1820s and early 1830s, Smith was teaching there was only one God.”
Author's sources: Not provided.
Accounts |
|
Historical context |
|
Doctrinal impact |
This doctrine is apparent in the Book of Mormon, and in the earliest friendly and non-friendly accounts of such matters from the Saints.
Such texts demonstrate that the supposed 'evidence' for Joseph altering his story later is only in the eyes of critical beholders. For example, Joseph's 1832 First Vision account focuses on the remission of his sins. However, critics who wish to claim that in 1832 Joseph had only a vaguely "trinitarian" idea of God (and so would see the Father and the Son as only one being) have missed vital evidence which must be considered.[1]
Martin dictated an account of his early spiritual search:
It would be very strange for Martin to feel so strongly on this point, only to embrace Joseph's teachings if Joseph taught creedal trinitarianism.
The Book of Mormon also begins (1 Nephi 1꞉8-10) with Lehi's vision of God on his throne. One [Christ] followed by twelve others descends from God to speak with Lehi—thus, Jesus and the Father are here both separate, and the role of Christ in giving instructions to the prophet while the Father looks on and approves is followed, just as it was in Joseph's First Vision. Here too, Lehi is described as praying to "the Lord," and yet has a vision of both God the Father and Christ.
Alma 11:45 makes clear that the resurrection is permanent and Mosiah 15:20 (along with several others) makes clear that the resurrection is brought about through Christ.
In 3 Nephi 28:10 the Savior is speaking to the 3 Nephites. After declaring that they would never endure the pains of death he states:
Since the verse is juxtaposed closely with not tasting death and the Savior stating that they would be even as he and the Father are, this verse may be used to argue for an embodied Christ and God (and likely an early conceptualization of deification) in the Book of Mormon. Furthermore, the phrase "fullness of joy" is used in D&C 93:33 (a revelation dated to 1833) to describe element (or man’s tabernacle as v. 35 expresses) and spirit inseparably connected.
Between June and October 1830, Joseph had dictated his revision (the "Joseph Smith Translation") to Genesis.[3] The first chapter of Moses was dictated in June 1830 (about a month after the Church's reorganization), and began:
2 And [Moses] saw God face to face, and he talked with him, and the glory of God was upon Moses; therefore Moses could endure his presence.
3 And God spake unto Moses, saying: Behold, I am the Lord God Almighty, and Endless is my name; for I am without beginning of days or end of years; and is not this endless?
4 And, behold, thou art my son; wherefore look, and I will show thee the workmanship of mine hands; but not all, for my works are without end, and also my words, for they never cease.
5 Wherefore, no man can behold all my works, except he behold all my glory; and no man can behold all my glory, and afterwards remain in the flesh on the earth.
6 And I have a work for thee, Moses, my son; and thou art in the similitude of mine Only Begotten; and mine Only Begotten is and shall be the Savior, for he is full of grace and truth; but there is no God beside me, and all things are present with me, for I know them all (Moses 1꞉2-6)
Here already, God distinguishes himself from the Only Begotten, Moses sees and speaks with God face to face, and says that Moses was created "in the similitude of mine Only Begotten."
Joseph's rendered Genesis 1:26 as:
And I, God, said unto mine Only Begotten, which was with me from the beginning, Let us make man in our image, after our likeness; and it was so....And I, God, created man in mine own image, in the image of mine Only Begotten created I him; male and female created I them. (Moses 2꞉26-27.)
There can be no doubt that Joseph understood "in mine own image" to refer to a physical likeness, rather than merely a moral or intellectual one. The JST of Genesis 5:1-2 reads
In the day that God created man, in the likeness of God made he him; in the image of his own body, male and female, created he them (Moses 6꞉8-9, emphasis added)
Thus, by 1830 Joseph was clearly teaching a separation of the Father and Son, and insisting that both had some type of physical form which could be copied in the creation of humanity.
Joseph's mother, Lucy Mack Smith, also noted that other Christian denominations took issue with the new Church because of its teachings about God, noting that in 1830:
the different denominations are very much opposed to us.... The Methodists also come, and they rage, for they worship a God without body or parts, and they know that our faith comes in contact with this principle.[4]
Anti-Mormon writers in 1831 noted that Joseph claimed to have received "a commission from God"; and the Mormons claimed that Joseph "had seen God frequently and personally."[5] That Joseph's enemies knew he claimed to have "seen God," indicates that the doctrine of an embodied God that could be seen was well-known early on.
John Whitmer would also write in 1831 of a vision enjoyed by Joseph in which Joseph saw Christ as separate from the Father, for he "saw the heavens opened, and the Son of Man sitting on the right hand of the Father making intercession for his brethren, the Saints." (emphasis added) [6] Of this same experience, Levi Hancock wrote:
Joseph Smith then stepped out onto the floor and said, 'I now see God, and Jesus Christ at his right hand, let them kill me, I should not feel death as I am now.' (emphasis added) [7]
Doctrine and Covenants 50, a revelation given to Joseph Smith in May 1831, states in the 43rd verse that:
One should first note that in the 1832 account of the First Vision, Jesus announces to Joseph that he will come "clothed in the glory of my Father." The Book of Mormon (translated three years earlier in 1829) also contains numerous passages which teach a physical separation and embodiment (even if only in spirit bodies, which are clearly not immaterial, but have shape, position, and form) of the members of the Godhead. (See: 3 Nephi 11, 1 Nephi 11꞉1-11, Ether 3꞉14-18.)
Furthermore, Joseph Smith and Sidney Rigdon were to receive a revelation of the three degrees of glory in the same year as Joseph's 1832 account was written; it clearly teaches a physical separation of the Father and Son, bearing witness of seeing both. (See D&C 76꞉14,20–24.)[9]
Two of Joseph's close associates reported their own visions of God in the winter of 1832–1833. Both are decidedly not in the trinitarian mold.
Zebedee Coltrin:
Joseph having given instructions, and while engaged in silent prayer, kneeling...a personage walked through the room from East to west, and Joseph asked if we saw him. I saw him and suppose the others did, and Joseph answered that this was Jesus, the Son of God, our elder brother. Afterward Joseph told us to resume our former position in prayer, which we did. Another person came through; He was surrounded as with a flame of fire. [I] experienced a sensation that it might destroy the tabernacle as it was of consuming fire of great brightness. The Prophet Joseph said this was the Father of our Lord Jesus Christ. I saw him...
He was surrounded as with a flame of fire, which was so brilliant that I could not discover anything else but his person. I saw his hands, his legs, his feet, his eyes, nose, mouth, head and body in the shape and form of a perfect man. He sat in a chair as a man would sit in a chair, but This appearance was so grand and overwhelming that it seemed that I should melt down in His presence, and the sensation was so powerful that it thrilled through my whole system and I felt it in the marrow of my bones. The Prophet Joseph said: "Brethren, now you are prepared to be the apostles of Jesus Christ, for you have seen both the Father and the Son and know that They exist and that They are two separate personages."[10]
John Murdock:
During the winter that I boarded with[Bro[ther] Joseph... we had a number of prayer meetings, in the Prophet’s chamber.... In one of those meetings the Prophet told us if we could humble ourselves before God, and exersise [sic] strong faith, we should see the face of the Lord. And about midday the visions of my mind were opened, and the eyes of my understanding were enlightened, and I saw the form of a man, most lovely, the visage of his face was sound and fair as the sun. His hair a bright silver grey, curled in a most majestic form, His eyes a keen penetrating blue, and the skin of his neck a most beautiful white and he was covered from the neck to the feet with a loose garment, pure white, whiter than any garment I had ever before seen. His countenance was the most penetrating, and yet most lovely. And while I was endeavoring to comprehend the whole personage from head to feet it slipped from me, and the vision was closed up. But it left on my mind the impression of love, for months, that I never felt before to that degree.[11]
In the School of the Prophets, the brethren were taught that
There are two personages who constitute the great, matchless, governing, and supreme power over all things, by whom all things were created and made, that are created and made. . . . They are the Father and the Son—the Father being a personage of spirit, glory, and power, possessing all perfection and fulness, the Son, who was in the bosom of the Father, a personage of tabernacle. (Lecture 5:1–2)
Here, the separateness of the Father and Son continues to be made clear.
A skeptical news article noted:
They believe that the true God is a material being, composed of body and parts; and that when the Creator formed Adam in his own image, he made him about the size and shape of God himself....[12]
In addition to all the non-trinitarian evidence above, as Milton Backman has noted, there is a great deal of evidence that we should find, but don't. For example, no one has "located a publication (such as an article appearing in a church periodical or statement from a missionary pamphlet) written by an active Latter-day Saint prior to the martyrdom of the Prophet that defends the traditional or popular creedal concept of the Trinity. . . ." Moreover, there are no references in critical writings of the 1830s (including statements by apostates) that Joseph Smith introduced in the mid-thirties the doctrine of separateness of the Father and Son.[13]
Critical sources |
|
Oliver Cowdery began publishing a history of the Church in the Messenger and Advocate in December 1834 which is commonly misunderstood:
In 1834, Oliver Cowdery began publishing a history of the Church in installments in the pages of the Latter Day Saints’ Messenger and Advocate. The first installment talks of the religious excitement and events that ultimately led to Joseph Smith’s First Vision at age 14. However, in the subsequent installment published two months later, Oliver claims that he made a mistake, correcting Joseph’s age from 14 to 17 and failing to make any direct mention of the First Vision. Oliver instead tells the story of Moroni’s visit, thus making it appear that the religious excitement led to Moroni’s visit.
This curious account has been misunderstood by some to be evidence that the "first" vision that Joseph claimed was actually that of the angel Moroni and that Joseph invented the story of the First Vision of the Father and Son at a later time. However, Joseph wrote an account of his First Vision in 1832 in which he stated that he saw the Lord, and there is substantial evidence that Oliver had this document in his possession at the time that he wrote his history of the Church. This essay demonstrates the correlations between Joseph Smith’s 1832 First Vision account, Oliver’s 1834/1835 account, and Joseph’s 1835 journal entry on the same subject. It is clear that not only did Oliver have Joseph’s history in his possession but that he used Joseph’s 1832 account as a basis for his own account. This essay also shows that Oliver knew of the First Vision and attempted to obliquely refer to the event several times in his second installment before continuing with his narrative of Moroni’s visit.[14]
After spending the previous installment leading up to the First Vision, Oliver abruptly skips three years ahead and does not mention the vision directly. However, before describing Moroni's visit, Oliver even takes the time to minimize the importance of the religious excitement that he described in the previous installment, stating,
And it is only necessary for me to say, that while this excitement continued, he continued to call upon the Lord in secret for a full manifestation of divine approbation, and for, to him, the all important information, if a Supreme being did exist, to have an assurance that he was accepted of him.
Oliver Cowdery, Messenger and Advocate (February 1835)
Note carefully what Oliver is saying. The religious "excitement," and the event that Oliver described in the first installment when he said that Joseph was 14 years of age, was when Joseph was seeking a "full manifestation of divine approbation" with the desire to know "if a Supreme being did exist." Oliver then alludes to the First Vision in the past tense by saying,
This, most assuredly, was correct—it was right. The Lord has said, long since, and his word remains steadfast, that for him who knocks it shall be opened, & whosoever will, may come and partake of the waters of life freely.
Oliver Cowdery, Messenger and Advocate (February 1835)
Oliver is stating that something of significance happened in Joseph’s life prior to the events that Oliver would be describing next, and he assures the reader that "this, most assuredly, was correct." Oliver then proceeds to describe Moroni's visit to Joseph at age 17.
Critical sources |
|
It cannot be successfully argued that before the missionaries made their statement in November 1830 Latter-day Saints would have understood "God" as a reference to Jesus Christ alone. When the missionaries (one of whom was Book of Mormon scribe Oliver Cowdery) were teaching that Joseph Smith had seen "God" personally they could have legitimately been referring to God the Father
The weakness of this argument is twofold. First and foremost, critics ignore the fact that the document which reports the missionaries’ teachings[15]refers to "God" twice but also to "Christ" once and the "Holy Spirit" once. Hence, all three members of the Godhead appear to be represented individually in the document. In this context, a natural interpretation demands that "God" refer to the Father and the statement made by the missionaries would therefore mean that sometime before November 1830 Joseph Smith had seen God the Father "personally."
The second problem with the critics’ argument is that the Book of Mormon and Doctrine and Covenants contain several contemporary texts that undercut their position. For instance, 1 Nephi 12꞉18 speaks of "the justice of the Eternal God, and the Messiah who is the Lamb of God, of whom the Holy Ghost beareth record." Here all three members of the Godhead are represented and "the Eternal God" is an obvious reference to God the Father. It becomes apparent from a reading of Alma 11꞉44, however, that this is a title that can be appropriately applied to all three divine Beings. This scriptural passage talks about being "arraigned before the bar of Christ the Son, and God the Father, and the Holy Spirit, which is one Eternal God." This concept is paralleled in D&C 20꞉28—a text written about April 1830—which says that the "Father, Son, and Holy Ghost are one God, infinite and eternal."
The Book of Mormon also begins (1 Nephi 1꞉8-10) with Lehi's vision of God on his throne. One bright being [Christ] followed by twelve others descends from God to speak with Lehi—thus, Jesus and the Father are here both separate, and the role of Christ in giving instructions to the prophet while the Father looks on and approves is followed, just as it was in Joseph's First Vision. Here too, Lehi is described as praying to "the Lord," and yet has a vision of both "God" and Christ.
A hostile account from someone who knew Joseph in 1827 reported:
I, Joseph Capron, became acquainted with Joseph Smith, Sen. in the year of our Lord, 1827. They have, since then, been really a peculiar people—fond of the foolish and the marvelous—at one time addicted to vice and the grossest immoralities—at another time making the highest pretensions to piety and holy intercourse with Almighty God. The family of Smiths held Joseph Jr. in high estimation on account of some supernatural power, which he was supposed to possess.[16]
Capron obviously dislikes and distrusts the Smiths, but he makes it clear that there were claims of holy intercourse (i.e., "communication" with)[17] "Almighty God." This sounds much more like a reference to the Father than to Christ.
In 1834, Oliver Cowdery began publishing a history of the Church in installments in the pages of the Latter Day Saints’ Messenger and Advocate. The first installment talks of the religious excitement and events that ultimately led to Joseph Smith’s First Vision at age 14. However, in the subsequent installment published two months later, Oliver claims that he made a mistake, correcting Joseph’s age from 14 to 17 and failing to make any direct mention of the First Vision. Oliver instead tells the story of Moroni’s visit, thus making it appear that the religious excitement led to Moroni’s visit.
This curious account has been misunderstood by some to be evidence that the "first" vision that Joseph claimed was actually that of the angel Moroni and that Joseph invented the story of the First Vision of the Father and Son at a later time. However, Joseph wrote an account of his First Vision in 1832 in which he stated that he saw the Lord, and there is substantial evidence that Oliver had this document in his possession at the time that he wrote his history of the Church. This essay demonstrates the correlations between Joseph Smith’s 1832 First Vision account, Oliver’s 1834/1835 account, and Joseph’s 1835 journal entry on the same subject. It is clear that not only did Oliver have Joseph’s history in his possession but that he used Joseph’s 1832 account as a basis for his own account. This essay also shows that Oliver knew of the First Vision and attempted to obliquely refer to the event several times in his second installment before continuing with his narrative of Moroni’s visit.
Critical sources |
|
Several LDS commentators - including one member of the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles - agree that D&C 20:5 (part of the Articles and Covenants of the Church) is the earliest published reference to the First Vision story. [19] The Articles and Covenants of the Church were presented to the Church membership and then published in the following order
24 And again it shall come to pass that the Lord shall say unto him that shall read the words that shall be delivered him:
25 Forasmuch as this people draw near unto me with their mouth, and with their lips do honor me, but have removed their hearts far from me, and their fear towards me is taught by the precepts of men—
26 Therefore, I will proceed to do a marvelous work among this people, yea, a marvelous work and a wonder, for the wisdom of their wise and learned shall perish, and the understanding of their prudent shall be hid.
"History, circa Summer 1832 - Historical Introduction," The Joseph Smith Papers:
In the early 1830s, when this history was written, it appears that JS had not broadcast the details of his first vision of Deity. The history of the church, as it was then generally understood, began with the gold plates. John Whitmer mentioned in his history "the commencement of the church history commencing at the time of the finding of the plates," suggesting that Whitmer was either unaware of JS’s earlier vision or did not conceive of it as foundational.5 Records predating 1832 only hint at JS’s earliest manifestation. The historical preamble to the 1830 "articles and covenants," for example, appears to reference JS’s vision in speaking of a moment when "it truly was manifested unto this first elder, that he had received a remission of his sins."6 Initially, JS may have considered this vision to be a personal experience tied to his own religious explorations. He was not accustomed to recording personal events, and he did not initially record the vision as he later did the sacred texts at the center of his attention. Only when JS expanded his focus to include historical records did he write down a detailed account of the theophany he experienced as a youth. The result was a simple, unpolished account of his first "marvilous experience," written largely in his own hand. The account was not published or widely circulated at the time, though in later years he told the story more frequently.[20]

This claim by critics is indeed strange. We are apparently to believe that the newspapers of the area would consider a claim from a 14-year-old boy as newsworthy. We know that Joseph didn't even tell his family about the vision at the time that it occurred—when his mother asked him, all he said to her was that he had found that Presbyterianism was not true.
Joseph did, however, make mention of his vision to a Methodist preacher. According to Richard Bushman, Joseph's perceived persecution for telling his story may not have actually been because it was a unique claim, but rather because it was a common one. According to Bushman,
The clergy of the mainline churches automatically suspected any visionary report, whatever its content...The only acceptable message from heaven was assurance of forgiveness and a promise of grace. Joseph's report of God's rejection of all creeds and churches would have sounded all too familiar to the Methodist evangelical, who repeated the conventional point that "all such things had ceased with the apostles and that there never would be any more of them."[21][22]

24 And again it shall come to pass that the Lord shall say unto him that shall read the words that shall be delivered him:
25 Forasmuch as this people draw near unto me with their mouth, and with their lips do honor me, but have removed their hearts far from me, and their fear towards me is taught by the precepts of men—
26 Therefore, I will proceed to do a marvelous work among this people, yea, a marvelous work and a wonder, for the wisdom of their wise and learned shall perish, and the understanding of their prudent shall be hid.
This scripture from Isaiah is exactly the scripture that Joseph either quotes or paraphrases in the 1832 and 1838 Account of the First Vision. Critics may dismiss this saying that it is simply a part of Joseph's fraudulent composition of the Book of Mormon but the verse still throws a huge wrench in their theories about there being no early mentions of the First Vision.
When the published 1830s fragments of the First Vision story are compared to the as-yet-unpublished 1838 recital, it becomes apparent that the Prophet's account of things stayed steady during this time frame and was probably known among a wider cross-section of the contemporary LDS population than has been previously acknowledged.
Here then are several early testimonies from friendly and non-LDS sources, confirming that Joseph Smith and/or the missionaries were talking about Joseph conversing with Jesus Christ, angels, Apostles (Peter, James and John?), and "Almighty God." Evidently the early Saints were doing a lot more talking about these things than the critics want their readers to know about.
The historical record supports the claim that the First Vision was mentioned in non-Mormon literature prior to 1843:
The majority of these reports are garbled, fragmentary, and out of proper context but this evidence still shows that the claim being made in the source cited above is not accurate.
This is clear evidence that even if an anti-Mormon had multiple authoritative, unambiguous, printed copies of the First Vision story sitting right in front of them they would NOT necessarily seize upon it as evidence of an imposture. Some of them simply did NOT pay close attention to what Joseph Smith was saying openly.
Hugh Nibley pointed out years ago that anti-Mormon authors often went to great lengths to distort, ignore, or omit Joseph's telling of the visit of the Father and the Son.[31]
Critical sources |
|
It is asserted by some that Joseph Smith fabricated the First Vision story in order to provide himself with a more prestigious line of authority than that of the "angel" who revealed the golden plates.
There is no doubt that before Joseph Smith produced his 1832 history of the Restoration he was telling other people that he had a directive from God to carry out a certain work and that he had received instruction directly from one of God's authorized representatives. Joseph Smith had no need to produce some type of authority claim by 'fabricating' the First Vision event in 1832. The line of Divine authority had already been long established.
This theory does not stand up to close scrutiny. There are numerous contemporary and reminiscent documents which indicate that before Joseph Smith recorded his 1832 history (September-November 1832) he was claiming - both implicitly and explicitly - to have authority from God to carry out his ministry.
Notice in the citations below that when the angel who revealed the plates is mentioned he is identified as God's messenger. Thus, Joseph Smith's interaction is not simply with a nondescript angel; the angel is an authorized representative of Deity.
November 1826
Spring 1827
Fall 1827
April 1828
1828
1829
April 1830
1830
November 1830
August 1831
September 1831
November 1831
Critical sources |
|
Joseph Smith actually omitted details from his earlier First Vision account in his later ones. For example, the presence of "many angels" in addition to the two main personages noted in the 9 November 1835 account is never noted in any subsequent account.
Even though some of Joseph Smith's critics believe that the First Vision story changing over time is evidence that it was fabricated to begin with, the documents provide for a different explanation. The core elements of the First Vision story do not change as time passes - they are simply being clarified by the addition of details. The Prophet did not seem too concerned about which explanatory notes were being presented to his audience at any particular time because the really important parts—the core elements—never changed.
The above claim is not accurate simply because 24 story elements found in the 1832 account do not show up again in later recitals. In other words, the story actually becomes significantly LESS detailed over time because it does not include all of the elements that were initially rehearsed.
The 24 missing story elements from the 1832 recital are as follows:
The same type of thing happens with the 9 November 1835 recital of the story. There are several story elements presented that do not show up in subsequent retellings. The later recitals are, therefore, LESS detailed.
The missing 1835 elements are:
A comparison of the Prophet's 1838 and 1842 recitals yields the same result. The following details from the 1838 recounting do not show up in the 1842—Wentworth Letter—rehearsal:
Again, it is apparent that the Prophet's later tellings of the First Vision story were LESS detailed than his earlier ones.
Critical sources |
|
It is claimed that in 1838 Joseph Smith revised his personal history to say that his original call came from God the Father and Jesus Christ rather than an angel. It is also claimed that his motive for doing this was to give himself a stronger leadership role because an authority crisis had recently taken place and large-scale apostasy was the result.
The idea that Joseph Smith modified the First Vision story in 1838 in order to quell a leadership crisis is a convenient mythology crafted by critics who seem to be woefully unfamiliar with the records of the past and were unaware that Joseph told the same story in 1835.
This argument is a reference to the Kirtland crisis of 1837–38. Warren Parrish was considered by some of the Saints to be the ringleader of the Kirtland crisis. It is, therefore, all the more interesting that it was this same Warren Parrish who acted as scribe in recording a First Vision recital given by the Prophet Joseph Smith on 9 November 1835. When Parrish's 1835 account of the theophany is compared to the 1838 account it becomes glaringly obvious that the story did NOT change over time, as the critics would like everyone to believe.
It should also be noted that both the 1835 and 1838 First Vision accounts are followed immediately thereafter by the Book of Mormon angel story. Thus, it is impossible for critics to claim a shift in historical content by the Prophet. Before the Kirtland crisis took place Joseph Smith spoke in the 1835 retelling of events about an 1820 vision of two personages followed by an 1823 visitation by an angel. After the Kirtland crisis took place Joseph Smith said the exact same thing in the 1838 retelling of events.
Anti-Mormons claim that because of the problems caused by apostates in Kirtland, Ohio Joseph Smith suffered in his role as leader of the restored Church. While it is true that the apostates claimed Joseph Smith to be a fallen prophet, and tried to take over his role, the historical record shows that he stayed firmly in charge of Church affairs. In other words, the anti-Mormon claim that he needed to somehow boost his role as leader by modifying his story to sound more impressive falls flat. Consider the following timeline which leads right up to the time of the recording of the 1838 First Vision account.
Clearly, this is not the picture of a man in a leadership crisis who needed to bolster his standing among the Saints by making up some impressive-sounding story. This is the picture of a man who was being targeted by a small band of thugs but who still retained leadership standing among the vast majority of the Saints. The story that he told before the apostate problems of the Kirtland era was the same story he told after the troublemakers were shown the door.
Milton Backman recounts the events surrounding the death of Alvin, Joseph's elder brother:
After the death of Joseph's brother, Alvin, who died November 19, 1823, someone circulated the rumor that Alvin's body had been "removed from the place of his interment and dissected." In an attempt to ascertain the truth of this report, Joseph Smith, Sr., along with neighbors gathered at the grave, removed the earth, and found the body undisturbed. To correct the fabrication, designed in the opinion of Joseph's father to injure the reputation of the Smith family, Joseph, Sr., placed in the Wayne Sentinel (which appeared on successive Wednesdays from September 30 to November 3, 1824) a public notice reciting his findings that the body was undisturbed. [50]
Richard Bushman noted:
What Joseph said explicitly was that the vision led to trouble, though his youthful sensitivity probably exaggerated the reaction. The talk with the minister, he remembered, brought on ridicule by "all classes of men, both religious and irreligious because I continued to affirm that I had seen a vision." Local people seemed to have discussed his case, even though he said nothing to his parents. Eighteen years later when he wrote his history, the memories of the injustices still rankled.[51] For what ever reason, his father's family suffered "many persecutions and afflictions," he recalled, deepening a previous sense of alienation. William Smith remembered people throwing dirt, stones, and sticks against the Smith house. Later, after Alvin died, it was rumored someone had disturbed his body, and Joseph Sr. published a notice in the paper that the body had been exhumed and found to be untouched. Once someone fired a short at young Joseph for no apparent reason.[52][53]
This kind of malicious gossip is cruel and requires some motive. The notice that Joseph Smith Sr. placed in the Wayne Sentinel appeared four years after the first vision and one year after the first visit of Moroni to Joseph Smith, the visit in which Joseph was first shown the location of the plates but was not allowed to obtain them. This event is thus three years before Joseph's more-widely-known acquisition of the plates and five years before the publication of the Book of Mormon. If the Smith family could be the subject of such malicious gossip when faced with a tragedy like Alvin's death, without any other known motive for the ill treatment, can we reasonably presume that Joseph's vision had something to do with it? This should be considered in assesments of Joseph's claims to persecution[54]
Lucy Mack Smith recalled,
From this time [the First Vision] until the twenty-first of September, 1823 [when he saw the angel Moroni] Joseph continued, as usual, to labour with his father, and nothing during this interval occurred of very great importance—though he suffered, as one would naturally suppose, every kind of opposition and persecution from the different orders of religionists. [55]
William Smith, Joseph's brother remembered:
We were all very much scoffed at and persecuted during all this time, while Joseph was receiving his visions and translating the plates. [56]
It has generally been stated that my father's family were lazy, shiftless and poor; but this was never said by their neighbors, or until after the angel appeared and the story of the golden Bible was told.... [57]
It is said that Joseph and the rest of the family were lazy and indolent. We never heard of such a thing until after Joseph told his vision, and not then by our friends. Whenever the neighbors wanted a good days work done they knew where they could get a good hand and they were not particular to take any of the other boys before Joseph either. We cleared sixty acres of the heaviest timber I ever saw. We had a good place, but it required a great deal of labor to make it a good place. We also had on it from twelve to fifteen hundred sugar trees, and to gather the sap and make sugar and molasses from that number of trees was no lazy job. We worked hard to clear our place and the neighbors were a little jealous. If you will figure up how much work it would take to clear sixty acres of heavy timber land, heavier than any here, trees you could not conveniently cut down, you can tell whether we were lazy or not, and Joseph did his share of the work with the rest of the boys.
["]We never knew we were bad folks until Joseph told his vision. We were considered respectable till then, but at once people began to circulate falsehoods and stories in a wonderful way." [58]
With William's accounts, we again see that the persecution was largely verbal, in the form of gossip and slander.
Thomas H. Taylor, was asked, ""What did the Smiths do that the people abused them so?" He replied:
They did not do anything. Why! these rascals at one time took Joseph Smith and ducked him in the pond that you see over there, just because he preached what he believed and for nothing else. And if Jesus Christ had been there, they would have done the same to him. Now I don't believe like he did; but every man has a right to his religious opinions, and to advocate his views, too; if people don't like it, let them come out and meet him on the stand, and shew his error. Smith was always ready to exchange views with the best men they had. [Why didn't they like Smith?, asked the interviewer.]
To tell the truth, there was something about him they could not understand; someway he knew more than they did, and it made them mad. [59]
The raw notes for the Taylor interview likewise mention Joseph Smith being "ducked in the creek in Manchester" despite the fact that the Smiths "did nothing" and "nothing has been sustained [a]gainst [Joseph] Smith". [60]
Here too, then, we see an element of physical persecution, though the gossip and slander identified by William and Lucy was likely far more common.
Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision account does not explicitly say that he was persecuted for relating his spiritual manifestation to others. Some have claimed that this stands as evidence that the Prophet's story evolved over time—probably to add a sense of drama. However, the Prophet's 1832 history of the Restoration talks about persecution in very close proximity to the First Vision recital. The persecution is situated squarely between the First Vision experience and the angel Moroni visitations. The documentary evidence presented above demonstrates conclusively that Joseph Smith did not see anything wrong with telling the basic elements of his First Vision story and either giving a passing reference to other elements or leaving them out altogether. Regardless, it was still a record of the very same experience that took place at the Smith homestead near Palmyra, New York.
Joseph Smith made some remarks in his 1832 First Vision account that have a marked degree of relevance to the argument being put forward by his critics. In relation to the period of time between the First Vision and the appearance of the Book of Mormon angel he said,
Since it is explicitly stated by Joseph Smith that nobody believed his story, it would be unreasonable to assume that all of the responses to it were friendly in nature. In fact, the Prophet says right in this text that before the Book of Mormon angel visited him his family was persecuted and afflicted for some unspecified reason(s). He did not elaborate upon the nature of the "many persecutions" that took place against his family because—as far as this particular document was concerned—he had elected not to write down "many things which transpired."
The following documentary evidence from the 1838 First Vision account strengthens the argument that the 1832 text is referring to some type of persecution that took place because of Joseph's initial spiritual experience.
This 1838 description corresponds very well with the "many persecutions and afflictions" that are mentioned in the 1832 account. It also matches closely with the 1832 statements that nobody would believe Joseph's story and he reflected upon this adverse situation in his heart.
It should be pointed out that even though the 'persecution' theme is very pronounced in the 1838 account it is a piece of the story that was not always mentioned or emphasized in subsequent retelling (both published and verbal).
This last example is especially significant because it is an obvious reference to the Methodist minister who is spoken of in the 1838 History of the Church account. The 1844 rehearsal of events is less detailed but it is, nevertheless, the same exact story. The 1844 document clearly demonstrates that Joseph Smith did not always include an equal amount of story elements in his recitals of the First Vision. Critics of this manifestation should, therefore, not expect any such thing when they scrutinize the pertinent documents. If an element of the story was not known by one particular audience it cannot be automatically assumed that it was not known by another.
| See also: | Did Joseph Smith not talk about persecution in his 1832 account? |
Online |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Joseph and Hiel Lewis were cousins of Emma Hale Smith; they would have been aged 21 and 11 respectively in 1828, and in 1879 reported:
...while he, Smith, was in Harmony, Pa., translating his book....that he joined the M[ethodist] [Episocpal] church. He presented himself in a very serious and humble manner, and the minister, not suspecting evil, put his name on the class book, the absence of some of the official members, among whom was the undersigned, Joseph Lewis, who, when he learned what was done, took with him Joshua McKune, and had a talk with Smith. They told him plainly that such a character as he was a disgrace to the church, that he could not be a member of the church unless he broke off his sins by repentance, made public confession, renounced his fraudulent and hypocritical practices, and gave some evidence that he intended to reform and conduct himself somewhat nearer like a christian than he had done. They gave him his choice, to go before the class, and publicly ask to have his name stricken from the class book, or stand a disciplinary investigation. He chose the former, and immediately withdrew his name. So his name as a member of the class was on the book only three days.--It was the general opinion that his only object in joining the church was to bolster up his reputation and gain the sympathy and help of christians; that is, putting on the cloak of religion to serve the devil in. [61]
However, the Lewis' account of Joseph's three-day membership leaves him neither the time, nor the searching assessment required to become a member of the Methodists. This scenario simply does not match how Methodists admitted or expelled members. At best, he was probably regarded as "on probation" or (in modern LDS parlance) "an investigator". The means by which the Methodists separated themselves from Joseph are inconsistent with him being a full member; they do, however, match how probationaries were handled, though in Joseph's case he seems to have had more abrupt and preemptory treatment than was recommended.
This, coupled with the late date of the reminiscences, the clearly hostile intent of the witnesses, and multiple reports from both friendly and skeptical sources that claim Joseph never formally joined another religion make the critics' interpretation deeply suspect.
The Lewis witness is late. There is a marked absence of any other witnesses of Joseph's supposed membership and involvement, even though there are many witnesses who could have given such testimony.
For example, Nathaniel Lewis, another family member, was a Methodist minister. In his 1834 affidavit against Joseph, he emphasized his "standing in the Methodist Episcopal Church" which led him to "suppose [Joseph] was careful how he conducted or expressed himself before me." Yet, though anxious to impugn Joseph's character, this Lewis said nothing about membership in (or expulsion) from the Methodists. [62]
Likewise, none of Emma's other family members said anything about a Methodist connection, though they were closest to and most aware of Joseph's actions at this juncture than at any other time. Yet, Isaac Hale, Alva Hale, Levi Lewis, and Sophia Lewis are silent on the matter of Joseph's Methodism.
As we examine Osmon Cleander Baker's A guide-book in the administration of the discipline of the Methodist Episcopal Church, we will discover that the scenario described by Joseph and Hiel Lewis of Joseph Smith's ejection from the Methodists simply does not match how Methodists admitted or expelled members. [63] (This work dates to 1855, but it often invokes Wesley himself, and is a good first approximation of how Methodists saw such matters.)
The Guide-Book is clear that considerable time needs to elapse before one is formally admitted as a member:
[23] The regularly-constituted pastor is the proper authority to admit suitable persons to the communion of the Church. The preacher in charge, acting at first under the authority of Mr. Wesley, received members into the society, and severed their relations from the Church, according to his own convictions of duty. In 1784 the assistant was restricted from giving tickets to any, until they had been recommended by a leader with whom they had met, at least two months, on trial. In 1789 the term of probation was extended to six months....Hence, [24] since the organization of our Church, none could be received into full communion who had not previously been recommended by a leader; and, since 1840, it has been required that the applicant pass a satisfactory examination before the Church, respecting the correctness of his doctrine and his willingness to observe the rules of the Church....
Joseph's experience would predate the 1840 requirement, but clearly the requirement of at least a six month probationary period was required, and this required a leader to meet with them and be recommended for membership. The Lewis' three days certainly make this impossible.
The Guide-Book indicates that orthodox Christians may have the waiting period waived:
6. "Persons in good standing in other orthodox Chruches, who desire to unite with us, may, by giving satisfactory answers to the usual inquiries, be received at once into full fellowship."....
This still requires membership in an orthodox denomination, which Joseph did not have. Further, he clearly could not give the "satisfactory answers" to the types of questions which the Guide-Book recommends, since the Lewis brothers insist that he was unwilling to do so only three days later. Furthermore, Joseph's views were clearly not "orthodox" by Methodist standards.
The Guide-Book is again specific about the length of time required to pass this stage, and the searching examination of conduct and belief that Methodist groups required:
[28]...it is a matter of vital importance to test, with deep scrutiny, the moral and Christian character of those who propose to enter her holy communion. No proselyte was admitted to Jewish fellowship without being well proved and instructed. The same care was observed by the early Christian Church. "None in those days," says Lord King, "were hastily advanced to the higher forms of Christianity, but according to their knowledge and merit, gradually [29] arrived thereto."...It is the prerogative of the preacher in charge alone to receive persons on trial. No one whose name is taken by a class-leader can be considered as a member on trial until the preacher recognizes the person as such....
[30] As the minister may not know whether the candidate makes a truthful declaration of his moral state, he is authorized "to admit none on trial except they are well recommended by one you know, or until they have met twice or thrice in class." As they are not supposed, at the time of joining on trial, to be acquainted with our doctrines, usages, and discipline, they are not required, at that time, to subscribe to our articles of religion and general economy; but if they propose to join in full connexion, "they must give satisfactory assurances both of the correctness of their faith and their willingness to observe and keep the rules of the Church."...
The Discipline does not specify the time when the probation shall terminate, but it has [31] fixed its minimum period. "Let none be received into the Church until they are recommended by a leader with whom they have met at least six months."...
Again, at least six months was required to end a probationary period. One could not even be a trial, or probationary member unless they were "well recommended" (which seems unlikely, given the reaction to those who did know about Joseph as soon as they heard) or had attended "twice or thrice in class"--this too seems unlikely given only three days of membership.
An earlier account from a Methodist magazine prior to 1828 also supports this reading. In a letter to the editor from a Methodist missionary in Connecticut, the missionary responds to the accusation by others (usually Calvinists) who claim the Methodists falsify their membership records: they are accused of counting only those who have been added, but subtracting those who had left. Part of the response includes line: ".... though the first six months of their standing is probationary, yet they are not during that time denied any of the privileges of our church" (page 33-34).
The letter writer speaks of a revival in New Haven, where he is based, in 1820. "My list of probationers, commencingt June 25, 1820, to this date [March 16, 1821], is one hundred and forty; between twelve and twenty of these have declined from us, some to the Congregationalists, and some back to the world, and some have removed, and one died in the triumphs of faith. I think we may count about one hundred and twenty since June last." (36-7)[64]
It seems likely, then, that the same procedures would have been in place in Joseph's 1828 encounter with Methodism, which occurred squarely between this 1822 letter and the 1855 manual.
[32] Nor is it the order of the Church for probationers, who have never been baptized, to partake of the holy sacrament. The initiatory rite should first be administered before the person is admitted to all the distinguishing rites of the new covenant.
Since we have no record that Joseph was baptized into Methodism or any other faith prior to his revelations and founding of a new religious movement, this is another bar to his membership with the Methodists. How did he compress his six-month probation, proper answers to all the questions, searching interview by his fellow parishioners, and his baptism, only to abandon the faith without complaint, all within three days?
The Guide-Book was also clear that (save for immorality in preachers), the Methodist Church had no jurisdiction over acts committed before the member had joined:
Thus, nothing that Joseph had said or done prior to his membership could have been grounds for action. Thus, only the events of a scant three days were under the jurisdiction of the Methodists, if he had been accepted as a full member. (The Lewises even admit that nothing Joseph had said or done was cause for suspicion, because those who did not know him saw no cause for concern. It was only those who knew his past who were concerned.)
If, however, he was seen as a probationary or "person on trial," then the church and its leaders and members had every right to assess anything about him and decide if he merited membership.
The Guide-Book is clear that those who have not formally joined the Methodists can leave the group relatively easily:
[30] A mere probationer enters into no covenant with the Church. Every step he takes is preliminary to this, and either party may, at any time, quietly dissolve the relation between them without rupture or specific Church labour.
The Lewis brothers claim they gave Joseph a choice: (1) repent and change his ways; or (2) remove himself from association with them, by either (a) telling the class publicly that he was doing so; or (b) being subject to a disciplinary investigation. This matches how the Guide-Book recommends that probationers or "person[s] on trial" be handled:
[32] A person on trial cannot be arraigned before the society, or a select number of them, on definite charges and specifications. "If he walk disorderly, he is passed out by the door at which he came in. The pastor, upon the evidence and recommendation required in the Discipline, entered his name as a candidate, or probationer, for membership, and placed him in a class for religious training and improvement; now if his conduct be contrary to the gospel, or, in the language of our rule, if he 'walk disorderly [33] and will not be reproved,' it is the duty of the pastor to discontinue him, to erase his name from the class-book and probationers' list. This is not to be done rashly, or on suspicion, or slight evidence of misconduct. It is made the duty of his leader to report weekly to his pastor 'any that walk disorderly and will not be reproved.' This implies that the leader, on discovering an impropriety in his conduct, first conversed privately with him, and, on finding that he had done wrong, attempted to administer suitable reproof that he might be recovered. Had he received reproof, this had been the end of the matter; but he 'would not be reproved,'--would not submit to reproof,--and the leader therefore reports the case to the pastor. But it is evidently the design that after this first failure on the part of the leader, further efforts should be made by the pastor; for the rule, after providing that such conduct shall be made known to the pastor, adds: 'We will admonish him of the error of his ways. We will bear with him for a season. But, then, if he repent not, he hath no more place among us.' The pastor, on consultation with the leader and others when convenient in country societies, and with the [34] leaders' meeting, where there is one, determines on the proper course, and carries the determination into effect. Here is a just correspondence between rights and duties." - Plat. Meth., p. 87.
The Guide-Book is very clear:
[35] When a Church relation is formed, the member, virtually, promises to observe the rules and usages of the society, and if he violates them, to submit to the discipline of the Church. And hence none can claim a withdrawal from the Church against whom charges have been preferred, or until the Church has had an opportunity to recognise the withdrawal. A solemn covenant cannot be dissolved until the parties are duly notified....
How is this discipline to be handled? The Guide-Book contains extensive rules for managing such trials, and insists that such a trial is the only way to challenge the membership of a full member:
[83] It is a principle clearly recognised by the Discipline of our Church, that no member, in full connexion, can be dropped or expelled by the preacher in charge until the select committee, or the society of which he is a member, declares, in due form, that he is guilty of the violation of some Scriptural or moral principle,, or some requisition of Church covenant....[96] The Discipline requires that an accused member shall be brought before "the society of which he is a member, or a select number of them." In either case it should be understood that only members in full connexion are intended....
The "select committee" was a quasi-judicial body of church members assembled to hear such charges, assess the evidence, and affix punishment if necessary. The Guide-Book emphasizes that this important right had been explicitly defined after Joseph's time (in 1848). For full members, it is clearly seen as a privilege which cannot be abridged:
[83] The restrictive rules guarantee, both to our ministers and members, the privilege of trial and of appeal; and the General Conference has explicitly declared that "it is the right of every member of the Methodist Episcopal Church to remain in said Church, unless guilty of the violation of its rules; and there exists no power in the ministry, either individually or collectively, to deprive any member of said right."—Rec. Gen. Con. [89] 1848, p. 73. The fact that the member is guilty of the violation of the rules of the Church must be formally proved before the body holding original jurisdiction in the case. If the administrator personally knows that the charges are substantially true, it does not authorize him to remove the accused member. The law recognises no member as guilty until the evidence of guilt is duly presented to the proper tribunal, and the verdict is rendered....
Thus, even if the Lewis brothers had personal knowledge of Joseph's guilt, if he had been a full member, they could not have simply told him to leave.
The Guide-Book seems to rule this option out, for full members:
[108] If an accused member evades a trial by absenting himself after sufficient notice has been given, and without requesting any one to appear in his behalf, it does not preclude the necessity of a formal trial....
Furthermore, the public removal in front of the congregation seems to be out of harmony with another rule regarding trials for full members:
[110] It is highly improper, ordinarily, to conduct a trial in a public congregation. None should be present except the parties summoned; at least, unless they are members of the Church....
| See also: | When did Joseph Smith become 'partial to the Methodist sect'? |
| When was Lucy Mack Smith baptized as a Presbyterian? |
Critical sources |
|
It is claimed that President Brigham Young taught in an 1855 sermon that the Lord did not appear to Joseph Smith and forbid him from joining any of the religious denominations of his day, and that it was an "angel" who delivered this message instead. [65]
| See also: | Note that the same critics also claim that Brigham Young never spoke about the First Vision at all |
An edited version of the 1855 sermon text—as it is presented by Church critics—reads as follows:
"The Lord did not come with the armies of heaven...But He did send His angel to...Joseph Smith Jun[ior]...and informed him that he should not join any of the religious sects of the day."[66]
A complete quotation of the relevant 1855 sermon text reads as follows (bolded words indicate anti-Mormon usage):
the Lord sent forth His angel to reveal the truths of heaven as in times past, even as in ancient days. This should have been hailed as the greatest blessing which could have been bestowed upon any nation, kindred, tongue, or people. It should have been received with hearts of gratitude and gladness, praise and thanksgiving.
- But as it was in the days of our Savior, so was it in the advent of this new dispensation. It was not in accordance with the notions, traditions, and pre-conceived ideas of the American people. The messenger did not come to an eminent divine of any of the so-called orthodoxy, he did not adopt their interpretation of the Holy Scriptures. The Lord did not come with the armies of heaven, in power and great glory, nor send His messengers panoplied with aught else than the truth of heaven, to communicate to the meek[,] the lowly, the youth of humble origin, the sincere enquirer after the knowledge of God. But He did send His angel to this same obscure person, Joseph Smith Jun., who afterwards became a Prophet, Seer, and Revelator, and informed him that he should not join any of the religious sects of the day, for they were all wrong; that they were following the precepts of men instead of the Lord Jesus; that He had a work for him to perform, inasmuch as he should prove faithful before Him.
The portion of the second paragraph that critics focus on in their argumentation contains distinct themes found in the official, previously-published history of Joseph Smith. It is, therefore, necessary to evaluate President's Young's remarks in that light. Consider the following comparison of texts -
Since President Young was obviously drawing his ideas from the official, published First Vision text it is reasonable to propose that he was referring to a completely different event after the comma that follows the word "Revelator" . . . while still referring to the "He" at the beginning of the sentence. Hence, "He" (the Lord) send His angel (Moroni) to Joseph Smith but "He" also—ON A DIFFERENT OCCASION—told Joseph Smith not to join any of the churches.
It should be noted that this sermon was not primarily about the foundational events of Mormonism, but about the United States government and its treatment of the Saints. President Young's remarks on foundational events were incidental, not central, to his message. It should also be pointed out that President Young did not personally deliver this sermon, but had Thomas Bullock read it to the audience which had assembled in the Salt Lake City tabernacle. Bullock served as a scribe on the Joseph Smith history project between 1845 and 1856. It is likely, therefore, that when Bullock delivered President Young's sermon in 1855 he was aware of the First Vision accounts found within the previously-published Joseph Smith history.
It should also be remembered that long before President Brigham Young's 1855 sermon was delivered in Salt Lake City his subordinates in the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles had published the First Vision story on nine different occasions: (Orson Pratt - 1840, 1850, 1851); (Orson Hyde - 1842); (John E. Page - 1844); (John Taylor - 1850); (Lorenzo Snow - 1850); (Franklin D. Richards - 1851, 1852). It is doubtful that President Young would have remained ignorant of these publications and their content. In fact, it is known that Elder Lorenzo Snow wrote to President Young on 1 November 1850 and mentioned explicitly that his publication contained accounts of "visions of Joseph" - including the First Vision story.[67]
The charge that President Brigham Young said an angel inaugurated the last dispensation instead of Deity cannot be supported. Evidence suggests that President Young's 1855 sermon is closely paraphrasing distinct First Vision story elements that were publicly available to all of the Saints in 1842.
What about the term "angel"? Is there anything wrong with Brigham Young or others using that term to refer to Jesus Christ? Malachi spoke of the Lord as the "messenger of the covenant whom ye delight in." (Mal.3:1) The word translated "messenger" is the Hebrew mal'ak which can also be translated as "an angel."[68] The Septugint of Isaiah 9:6, traditionally thought by Christians to refer to Christ speaks of the "messenger of great counsel." This term for Jesus was frequently used by early Christians. Eusebius stated that Christ "was the first and only begotten of God; the commander-in-chief of the spiritual and immortal host of heaven; the angel of mighty counsel; the agent of the ineffable purpose of the Father." [69] The Martyrdom and Ascension of Isaiah (an apocryphal work, thought to have been written before the fourth century states that when Christ descended to earth he "made himself like the angels of the air, that he was like one of them." [70] The Epistula Apostolorum (another important early Christian work, thought to have been written by 2nd Century Christians quotes the resurrected Jesus as saying,"I became like an angel to the angels...I myself was a servant for myself, and in the form of the image of an angel; so will I do after I have gone to my Father." [71] At least the use of the term "angel" in Christianity does not seem unknown.
How did Joseph Smith understand the term "angel"? One revelation calls Jesus Christ "the messenger of salvation" (D&C 93꞉8) Another states,"For in the Beginning was the Word, even the Son, who is made flesh, and sent unto us by the will of the Father." (JST John 1:16). The Father sends Jesus because he is the angel of salvation. Joseph Smith himself taught that angels of God are resurrected beings who have bodies of flesh and bone. [72] "Jesus Christ became a ministering spirit (while his body was lying in the supulchre) to the spirits in prison...After His resurrection He appeared as an angel to His disciples." [73] In Mormon theology the term "angel" has a unique doctrinal significance.
Since Joseph Smith frequently taught this doctrine, is it any wonder that those who knew him best (Brigham Young, Orson Pratt, Heber C. Kimball, George A. Smith, etc.), would frequently refer to the Lord's visit to Joseph Smith as the visit of an angel (i.e. a resurrected personage of flesh and bone)?
Günther Juncker (at the time of this writing), Master of Divinity candidate at Trinity Evangelical Divinity School:
Unknown to many, the early church fathers often referred to Jesus as an Angel. And they gave him this appellation long before the (alleged) distortions of Constantine, the Controversies, the Councils, and the Creeds.... the word Angel has a prima facie claim to being a primitive, if not an apostolic, Christological title. Before pronouncing judgement on the Fathers, men who were often quite close to first-century apostles and eyewitnesses, we may recall that in antiquity the word "angel" had a broader semantic range than at present. When we think of angels, we immediately think of super-human, bodiless spirits, all of whom were created and some of whom fell with Satan in his rebellion. But in antiquity the word "angel" meant "messenger." It was primarily a functional (as opposed to an ontological) description and, thus, could refer to messengers who were human, angelic, or divine (the best known of the latter being Hermes, "the messenger god"). Likewise in Scripture, in both the OT and the NT, the term angel refers to human as well as to angelic messengers.[74]
Milton V. Backman, "I Have a Did Brigham Young confirm or expound on Joseph Smith’s first vision?," Ensign, Apr. 1992, 59:
President Young’s conviction of the divine calling of Joseph Smith included an unwavering acceptance of Joseph’s testimony regarding the First Vision. In 1842, Joseph Smith published two accounts of his 1820 theophany in the Times and Seasons—one he had written and included earlier in the Wentworth Letter, and the other a more extended history that appeared in serial form. This latter account (the account which appears in the current edition of the Pearl of Great Price) was reprinted in the Deseret News, the Millennial Star, and the first editions of the Pearl of Great Price during the presidency of Brigham Young. That President Young was well acquainted with this history is evident by the fact that he periodically cited the work in his sermons and writings.[75] —(Click here to read more)
It has been claimed that "Brigham Young never once mentioned the First Vision of God the Father and his Son in his 30 years of preaching as President of the Church." Note that the same critics also claim that Brigham Young taught only that an angel came: a strange claim to make while insisting that Brigham never spoke of the First Vision at all.
| See also: | Note that the same critics also claim that Brigham Young denied God or Christ appeared in the First Vision |
It cannot be denied that Brigham Young was aware of the official version of the First Vision as published by Joseph Smith in Nauvoo, Illinois. And it is almost beyond comprehension to believe that President Young was not aware of numerous First Vision story recitals (both in print and over the pulpit) by high Church authorities such as Orson Pratt, Lorenzo Snow, John E. Page, George Q. Cannon, Orson Hyde, John Taylor, Franklin D. Richards, and George A. Smith.
This charge is not historically accurate. It can be plainly seen in the information provided below that Brigham Young was aware of the First Vision story during his tenure as President of the Church and not only shared it with non-Mormons in written form but also spoke to the Saints about it over the pulpit.
On the 4th June I started for home, in company with Elders Young and Taylor.—Elder O. Pratt remained in New York to republish the book he had printed in Edinburgh, Scotland, giving a history of the coming forth of the Book of Mormon, and of which he intended to publish 5,000 copies…. [78] Elder Orson Pratt arrived here this week…[87]
Brigham Young:
The Lord chose Joseph Smith, called upon him at fourteen years of age, gave him visions, and led him along, guided and directed him in his obscurity until he brought forth the plates and translated them, and Martin Harris was prevailed upon to sustain the printing of the Book of Mormon. All this was done in the depths of poverty, obscurity, and weakness. [125]
Key sources |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Richard Abanes refers to "…the discrepancy between today’s official First Vision and the versions of it told by early Mormons, who taught that the First Vision involved an angel (or angels)." In a footnote to this comment he cites several church leaders, including John Taylor. The only citation Abanes gives for President Taylor is for March 2, 1879, but is incorrectly documented.[126]
Critic Isaiah Bennett has written:
Complications arise when one considers the statements of Smith’s successors as Mormon prophets [including John Taylor]. According to them, Smith had been visited by an angel, from whom he asked advice as to which church to join.[127]
Bennett cites the same March 2, 1879 sermon, and one other.
Jerald and Sandra Tanner have also cited Taylor’s comments of March 2, 1879.[128]:164 They later write that "Many other confusing statements about the first vision were made by Mormon leaders after Joseph Smith’s death." [128]:166 Elsewhere the Tanners have stated that "Before the death of Brigham Young in 1877 the first vision was seldom mentioned in Mormon publications. When Mormon leaders did mention it they usually gave confusing accounts."[129]
This warped perspective has unfortunately spilled over into less overtly anti-Mormon reference works. A past revision of the Wikipedia article on the First Vision states that "The First Vision was not emphasized in sermons by [subsequent leaders such as] John Taylor. This implies that Smith did not stress it strongly during his life, and that many early church leaders had little understanding of its prominence."[130]
These claims are simply false, with reference to the oft-misused John Taylor.[131] Consider the following evidence, from sermons, letters, and writings, which demonstrate Taylor’s complete awareness of that event, many well before the death of Brigham in 1877.
John Taylor became one of the editors of the Times and Seasons newspaper in Nauvoo, Illinois on 3 February 1842.[132]:102 He was serving in this capacity when the Wentworth Letter version of the First Vision was printed on 1 March 1842 and also when the History of the Church version of the First Vision was printed on 1 April 1842. John Taylor became chief editor of the Times and Seasons newspaper on 15 November 1842. There can be no doubt that Elder Taylor knew about the First Vision story as early as 1842.
In 1850, John Taylor was assigned to open France for the missionary activities of the Church. Upon arrival he wrote a letter, which was published in the French and English language paper. In that letter he wrote, in part:
The church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints was first organized in the Town of Manchester, Ontario County, State of New York, U.S.A., 6th April 1830. Previous to this an holy angel appeared unto a young man about fifteen years of age, a farmer's son, named Joseph Smith, and communicated unto him many things pertaining to the situation of the religious world, the necessity of a correct church organization, and unfolded many events that should transpire in the last days, as spoken of by the Prophets. As near as possible I will give the words as he related them to me. He said that "in the neighborhood in which he resided there was a religious revival, (a thing very common in that country) in which several different denominations were united; that many professed to be converted; among the number, two or three of his father's family. When the revival was over, there was a contention as to which of these various societies the person who was converted should belong. One of his father's family joined one society, and another a different one. His mind was troubled, he saw contention instead of peace, and division instead of union; and when he reflected upon the multifarious creeds and professions there were in existence, he thought it impossible for all to be right, and if God taught one, He did not teach the others, "for God is not the author of confusion." In reading his bible, he was remarkably struck with the passage in James, 1st chapter, 5th verse. 'If any of you lack wisdom, let him ask of God, that giveth to all men liberally and upbraideth not, and it shall be given him'. Believing in the word of God, he retired into a grove, and called upon the Lord to give him wisdom in relation to this matter. While he was thus engaged, he was surrounded by a brilliant light, and two glorious personages presented themselves before him, who exactly resembled each other in features, and who gave him information upon the subjects which had previously agitated his mind. He was given [236] to understand that the churches were all of them in error in regard to many things; and he was commanded not to go after them; and he received a promise that the fulness of the gospel should at some future time be unfolded unto him; after which the vision withdrew leaving his mind in a state of calmness and peace".[133]
Elder Taylor continued with his narration, indicating that "some time later" as Joseph prayed another ‘being’ appeared surrounded by light who "declared himself to be an angel of God, sent forth by commandment, to communicate to him that his sins were forgiven…[and] that the great preparatory work for the second coming of the Messiah was speedily to commence." The angel also told him about the plates, and the restoration about to begin. In October of that same year Elder Taylor published a pamphlet containing an expanded version of this letter, translated into French.[134] The pamphlet was reprinted again in 1852.
On 13 August 1857 John Taylor and several members of the First Presidency and Quorum of the Twelve placed a copy of the Pearl of Great Price (containing the First Vision story) inside the southeast cornerstone of the Salt Lake Temple.[135]
On 7 October 1859 John Taylor recited portions of the First Vision story in the Salt Lake City tabernacle. Among the details mentioned was the fact that Joseph Smith believed in the promise found in James 1:5 and went in secret to seek wisdom from God.[136]
In 1876 Elder Taylor spoke at a funeral service, and he stated:
Again, there are other things associated with these matters, all bearing more or less upon the same points. When God selected Joseph Smith to open up the last dispensation, which is called the dispensation [326] of the fullness of times, the Father and the Son appeared to him, arrayed in glory, and the Father, addressing himself to Joseph, at the same time pointing to the Son, said, "This is my beloved Son, in whom I am well pleased; hear ye him." As there were great and important events to be introduced into the world associated with the interests of humanity, not only with the people that now are, but with all people that have ever lived upon the face of the earth, and as what is termed the dispensation of the fullness of times was about to be ushered in, Moroni, who held the keys of the unfolding of the Book of Mormon, which is a record of the people who lived upon this American continent, came to Joseph Smith and revealed to him certain things pertaining to the peoples who had lived here and the dealings of God with them, and also in regard to events that are to transpire on this continent.[137]
Later in the same sermon he stated that Joseph had also been visited by Moroni, John the Baptist, and Peter, James and John. Isaiah Bennett makes reference to this sermon, but only to page 329: and the only plausible explanation for that reference is that Taylor makes reference to the angel which appeared to John the Revelator, on the island of Patmos. Otherwise that page tells of the visitation of Moroni and the others. Earlier in the sermon, however, Taylor made clear reference to the Father and the Son appearing, as contained in the above paragraph. Bennet and those who follow his tactics deceive their readers by omitting material which disproves their case.
In General Conference October 1877, President Taylor stated:
The work we are engaged in emanated from God, and what did Joseph Smith know about it until God revealed it? Nothing. What did President Young, or the Twelve, or anybody else, know about it before the heavenly messengers, even God himself, came to break the long, long silence of ages, revealing through his Son, Jesus Christ, and the holy angels, the everlasting Gospel? Nothing at all. We were all alike ignorant until heaven revealed it.[138]
The following month President Taylor stated:
[W]e are told that no man knows the [152] things of God but by the Spirit of God. And if they cannot obtain a knowledge of God only by the Spirit of God, unless they receive that Spirit they must remain ignorant of these principles. And it matters not what the learning, what the intelligence, what the research, the philosophy, or religion of man may be, the things of God cannot be comprehended, except through and by the Spirit and revelations of God. And this can only be obtained through obedience to the principles which God has and shall ordain, sanction and acknowledge. And hence, in these last times, he first communicated a knowledge of himself to Joseph Smith, long ago, when he was quite young. Who in that day knew anything about God? Who had had any revelations from Him, or who knew anything in relation to the principles of life and salvation? If there were any persons I never heard of them, nor read of them, nor never met them. But when the Lord manifested himself to Joseph Smith, presenting to him his Son who was there also, saying, "This is my beloved Son, hear ye him;" he then knew that God lived; and he was not dependent upon anybody else for that knowledge. He saw him and heard his voice, and he knew for himself that there was a God, and of this he testified, sealing his testimony with his blood.[139]
President Taylor also defended the First Vision in letters: In 1879 he wrote to a friend
We of all others on the earth ought to be the last to oppress the Lamanites. Through the development of their record, by the ministrations of one of their old prophets, we are indebted for the introduction of the Everlasting Gospel; and of so great importance was this action considered that God Himself, accompanied by the Savior, appeared to Joseph.[140]
It was mentioned above that several of the critics point to a sermon given by John Taylor in Kaysville, Utah, in the afternoon of March 2, 1879, to ‘prove’ that Taylor did not have a clear understanding of the First Vision. However, they fail to notice that President Taylor said earlier the same day, just a few miles away, in Ogden, Utah:
When the Father and the Son and Moroni and others came to Joseph Smith, he had a priesthood conferred upon him which he conferred upon others for the purpose of manifesting the laws of life, the Gospel of the Son of God, by direct authority, that light and truth might be spread forth among all nations.[141]
Clearly President Taylor was not confused regarding what happened early in Joseph Smith’s life.
Six months later he again testified to the visitation of the Father and the Son:
The Lord has taken a great deal of pains to bring us where we are and to give us the information we have. He came himself, accompanied by his Son Jesus, to the Prophet Joseph Smith. He didn't send anybody but came himself, and introducing his Son, said: ‘This is my beloved Son, hear him.’ And he permitted the ancient prophets, apostles and men of God that existed in different ages to come and confer the keys of their several dispensations upon the prophet of the Lord, in order that he should be endowed and imbued with the power and Spirit of God, with the light of revelation and the eternal principles of the everlasting Gospel.[142]
Ten days later he again testified to that transcendent event:
Now, we will come to other events, of later date; events with which we are associated—I refer now to the time that Joseph Smith came among men. What was his position? and how was he situated? I can tell you what he told me about it. He said that he was very ignorant of the ways, designs and purposes of God, and knew nothing about them; he was a youth unacquainted with religious matters or the systems and theories of the day. He went to the Lord, having read James' statement, that "If any of you lack wisdom let him ask of God that giveth to all men liberally and upbraideth not; and it shall be given him." [James 1.5] He believed that statement and went to the Lord and asked him, and the Lord revealed himself to him together with his Son Jesus, and, pointing to the latter, said: ‘This is my beloved Son, hear him.’ He then asked in regard to the various religions with which he was surrounded.[143]
Again, just a few weeks later he stated that
as a commencement the Lord appeared unto Joseph Smith, both the Father and the Son, the Father pointing to the Son said ‘this is my beloved Son in whom I am well pleased, hear ye him.’ Here, then, was a communication from the heavens made known unto man on the earth, and he at that time came into possession of a fact that no man knew in the world but he, and that is that God lived, for he had seen him, and that his Son Jesus Christ lived, for he also had seen him. What next? Now says the Father, "This is my beloved Son, hear him." The manner, the mode, the why, and the wherefore, he designed to introduce through him were not explained; but he, the Son of God, the Savior of the world, the Redeemer of man, he was the one pointed out to be the guide, the director, the instructor, and the leader in the development of the great principles of that kingdom and that government which he then commenced to institute.[144]
Later, in Hooperville, Utah, he stated:
Hence when the heavens were opened and the Father and Son appeared and revealed unto Joseph the principles of the gospel, and when the holy priesthood was restored and the Church and kingdom of God established upon the earth, there were the greatest blessings bestowed upon this generation which it was possible for man to receive.[145]
Two months later he again spoke of it:
Finally, when all the preparations were made and everything was ready, or the time had fully come, the Father and the Son appeared to the youth Joseph Smith to introduce the great work of the latter days. He who presides over this earth and he who is said to be the maker of all things, the Father, pointing to his well-beloved Son, says, this is my beloved Son, hear him. He did not come himself to regulate and put in order all things, but he presented his Only Begotten Son, the personage who should be, as he is termed in the Scriptures, the Apostle and great High Priest of our profession, who should take the lead in the management and regulation of all matters pertaining to the great dispensation that was about to be ushered in.[146]
Two months later he was in Idaho speaking:
In the commencement of the work, the Father and the Son appeared to Joseph Smith. And when they appeared to him, the Father, pointing to the Son, said, ‘This is My Beloved Son, Hear Him!’ As much as to say, ‘I have not come to teach and instruct you; but I refer you to my Only Begotten, who is the Mediator of the New Covenant, the Lamb slain from before the foundation of the world; I refer you to him as your Redeemer, your High Priest and Teacher. Hear him.’ Continuing, he pointed out that Joseph was also visited by Moroni, John the Baptist, and Peter, James, and John.[147]
In 1882 President John Taylor wrote a book on the subject of the mediation and atonement of the Savior, and its role in the life of the Restored Gospel. He included this statement:
…when the Father and the Son appeared together to the Prophet Joseph Smith they were exactly alike in form, in appearance, in glory; and the Father said, pointing to His Son, ‘This is my beloved Son; hear Him.’[148]
That same year the President said in a sermon:
we declare that God himself took part in it, and that Jesus, the Mediator of the new covenant, accompanied him, both of whom appeared to Joseph Smith, upon which occasion the Father, pointing to the Son said, ‘This is my beloved Son, hear him.’…. …..[32] After the Lord had spoken to Joseph Smith, and Jesus had manifested himself to him…. [He later refers to the visitation of Moroni, John the Baptist, and Peter, James and John.][149]
During the October 1882 General Conference three of the General Authorities referred to the appearance of the Father and the Son. President Taylor stated that
A message was announced to us by Joseph Smith, the Prophet, as a revelation from God, wherein he stated that holy angels had appeared to him and revealed the everlasting Gospel as it existed in former ages; and God the Father, and God the Son, both appeared to him; and the Father, pointing, said, this is my beloved Son, in whom I am well pleased, hear ye him.[150]
Later that same year he said:
In the first place He has Himself spoken to us from the heavens, as also has His Son Jesus Christ…. [323] Now, it is the rule of God which is desired to be introduced upon the earth, and this is the reason why the Father and the Son appeared to Joseph Smith….It is true that God appeared to Joseph Smith, and that His Son Jesus did…
President Taylor then went on to testify that Joseph Smith claimed that John the Baptist, Peter, James and John, and Moses had also appeared to him.[151]
At the dedication of the Logan Temple in 1884 President Taylor said:
I have heard some remarks in the Temple pertaining to these matters, and also here, and it has been thought, as has been expressed by some, that we ought to look for some peculiar manifestations. The question is, What do we want to see? Some peculiar power, some remarkable manifestations? All these things are very proper in their place; all these things we have a right to look for; but we must only look for such manifestations as are requisite for our circumstances, and as God shall see fit to impart them. Certain manifestations have already occurred. When our Heavenly Father appeared unto Joseph Smith, the Prophet, He pointed to the Savior who was with him, (and who, it is said, is the brightness of the Father's glory and the express image of His person) and said: ‘This is my beloved Son, hear Him.’ [Later in the sermon he mentions the appearance of John the Baptist, and Peter, James and John; and Moroni.][152]
In 1886, shortly before he died, President Taylor wrote a letter to his family, part of which reads:
We are engaged in a great work, and laying the foundation thereof—a work that has been spoken of by all the holy prophets since the word was; namely, the dispensation of the fullness of times, wherein God will gather together all things in one, whether they be things in the earth, or things in the heaven; and for this purpose God revealed Himself, as also the Lord Jesus Christ, unto His servant the Prophet Joseph Smith, when the Father pointed to the Son and said: ‘This is my beloved Son, in whom I am well pleased, hear ye Him.’[132]:394
As evidence that President Taylor had been telling the Saints about the First Vision throughout his life a comment made at his funeral would be pertinent; it was said there that
Brother Taylor took the testimony that Joseph gave him, that Jesus delivered unto Joseph, that God bade Joseph to listen to from the lips of His beloved Son, as he bore those tidings to foreign lands…[153]
The following two statements were made by John Taylor in different discourses on the same day, 2 March 1879. In one, Taylor talks of Joseph Smith asking "the angel" which church was right, and in the other, Taylor clearly states that "the Father and the Son...came to Joseph Smith." This demonstrates how early Church leaders often used the term "angel" to refer to the personages that appeared in the First Vision, even though they clearly knew that they were the Father and the Son.
None of them was right, just as it was when the Prophet Joseph asked the angel which of the sects was right that he might join it. The answer was that none of them are right.[154]
When the Father and the Son and Moroni and others came to Joseph Smith, he had a priesthood conferred upon him which he conferred upon others for the purpose of manifesting the laws of life... [155]
Notice how one refers to an "angel" and the other refers to "the Father and the Son." Taylor was clearly aware of the details of the First Vision. This also demonstrates how early Church leaders used the term "angel" to represent the personages that Joseph saw, even at the same time that they recognized that these personages were the Father and the Son.
Critical sources |
|
If Latter-day Saint belief about the First Vision is correct, Joseph’s narrative reports a memory of his early experience. If, on the other hand, Vogel, Palmer, and other skeptical interpreters were to be correct, Joseph’s narrative was created to meet his needs as a church leader in the 1830s, bolstering his authority as prophet.
These two radically different understandings of the First Vision lead us to two radically different predictions about how well Joseph’s First Vision accounts will align with the events of the early 1820s. On the first, the believing, view, Joseph’s narrative should match the 1820s context in some detail. On the second, skeptical, view, his narrative should match the claimed 1820s context poorly or only superficially.
Because these two views lead to such different predictions, we can determine which view is correct by testing those predictions. And this is what we’ll do today.
A history article printed in 1888 by assistant Church historian Andrew Jenson twice referred to one of the visitors as an "angel".[156] Two years later Church leaders revised Jenson's text to clear up the discrepancy but did not provide any notation about the change.
When the light of historical scholarship shines upon this particular charge of the critics, it quickly becomes apparent that this is really a non-issue. By the time that Andrew Jenson had published his anomalous First Vision account in 1888 the Pearl of Great Price rendition of the same story had already been canonized by the Church for eight years. Latter-day Saints had long been familiar with the official version of events that took place in the Sacred Grove and the precise identities of Joseph Smith's celestial visitors.
The publication that anti-Mormon critics are referring to was called The Historical Record and it was printed in Salt Lake City, Utah. Volume 7 of this collection contains the reference that critics utilize to try and cast doubt upon the veracity of the First Vision account.
Andrew Jenson was not a Church historian ('assistant' or otherwise) in 1888 when he wrote the text in question. A book produced by Jenson himself indicates that "his services were engaged by the First Presidency, and he was blessed and set apart by Apostle Franklin D. Richards [on] April 16, 1891, as ‘an historian’ in the Church."[157] Jenson was not sustained as the Assistant Church Historian until 10 April 1898. [158] Since Andrew held no position of authority in the LDS Church when he made his "angel" comments, they cannot be looked upon as having any kind of evidentiary value in regard to what Church leaders believed at the time.
Church critics neglect to tell their readership that Andrew Jenson is plainly listed as the editor and the publisher of both the initial 1888 text and the revision which they allege was printed in 1890. Furthermore, they fail to make note of the fact that when volumes 5-8 of The Historical Record were advertised for sale in a Utah newspaper in 1889 it was noted that this was a "work which Brother Jenson offers" to the public. [159] There is, therefore, no justification whatever in claiming that the LDS Church was somehow responsible for the content of Andrew Jenson's original 1888 article or the revised text that was issued later.
Critical sources |
|
A history article printed in 1888 by assistant Church historian Andrew Jenson twice referred to one of the visitors as an "angel".[160] Two years later Church leaders revised Jenson's text to clear up the discrepancy but did not provide any notation about the change.
When the light of historical scholarship shines upon this particular charge of the critics, it quickly becomes apparent that this is really a non-issue. By the time that Andrew Jenson had published his anomalous First Vision account in 1888 the Pearl of Great Price rendition of the same story had already been canonized by the Church for eight years. Latter-day Saints had long been familiar with the official version of events that took place in the Sacred Grove and the precise identities of Joseph Smith's celestial visitors.
The publication that anti-Mormon critics are referring to was called The Historical Record and it was printed in Salt Lake City, Utah. Volume 7 of this collection contains the reference that critics utilize to try and cast doubt upon the veracity of the First Vision account.
Andrew Jenson was not a Church historian ('assistant' or otherwise) in 1888 when he wrote the text in question. A book produced by Jenson himself indicates that "his services were engaged by the First Presidency, and he was blessed and set apart by Apostle Franklin D. Richards [on] April 16, 1891, as ‘an historian’ in the Church."[161] Jenson was not sustained as the Assistant Church Historian until 10 April 1898. [162] Since Andrew held no position of authority in the LDS Church when he made his "angel" comments, they cannot be looked upon as having any kind of evidentiary value in regard to what Church leaders believed at the time.
Church critics neglect to tell their readership that Andrew Jenson is plainly listed as the editor and the publisher of both the initial 1888 text and the revision which they allege was printed in 1890. Furthermore, they fail to make note of the fact that when volumes 5-8 of The Historical Record were advertised for sale in a Utah newspaper in 1889 it was noted that this was a "work which Brother Jenson offers" to the public. [163] There is, therefore, no justification whatever in claiming that the LDS Church was somehow responsible for the content of Andrew Jenson's original 1888 article or the revised text that was issued later.
| See also: | Is there anything wrong with referring to Jesus as 'an angel'? |
Author's source(s)
Doctrine and Covenants (Kirtland, Ohio: F.G. Williams & Co., 1835), 52-58. See also Tanner, ‘’Mormonism-Shadow or Reality?’’ 143-62.
Response
In the beginning, the head of the Gods called a council of the Gods; and they came together and concocted [prepared] a plan to create the world and people it. When we begin to learn this way, we begin to learn the only true God, and what kind of a being we have got to worship. Having a knowledge of God, we begin to know how to approach Him, and how to ask so as to receive an answer.
In Joseph’s 1832 First Vision account, he said he was fifteen when “the Lord” appeared to him. Not only is his age different, but he described only one being, as opposed to the ‘two personages’ he had previously accounted for, in the vision.”
Author's sources: Joseph Smith’s 1832 history
Accounts |
|
Historical context |
|
Doctrinal impact |
Video published by the Church History Department.
Video from FAIR
Joseph's concern about religion started when he was twelve years old, close on the heels of the revival of 1817. In his 1832 account, Joseph notes that his concern about religion began at age 12 (1817-1818):
At about the age of twelve years my mind become seriously imprest with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul which led me to searching the scriptures believeing as I was taught, that they contained the word of God thus applying myself to them and my intimate acquaintance with those of different denominations led me to marvel excedingly for I discovered that they did not adorn instead of adorning their profession by a holy walk and Godly conversation agreeable to what I found contained in that sacred depository this was a grief to my Soul... (Joseph Smith's 1832 account of the First Vision)
Richard Bushman notes that this "would have been in late 1817 and early 1818, when the after-affects of the revival of 1816 and 1817 were still felt in Palmyra." [1]
Joseph Smith talked of observing, as a 14-year-old, "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion" in the Palmyra area during the Spring of 1820. Joseph notes that "It commenced with the Methodists, but soon became general among all the sects in that region of country." There is documented evidence of at least one Methodist camp meeting in the Palmyra area during that period, which only by chance happened to be mentioned in the local newspaper because of a specific death that seemed to be associated with it. In addition, there are newspaper articles talking of large-scale revival activity in the larger region surrounding Palmyra during the same general period when Joseph Smith said that it was taking place.
It is reasonable to assume based upon the facts that the Methodists had more than one camp meeting during this period. This could easily account for the religious excitement in Palmyra that, in Joseph's mind at age 14, began with the Methodists.
Joseph continues in his 1832 account: "[T]hus from the age of twelve years to fifteen I pondered many things in my heart concerning the sittuation of the world of mankind the contentions and divi[si]ons the wicke[d]ness and abominations and the darkness which pervaded the of the minds of mankind my mind become excedingly distressed for I become convicted of my sins." In July, 1819, several years after Joseph said his mind became "seriously imprest," a major Methodist conference was held near Palmyra:
[T]he Methodists of the Genesee Conference met for a week in Vienna (later Phelps), a village thirteen miles southeast of the Smith farm on the road to Geneva. About 110 ministers from a region stretching 500 miles from Detroit to the Catskills and from Canada to Pennsylvania met under the direction of Bishop R. R. Robert to receive instruction and set policy. If we are to judge from the experience at other conferences, the ministers preached between sessions to people who gathered from many miles around. It was a significant year for religion in the entire district. . . . The Geneva Presbytery, which included the churches in Joseph's immediate area, reported in February, 1820, that "during the past year more have been received into the communion of the Churches than perhaps in any former year." Methodists kept no records for individual congregations, but in 1821 they built a new meetinghouse in town. [2]

Some claim that there were no religious revivals in the Palmyra, New York area in 1820, contrary to Joseph Smith's claims that during that year there was "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion...indeed, the whole district of country seemed affected by it" Joseph Smith—History 1:5 Joseph Smith talked of observing, as a 14-year-old, "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion" in the Palmyra area during the Spring of 1820. Joseph notes that "It commenced with the Methodists, but soon became general among all the sects in that region of country."
Abundant evidence of religious excitement exists to substantiate Joseph’s account. This has been thoroughly summarized by Pearl of Great Price Central. Their analysis may be accessed by clicking on the hyperlinked text.
One should keep in mind that Joseph Smith never used the term "revival" in his description - he simply described it as "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion." To a 14 year old who had been concerned about religion starting at age 12 after the 1817 revival, the ongoing camp meetings in the town in which he lived would certainly qualify.

Critics of Joseph Smith claim that no revival is mentioned in the 1832 First Vision account because the actual word 'revival'—or something similar—is not found within the text. But they have failed to notice a distinct pattern of words that demonstrate a definite link between the various First Vision accounts.
When the September—November 1832 First Vision account is compared with subsequent recitals (especially 1838), and one partial previous rendition, it appears that they are all telling the same story: Prior to the First Vision event there were contentions and divisions among the different religious denominations in connection with a revival. It seems, therefore, that the Prophet's handwritten 1832 account does indeed make a passing reference to revival activity.
There are several other phrases in the Prophet's 1832 account that can be interpreted as references to revivals. For instance, Joseph Smith said that when he was "about the age of twelve years" (23 December 1817—23 December 1818) he became seriously concerned about the welfare of his soul. Why did these feelings arise at this point in time? Possibly because there was a Methodist camp-meeting/revival from June 19th through the 22nd, 1818 held in Palmyra, New York.[8]
Joseph Smith pointed to a time period "from the age of twelve years to fifteen" (i.e., between 23 December 1817 and 23 December 1821) when he –
Some of the themes enumerated above can be matched with the Prophet's other descriptions of things that happened during the revival activity of Palmyra and its vicinity. This matching of themes tends to support the argument that the 1832 text does indeed refer to revival activity.
The phrase "I cried unto the Lord for mercy" in Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision account also has a strong ring of revivalism to it. Rev. George Peck recounted the happenings at a Methodist camp meeting held on 4 July 1816 in Plymouth, New York. He said that "There was an unbroken roar of fervent supplication all over the ground, while the awful voice of the preacher resounded." One person then fell to the ground and cried for mercy.[9]
Wiki links |
|
Online |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Joseph Smith's stated motivation for praying to the Lord changes between the first known account of the First Vision (1832) and the official version of it (1838). The 1832 account emphasizes his desire for a forgiveness of sins, and the 1838 (official) account emphasizes his desire to know which church was right. Some critic claim that Joseph changed his story in later years.
The texts that are employed by critics to justify the charge of 'differing motivations' are as follows:
1832
1838
The words that precede the point at which Joseph Smith offers his prayer in the 1832 text demonstrate that the anti-Mormon claim about his motivation changing is not sustainable. These words read as follows (standardized for readability):
Historian Christopher Jones has observed that Joseph Smith's 1832 account (and indeed much of his other three accounts) are shaped as Methodist conversion narratives. Within Methodism (and indeed the broader religious culture of Joseph Smith's day), finding forgiveness of sins and joining the right Church rode in tandem. You receive forgiveness of sins by joining the right Church. If you don't follow the correct, "biblical" doctrine then you can't receive such forgiveness.[10] In the case of Joseph Smith, he receives forgiveness of sins and is told not to join any church with which he was acquainted at the time.
There are those who claim that Joseph Smith only claims to seek forgiveness of sins in his 1832 account. These critics ignore the larger historical context under which the 1832 account was written (documented by Jones) and also fail to take notice of scriptural passages quoted near the end of the account in which Christ echoes Matthew 15:8-9:
This clearly does not refer to young Joseph's seeking of a forgiveness of sins. It must refer to an apostasy and restoration of a Church—the true Church of Christ that Joseph had already proclaimed to restore as Doctrine and Covenants 1 (revealed in 1831) makes clear:
Some may counter that this only refers to corrupt people and not corrupt churches or religions. Going back to the passage from the 1832 account cited above, one reads "the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doth good no not one..." This phrase ('and none doeth good no not one') is echoed in a few scriptural passages (Psalm 53: 3; Romans 3: 10, 12; Moroni 7:17) but for our purposes we will highlight one of these occurrences in JST Psalm 14:2. The Church still describes this passage in its heading as lamenting "the loss of truth in the last days[.]" The passage "looks forward to the establishment of Zion." The italics represent edits made by Joseph Smith to the text:

Joseph Fielding McConkie said, 'The JST rendering of this Psalm reads like another account of the First Vision.'[11]
The late Matthew Brown suggested that Joseph's translation of Psalm 14 took place 'shortly after late July 1832.'[12] He even goes so far to say that 'the JST Psalm 14 text may have served as a prototype of sorts for the composition of the 1832 historical document.'[13]
The 1838–39 account’s mention of 'corrupt professors' seems to be reflected in the JST’s 'their teachers are workers of iniquity.' . . . JST Psalm 14:2-4 features 'all these who say they are [the Lord’s]' being rejected by the Lord due to them having 'gone aside,' 'become filthy,' and 'none of them…doing good.' And this is laid at the feet of their teachers who 'are workers of iniquity' [14] This use of Psalm 14 to be explanatory for Joseph's use of no one doing good is strengthened by the fact that Psalm 14 is quoted specifically earlier in the 1832 account ("And when I considered upon these things my heart exclaimed, 'Well hath the wise man said, It is a fool that saith in his heart there is no God.'")
Thus, to summarize again, those who don't do good are all people and this is caused by false teachers teaching incorrect doctrine.
The 1832 account emphasizes Joseph's want of forgiveness as a means to the end of restoring the true Church of Christ. This is completely in line with the rest of the accounts and thus the standard narrative of the First Vision and Joseph's motives in seeking such a vision as taught officially by the Church.
A longer version of this argument is made by Walker Wright and historian Don Bradley in a 2023 paper for BYU Studies.[15]
The First Vision has been a center of both faith and controversy. While millions of Latter-day Saints affirm it as the beginning of the Restoration, others see it as an ever-growing fish tale. The multiple accounts of the First Vision vary in detail, with Joseph Smith’s earliest written account (1832) lacking some of the elements found in his later accounts. However, some of these elements—particularly the appearance of God the Father as part of the First Vision experience—are laced throughout Joseph Smith’s translation of the Bible. These historical threads ultimately culminate in his translation of Psalm 14, which weaves together many of the elements supposedly lacking in Smith’s earliest account of the First Vision. But why bring these threads together in Psalm 14? What was its connection with his First Vision? A basic comparison of Psalm 14 with elements of the First Vision shows that elements of this psalm are found in the background of the vision, as Joseph Smith narrated it, and even in the words of Deity spoken within the vision itself.
It is clear from a consultation of the 1832 text that Joseph Smith's desire to be forgiven of his personal sins was NOT the only motivation for his prayer in the wilderness. He prayed (as he explicitly states) because of "all" of the things he mentions - including the desire to worship God in truth; according to His laws (which Joseph did not believe was the case among any of the Christians denominations that he knew of).
The 1832 textual pattern of (1) desire to prepare for eternity / worship God in truth and (2) desire for forgiveness of personal sins can be detected in subsequent First Vision recitals, demonstrating that there is no change in his declared motive over time. The confusion of the critics on this issue arises when they do not see exact matches in themes across documents or insist that every detail of the story be present in every text that relates it.
1832 (Smith)
1834 (Cowdery/Smith)
1835 (Smith)
1838 (Smith)
1840 (Pratt)
1842 (Smith)
1842 (Hyde)
Critical sources |
|
Critics claim that there is a contradiction between the 1832 account of Joseph Smith's First Vision and the rest of his first-hand accounts. They also claim that the same contradiction occurs internally in the 1838 account. It is alleged that Joseph Smith concluded prior to going to the grove of trees to pray that all the denominations on the earth were false. This supposedly contradicts the 1835 and 1838 accounts in which Joseph expresses doubt as to which Church was true prior to going to the grove.
In his 1832 history, Joseph Smith said:
I found [by searching the scriptures] that mankind did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatized from the true and living faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament
In his 1835 account, Joseph Smith said, "I knew not who [of the denominations] was right or who was wrong."
In his 1838 account of the Vision, Joseph writes:
The 1832 account then, according to some critics, contradicts the 1835 and 1838 account in that Joseph had already determined before seeing God and Jesus that there was no true Church and thus the only motive for going to the grove in the 1832 account would be to obtain a forgiveness of sins and not to find the true Church.
Author J.B. Haws describes the criticism as it relates to the 1838 account specifically:
Here is the essence of that trouble, as some have seen it. In Joseph’s 1838–39 dictated account (the account that would eventually find its way into the LDS Church’s canon as the official Joseph Smith—History), he described his youthful confusion about the competing religious sects that he encountered in these words: "In the midst of this war of words and tumult of opinions, I often said to myself: What is to be done? Who of all these parties are right; or, are they all wrong together?" (Joseph Smith History 1:10). According to this narrative, it seems that fourteen-year-old Joseph had already considered the possibility that all churches could be "wrong together." Yet only eight verses later (by the account’s current scriptural format), Joseph reported what seems like surprise in response to the divine injunction that he must join no church, "for they were all wrong"—and "it had never entered into [his] heart that all were wrong" (JS—H 1:18–19). But didn’t we just read that the "all were wrong" possibility had entered his heart in verse 10? Why such an apparently careless and contradictory oversight in the narrative?[16]
Critics claim that this is a contradiction and evidence that the First Vision story evolved over time.
Such a claim is a false dilemma, as we will now see.
Historian Christopher Jones has observed that Joseph Smith's 1832 account (and indeed much of his other three accounts) are shaped as Methodist conversion narratives. Within Methodism (and indeed the broader religious culture of Joseph Smith's day), finding forgiveness of sins and joining the right Church rode in tandem. You receive forgiveness of sins by joining the right Church. If you don't follow the correct, "biblical" doctrine then you can't receive such forgiveness.[17] In the case of Joseph Smith, he receives forgiveness of sins and is told not to join any church. Thus even if Joseph's main emphasis is forgiveness of sins in the 1832 account, that doesn't mean he's not talking about what Church is true.
Those critics who claim that Joseph is only speaking about the forgiveness of sins in the 1832 account are ignorant of the larger historical context under which the 1832 account was written (documented by Jones) and also fail to take notice of important scriptural passages quoted near the end of the account. Speaking about the condition of the world, Christ, speaking to Joseph, echoes Matthew 15:8-9:
'[T]hat which hath been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Apostles' might easily refer to an apostasy and restoration.
Some may counter that this only refers to corrupt people and not corrupt churches or religions. Going back to the passage from the 1832 account cited above, one reads "the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doth good no not one..." This phrase ('and none doeth good no not one') is echoed in a few scriptural passages (Psalm 53: 3; Romans 3: 10, 12; Moroni 7:17) but for our purposes we will highlight one of these occurrences in JST Psalm 14:2. The Church still describes this passage in its heading as lamenting "the loss of truth in the last days[.]" The passage "looks forward to the establishment of Zion." The italics represent edits made by Joseph Smith to the text:

Joseph Fielding McConkie said, 'The JST rendering of this Psalm reads like another account of the First Vision.'[18]
The late Matthew Brown suggested that Joseph's translation of Psalm 14 took place 'shortly after late July 1832.'[19] He even goes so far to say that 'the JST Psalm 14 text may have served as a prototype of sorts for the composition of the 1832 historical document.'[20]
"The 1838-39 account’s mention of 'corrupt professors' seems to be reflected in the JST’s 'their teachers are workers of iniquity.' . . . JST Psalm 14:2-4 features 'all these who say they are [the Lord’s]' being rejected by the Lord due to them having 'gone aside,' 'become filthy,' and 'none of them…doing good.' And this is laid at the feet of 'their teachers' who 'are workers of iniquity.'"[21] This use of Psalm 14 to be explanatory for Joseph's use of no one doing good is strengthened by the fact that Psalm 14 is quoted specifically earlier in the 1832 account ("And when I considered upon these things my heart exclaimed, 'Well hath the wise man said, It is a fool that saith in his heart there is no God.'")
Thus, to summarize again, those who don't do good are all people and this is caused by false teachers teaching incorrect doctrine. Under this understanding, the 1832 account of Joseph Smith's First Vision is giving implicit credence that Joseph was indeed seeking to know from God which Church to join because the teachers of other denominations had become corrupt.
Author Jim Bennet describes one approach that a person can take while seeking to reconcile this with their faith and that is to focus interpretation on the phrase "entered into my heart":
The key phrase is "entered into my heart."
We can have confidence in what Joseph means by this because it is not the only time he uses variations of this phrase. Here’s what he says about his experience reading James 1:5.
- Never did any passage of scripture come with more power to the heart of man than this did at this time to mine. It seemed to enter with great force into every feeling of my heart. [JSH 1:12, emphasis added]
This is a phrase Joseph uses to describe something more powerful than mere intellectual assent. He’s describing a spiritual experience, where the feelings of the heart complement and contribute to clarity of mind. It’s a concept that shows up in the Doctrine and Covenants, too:
- Yea, behold, I will tell you in your mind and in your heart, by the Holy Ghost, which shall come upon you and which shall dwell in your heart.
- Now, behold, this is the spirit of revelation; behold, this is the spirit by which Moses brought the children of Israel through the Red Sea on dry ground. [D&C 8:2-3, emphasis added]
Joseph had clearly considered the possibility all churches were in error in verse 10 (and in the 1832 account,) but the idea hadn’t really sunk in – i.e. entered into his heart – until after verse 18.
I think all of us have had this experience – things happen that we choose not to believe. Even when we have solid information, we don’t allow our intellectual knowledge to become wisdom and "enter into our hearts." He’s describing the very human process of denial, much like Amulek from the Book of Mormon, who once said of his own testimony, "I knew concerning these things, yet I would not know." (Alma 10:6)
Make up your mind, Amulek! Did you know or didn’t you know?! That’s a direct contradiction!
In the case of "Forgiveness of Sins v. Which Church is True,"... Joseph was preoccupied with what he needed to do to prepare to meet God. You see that in all of Joseph’s firsthand accounts.
"[M]y mind become seriously imprest with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul," he wrote in 1832. "I considered it of the first importance that I should be right, in matters that involve eternal consequ[e]nces;" he wrote in 1835. "My mind was called up to serious reflection and great uneasiness... my feelings were deep and often poignant... What is to be done?" he wrote in 1838. "I began to reflect upon the importance of being prepared for a future [i.e. eternal] state," he wrote in 1842. These are different words, to be sure, but there’s no mistaking the commonality of their underlying meaning. I believe that all these accounts show that Joseph’s deepest desire was to know what he had to do to be saved. That was the one and only item on his agenda in the Sacred Grove.
The question he asked, then, about which church he should join tells us about young Joseph’s theological assumptions. It’s clear in all accounts that salvation and church membership were inextricably linked in his mind. Even in 1832, where he doesn’t specify what question he asked the Lord before his sins were forgiven, he goes on at great length about his concern for the error he sees in all the churches.The possibility that a church might not be necessary doesn’t seem to occur to Joseph, nor would it have been likely to occur to anyone in the early 19th Century. Christ without a church in 1820? Who could imagine such heresy? Certainly not an illiterate farmboy who, at that point, had no inkling what the Lord had in store for him.
In Joseph’s mind, "which church is the right one" and "how can I get my sins forgiven" were variations on the same theme, and only minor variations at that. Rather than show inconsistency, the two accounts are remarkably united in their depiction of Joseph’s concern for his soul and his assumptions about what was necessary to save it.
So with that understanding, the apparent contradiction about whether or not he had decided that all the churches were wrong prior to praying becomes far less problematic. The 1832 account spends more time detailing the specific problems with all the churches than the 1838 account, indicating that Joseph still believed in the importance of joining a church to gain access to the Atonement. True, he doesn’t explicitly say that any church membership is necessary, but he didn’t have to – those reading his account in the 19th Century would have had the same assumptions, and neither Joseph nor his audience would have even considered the modern/post-modern idea of an effectual Christian life outside the boundaries of organized religion. Even if all the churches were wrong to one degree or another, surely Joseph would still have felt it necessary to join the best one... [22]
Speficially addressing the passages from JS History 1: 10 and 18, J.B. Haws wrote:
In a draft of Joseph Smith’s history that was written sometime in 1840–41 by scribe Howard Coray (but only essentially rediscovered in the Church’s archival holdings in 2005), the corresponding passage reads differently:
Joseph Smith—History 1:18–19
- I asked the Personages who stood above me in the light, which of all the sects was right (for at this time it had never entered into my heart that all were wrong)—and which I should join. I was answered that I must join none of them, for they were all wrong . . .
Howard Coray’s 1839–41 history (labeled Draft 3 in Histories, Volume 1 of The Joseph Smith Papers)
- I asked the Personages who stood in the light; Which of the sects were right. (for I supposed that one of them were so.) and which I should join. I was answered "join none of them; they are all are wrong . . ."
Coray’s version suggests that Joseph still "supposed"—still believed, still considered it most likely—that one of the sects was right, even if he had considered the possibility that such was not the case. Thanks to the careful editorial scrutiny of The Joseph Smith Papers scholars, it is apparent that Coray’s draft was written after the draft of Joseph Smith’s history (labeled Draft 2 in the handwriting of James Mulholland) that was eventually published in the Times and Seasons and then the Pearl of Great Price. The Joseph Smith Papers volume editors note that, "for whatever reason," Joseph Smith chose that Draft 2 (Mulholland) version for eventual publication, even though there is evidence to suggest that Coray transcribed as Joseph "read aloud from Draft 2 in the large manuscript volume, directing editorial changes as he read." With that background in mind, the parallel phrases above suggest an affinity of sentiment, such that the phrase "it had never entered into my heart" meant, essentially, "I [still] supposed one of them were [right]"—which reinforces the reading that Joseph held out hope in his heart that he would be pointed to the true denomination.[16]:99–100
Haws describes another way to view both the 1832 account and 1838 account:
One minor drawback in reading Joseph Smith’s history in its current scriptural format is that the verse divisions might inadvertently separate his thoughts too starkly. Because of that potential challenge, the second possibility proposed here is that the contradiction between verses 10 and 18 might simply be a question of antecedents in verse 10. Thus one final alternate reading (and reconciliation) of those verses becomes clearer in the paragraph format of the Draft 2 (Mulholland) manuscript version of Joseph Smith’s history. In what is now verse 9 in the Pearl of Great Price version, Joseph describes the furious activity of three named denominations: the Presbyterians, the Baptists, and the Methodists. Those were the major players in the religious competition that was all around him in that region of New York. And those three groups preached, importantly, distinct soteriological visions of Christianity. If, however, verse 10 is not seen as completely separate from verse 9, then we might understand Joseph’s questions as being much more specific.
Here is how the passage appears in Draft 2 (Mulholland) of Joseph Smith’s history:
- My mind at different times was greatly excited for the cry and tumult were so great and incessant. The Presbyterians were most decided against the Baptists and Methodists, and used all their powers of either reason or sophistry to prove their errors, or at least to make the people think they were in error. On the other hand the Baptists and Methodists in their turn were equally Zealous in endeavoring to establish their own tenets and disprove all others.
- In the midst of this war of words, and tumult of opinions, I often said to myself, what is to be done? Who of all these parties are right? Or are they all wrong together? and if any one of them be right which is it? And how shall I know it?
Read in that way, new attention to the determiners and pronouns might be in order. Which of all of these parties—that is, the Presbyterians, Baptists, or Methodists—is right? Or are they—Presbyterians, Baptists, Methodists— all wrong together? If any of them—Presbyterians, Baptists, Methodists—be right, which is it? It seems reasonable to conclude that Joseph wondered not about the possibility that there was no true religion on the earth, but only that the principal religions represented in his area might all be wrong. Hence, his crucial question—his "object in going to enquire of the Lord"— was "to know which of all the sects was right," and perhaps it was the subsequent instruction to join no sect anywhere ("for they were all wrong") that would have been surprising; in that case, this latter possibility was the one that had never entered into his heart.
Again, this is only suggested as one way to read the text—but it is one that also seems to fit with a telling line in the earliest known written account of the First Vision, one from 1832 that Joseph Smith partly dictated and partly wrote. The key is something he stated about personal familiarity:
In that 1832 history, Joseph wrote in his own hand:
- At about the age of twelve years my mind become seriously [impressed] with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul which led me to searching the scriptures believeing as I was taught, that they contained the word of God thus applying myself to them and my intimate acquaintance with those of differant denominations led me to marvel exceedingly for I discovered that <they did not adorn> instead of adorning their profession by a holy walk and Godly conversation agreeable to what I found contained in that sacred depository this was a grief to my Soul . . .
The fact that his conclusions were based on an "intimate acquaintance with those of differant denominations" should not be overlooked. His subsequent recollections do seem to reflect an expanded understanding of a broader apostasy: "by searching the scriptures I found that mand <mankind> did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatised from the true and liveing faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the new testament." Yet his choice of words ("no society or denomination") and his declaration that "I cried unto the Lord for mercy for there was none else to whom I could go and to obtain mercy" seem to reflect his discouragement with his local options and his growing assurance that only divine intervention could help him transcend that confusion.
It may, then, have been the sheer universality of the apostasy ("join none of them") that had not entered into his heart. It may have been Joseph Smith’s original hope and assumption, as expressed in the Howard Coray draft, that "one of them were" right, even if he had considered the theoretical possibility that the three denominations with which he had "intimate acquaintance" were all "wrong together" and that he would have to seek a religious home among another, less familiar one of "all the sects."[16]:101–102
If you had come to the conclusion that mankind has apostatized from the true faith, and you suddenly found Jesus standing in front of you, wouldn't you ask Him if any of those churches was the correct one? Or would you simply tell Him, "never mind, I already figured it out for myself"?
Could it be that Joseph simply misremembered? Why must one automatically have to be assumed that he was simply embellishing the story?
There are several interpretive possibilities for the supposed discrepancies between the accounts. Is it possible that Joseph Smith contradicted himself? Certainly. But it only remains just that: a possibility—one interpretive option among others. If we presume that Joseph was lying, our hostile reading will lead us to pick this option. If we grant that Joseph might be telling the truth, the other options will not be summarily rejected.
The answer to this apparent contradiction lies in a detailed examination of relevant texts. It is important to first compare Joseph Smith’s November 1832 text (which is in his own handwriting) with a newspaper article printed earlier that same year which refers to the Prophet’s inaugural religious experiences.
When both of these texts are taken into consideration the following storyline suggests itself: Joseph Smith had come to the conclusion, through personal scripture study, that none of the denominations WITH WHICH HE HAD AN INTIMATE ACQUAINTANCE was built upon the New Testament gospel. He prayed for guidance because he was "in doubt what his duty was." This doubt is obliquely referred to again in Oliver Cowdery’s February 1835 Messenger and Advocate partial First Vision recital where he said that because of the religious excitement the Prophet had "determination to know for himself of the certainty and reality of pure and holy religion."[24]
Doubt is present again in the Prophet’s November 1835 diary entry: "I knew not who was right or who was wrong and I considered it of the first importance that I should be right, in matters that involve eternal consequences."[25] So the conclusion this fourteen-year-old boy had reached through personal scripture study did not altogether solve his dilemma. In fact, in the May 1838 account he clarifies that because of his youth and inexperience in life he could not make an absolute decision with regard to this matter: "it was impossible for a person young as I was and so unacquainted with men and things to come to any certain conclusion who was right, and who was wrong"; "I often said to myself, what is to be done? Who of all these parties are right? Or, are they all wrong together? If any one of them be right which is it, and how shall I know it?"; "if any person needed wisdom from God I did, for how to act I did not know, and unless I could get more wisdom than I then had [I] would never know."
Orson Pratt’s 1840 First Vision account helps to explain why the ‘Joseph-decided-every-existing-church-was-wrong’ theory cannot possibly be valid. Elder Pratt reports, "He then reflected upon the immense number of doctrines now in the world which had given rise to many hundreds of different denominations. The great question to be decided in his mind was—if any one of these denominations be the Church of Christ, which one is it?" This expansive view is reflected in the Prophet’s 1838 account. There he states, "My object in going to enquire of the Lord was to know which of all the sects was right that I might know which to join. No sooner therefore did I get possession of myself, so as to be able to speak, than I asked the personages who stood above me in the light, which of all the sects was right (for at this time it had never entered into my heart that all were wrong) and which I should join."

In the 1832 account, Frederick G. Williams inserted the "in the 16th year of my age" above Joseph's text after Joseph had already written it. (See: "History, circa Summer 1832," The Joseph Smith Papers)

In Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision recital he said that he was "in the 16th year of [his] age" when the manifestation took place but in all other accounts in which he mentions his age, he was in his "fifteenth year."
The only First Vision account that provided a different age was the 1832 account written in Joseph Smith's own handwriting. In 1832, 12 years after the First Vision, Joseph wrote, "we were deprived of the bennifit of an education suffice it to say I was mearly instructid in reading and writing and the ground rules of Arithmatic which constuted my whole literary acquirements."
Although the portion of Joseph's 1832 history is in his own handwriting, the text insertion of "in the 16th year of my age" was in the handwriting of Frederick G. Williams, Joseph's scribe. It is likely that Joseph's dating schemes were slightly off when he dictated his age to Williams, many years afte the fact. There is nothing nefarious in Joseph Smith correcting his own slight mathematical miscalculations.
Two years later, Oliver Cowdery had Joseph's 1832 history in his possession when he began publishing history of the Church in late 1834 in the Latter-day Saints' Messenger and Advocate. Oliver clearly established Joseph's age as 14 ("the 15th year of his life") during the period of religious excitement (although Oliver ultimately never described the actual First Vision at this time). Once the date of the First Vision was correctly established it remained steady throughout all subsequent recitals as the "15th year" or "age 14."

The ages are not, as one critic states, "all over the place." [26] The only account produced by Joseph Smith that indicated a different age was the 1832 account (age 15 rather than 14, based upon a text insertion above the line by Frederick G. Williams after Joseph had already written his account). All remaining accounts indicate age 14 (the "15th" year).
In the 1832 account, Frederick G. Williams inserted the "in the 16th year of my age" above Joseph's text after Joseph had already written it. (See: "History, circa Summer 1832," The Joseph Smith Papers)

The 'one-year-off-the mark' dating anomaly of the 1832 First Vision account can best be understood by taking a look at all of the dates and time frame indicators that are provided within the document. It can then be seen that the farther back in time Joseph Smith goes, the more inexact his dating scheme becomes.
Notice that the date of the First Vision is an above-the-line insertion in the handwriting of Frederick G. Williams, meaning that it was not placed in the text initially but was added at a later time than the creation of the main text.
(17 years back in time)
(15 years back in time)
(12 years back in time)
(7 years back in time)
(5 years back in time)
We should carefully note that Joseph Smith correctly stated that he was "seventeen years of age" when the angel Moroni appeared to him on 22 September 1823, he got the time of that manifestation wrong by one year. A clue as to why this incorrect date was placed by the Prophet in this historical account can be found right in the 1832 document itself. Near the beginning of the narrative Joseph writes: "being in indigent circumstances [we] were obliged to labor hard for the support of a large family having nine children. And as it required the exertions of all that were able to render any assistance for the support of the family therefore we were deprived of the benefit of an education. Suffice it to say [that] I was merely instructed in reading and writing and the ground <rules> of arithmetic which constituted my whole literary acquirements". Elder Orson Pratt once asked rhetorical questions of the Prophet to illustrate his meager level of formal education: "Had you been to college? No. Had you studied in any seminary of learning? No. Did you know how to read? Yes. How to write? Yes. Did you understand much about arithmetic? No. About grammar? No. Did you understand all the branches of education which are generally taught in our common schools? No." (Journal of Discourses, 7:220-21). And when Elder Pratt wrote specifically about the First Vision he was even more specific about the level of the Prophet's math skills, saying that he had "a very limited understanding of the elementary rules of arithmetic." (Orson Pratt, An Interesting Account of Several Remarkable Visions [Edinburgh, Scotland: Ballantyne and Hughes, 1840],—-).
The 1832 history is not the only one where the Prophet made a dating mistake that was one year off the mark. He did the same thing when he created the 1838 Church history, but this time he got the year of his own brother's death wrong. He erroneously remembered that it was 1824 instead of 1823. The significant thing about this particular dating blunder is that four years after the Prophet recorded the initial information he came to the realization that it was not correct and had his scribe, Willard Richards, make the appropriate adjustment. Perhaps the problem with the date was brought to the Prophet's attention by a member of his own family after the information had been printed and made available for public perusal [publication in May 1842; correction in December 1842].
Initial Manuscript Record (2 May 1838)
Publication ( 15 March 1842 / 2 May 1842)
Post-Publication Manuscript Correction (2 December 1842)
A similar type of dating correction scenario, as mentioned above, may have taken place in connection with the 1832 history. Oliver Cowdery claimed that he had the Prophet's help in creating his December 1834 Church history article and despite the fact that he had the erroneously-dated 1832 document sitting in front of him [see paper on this subject] he provided the correct year for the Prophet's First Vision - "in the 15th year of his life" (i.e., between 23 December 1819 and 23 December 1820). And just nine months later the Prophet himself was telling a non-Mormon that the First Vision took place when he was "about 14 years old" (Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835).

An image from "mormoninfographics" is in circulation on the internet which mistakenly states that Joseph claimed that he was age 17 when the First Vision occurred. However, this was a misreading of Joseph Smith's 1835 journal entry, which clearly states that Joseph was age 14 at the time of the first vision, and age 17 at the time of Moroni's visit.

Is this evidence that this visionary tale evolved over time by becoming more dramatic and elaborate?
The 'struggle' motif is absent from the first known self-written account of the Prophet's visionary experience (1832) but it is also absent from his self-written Wentworth Letter account (1842). It is clear from the available documentary evidence that the Prophet did not feel constrained by the arbitrary rule of his modern critics that he must include every aspect of his First Vision story in every single retelling of it, and no reasonable person should be bothered that he doesn't.
The following timeline displays the 'struggle' material found in First Vision recitals that were produced during the Prophet's lifetime. The corresponding text from the 1832 document is also provided for purposes of comparison.
Several observations about the information presented below may prove useful.
September–November 1832
I cried unto the Lord for mercy. . . and while in the attitude of calling upon the Lord . . . a pillar of fire [or] light above the brightness of the sun at noonday came down from above and rested upon me and I was filled with the Spirit of God.
9 November 1835
I called on the Lord for the first time in the place above stated, or in other words, I made a fruitless attempt to pray. My tongue seemed to be swollen in my mouth, so that I could not utter. I heard a noise behind me like some one walking towards me. I strove again to pray, but could not. The noise of walking seemed to draw nearer. I sprang upon my feet and looked round, but saw no person or thing that was calculated to produce the noise of walking. I kneeled again, my mouth was opened and my tongue loosed. I called on the Lord in mighty prayer. A pillar of fire appeared above my head, which presently rested down upon me and filled me with unspeakable joy.
2 May 1838
I kneeled down and began to offer up the desires of my heart to God, I had scarcely done so, when immediately I was seized upon by some power which entirely overcame me and had such astonishing influence over me as to bind my tongue so that I could not speak. Thick darkness gathered around me and it seemed to me for a time as if I were doomed to sudden destruction. But exerting all my powers to call upon God to deliver me out of the power of this enemy which had seized upon me, and at the very moment when I was ready to sink into despair and abandon myself to destruction, not to an imaginary ruin but to the power of some actual being from the unseen world who had such a marvelous power as I had never before felt in any being, just at this moment of great alarm I saw a pillar of light exactly over my head above the brightness of the sun, which descended gradually until it fell upon me. It no sooner appeared than I found myself delivered from the enemy which held me bound.
September 1840
He therefore, retired to a secret place in a grove, but a short distance from his father's house, and knelt down, and began to call upon the Lord. At first, he was severely tempted by the powers of darkness, which endeavored to overcome him; but he continued to seek for deliverance, until darkness gave way from his mind, and he was enabled to pray in feverency of the spirit, and in faith. And while thus pouring out his soul, anxiously desiring an answer from God, he at length, saw a very bright and glorious light in the heavens above; which, at first, seemed to be a considerable distance. He continued praying, while the light appeared to be gradually descending towards him.
June 1841
He, therefore, retired to a secret place, in a grove, but a short distance from his father's house, and knelt down and began to call upon the Lord. At first, he was severely tempted by the powers of darkness, which endeavored to overcome him. The adversary benighted his mind with doubts, and brought to his soul all kinds of improper pictures and tried to hinder him in his efforts and the accomplishment of his goal. However, the overflowing mercy of God came to buoy him up, and gave new impulse and momentum to his dwindling strength. Soon the dark clouds disappeared, and light and peace filled his troubled heart. And again he called upon the Lord with renewed faith and spiritual strength. At this sacred moment his mind was caught away from the natural objects with which he was surrounded, and he was enwrapped in a heavenly vision.
1 March 1842
I retired to a secret place in a grove and began to call upon the Lord, while fervently engaged in supplication my mind was taken away from the objects with which I was surrounded, and I was enwrapped in a heavenly vision.
11 June 1843
he went into the grove & enquired of the Lord which of all the sects were right.
29 August 1843
I kneeled down, and prayed, saying, O Lord, what Church shall I join? Directly I saw a light.
24 May 1844
Went into the Wood to pray, kneels himself down, his tongue was close[d,] cleave[t]h to his roof—could utter not a word, felt easier after awhile—saw a fire toward heaven came near and nearer. . . . the fire drew nigher, rested upon the tree, enveloped him[, and] comforted [him].
Critical sources |
|
The theophany portion of the 1832 account does not specifically indicate that the Father appeared to Joseph Smith together with Jesus Christ. The relevant text (in its original form) reads as follows:
a piller of fire light above the brightness of the sun at noon day c[a]me down from above and rested upon me and I was filled with the spirit of god and the <Lord> opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord and he spake unto me saying Joseph <my son> thy sins are forgiven thee. go thy <way> walk in my statutes and keep my commandments behold I am the Lord of glory I was crucifyed for the world that all those who believe on my name may have Eternal life <behold> the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doeth good no not one they have turned asside from the gospel and keep not <my> commandments they draw near to me with their lips while their hearts are far from me and mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them acording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father.[29]
Even though the Savior makes a direct reference to the Father there is no indication in this portion of the 1832 document that God appeared to Joseph Smith alongside His Son.
This type of pattern is seen in the Book of Mormon, translated in 1829: The Book of Mormon begins (1 Nephi 1꞉8-10) with Lehi's vision of God on His throne. One [Christ] followed by twelve others descends from God to speak with Lehi—thus, Jesus and the Father are here both separate, and the role of Christ in giving instructions to the prophet while the Father looks on and approves is followed, just as it was in Joseph's First Vision. Here too, Lehi is described as praying to "the Lord," and yet has a vision of both God the Father and Christ.

There is a very significant phrase located in the introductory paragraph of the Prophet's historical narrative. There he indicates that the 1832 document is . . .
A History of the life of Joseph Smith Jr. an account of his marvilous experience and of all the mighty acts which he doeth in the name of Jesus Ch[r]ist the son of the living God of whom he beareth record and also an account of the rise of the church of Christ in the eve of time according as the Lord brough<t> [it] forth and established [it] by his hand <firstly> he receiving the testamony from on high secondly the ministering of Angels thirdly the reception of the holy Priesthood by the ministring of Aangels to adminster the letter of the Gospel—<—the Law and commandments as they were given unto him—>and the ordinencs, forthly a confirmation and reception of the high Priesthood after the holy order of the son of the living God.
This paragraph not only introduces the document with a heavy emphasis on the Son of God but it also chronologically outlines four inaugural events of the Restoration.
The significant phrase in the introductory paragraph is the one associated with the First Vision—"receiving the testimony from on high" (spelling standardized). When this phrase is placed in conjunction with the Prophet's 1835 and 1838 accounts of the First Vision it becomes obvious that the 1832 phraseology closely corresponds with the words spoken by God the Father when He introduced His Son in the Sacred Grove.
The Father's identification of Jesus Christ as His Son was His "testimony" of Him.
Critics have objected that—in their minds—the phrase "from on high" cannot be so easily equated with God the Father. But there is a sizable amount of corroborating evidence for this idea. Consider the following points of connection.
The Father's voice . . . came out of heaven [i.e., 'from on high'] and testified of His Beloved Son.
Joseph Smith stated, "the Lord God has spoken it; and we . . . have heard . . . the words of the glorious Majesty on high."
There are five New Testament scriptures (which Joseph Smith would have been familiar with from his work on the JST) that have distinct parallels to the First Vision story. Jesus Christ's Old World disciples heard the Father's voice come "from heaven" (Mt. 3:17; Mk. 1:11; Lk. 3:22; 2 Pt. 1:17-18) [i.e, 'from on high'] or "out of the cloud" (Mt. 17:5) [i.e., 'from on high'] and in each of these instances the Father testified of His Son and employed the same phraseology that Joseph Smith said He utilized during the First Vision
This chronological evidence points to the conclusion that Joseph Smith appears to have equated the voice "from on high" with God the Father both before and after he penned his 1832 First Vision account.
There is another line from the 1832 account that may be referring to two people:
I was filled with the spirit of God, and the Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord
It has been argued that the seperation of "Lord" into two may be referring to the Lord God [i.e., the Father] and the Lord Jesus Christ. Three pieces of evidence can be used to argue for this interpretation.
Some critics have taken issue with this evidence for the interpretation—claiming that since Psalm 110:1 was originally written in Hebrew with two different words for Lord (rendering "Lord" and "LORD" in all caps for the second mention) that the argument fails.[31]
Robert S. Boylan has responded by showing how Psalm 110:1 is the most quoted, echoed, and/or alluded to passage in the New Testament which Joseph would have been working on revising in his Inspired Translation of the Bible. He then shows that the revelations in Doctrine and Covenants leading up chronologically to the publication of the history containing the 1832 account of Joseph’s vision deliberately echo that verse (Doctrine and Covenants 20:24; 49:5-6; 76: 20, 23). If Joseph were familiar with that verse close to the publication of the account by way of the Old and/or New Testament and as echoed in his revelations published in the Doctrine and Covenants, it seems reasonable to assume that he could have used that verse as a template for rendering his account of events surrounding the First Vision.[32] This is even if one mention is capitalized and the other not. If the structure is deliberate and clear (and it appears so), then it seems odd to be upset that Joseph doesn't use capitals for the second "Lord" he writes about.
The 1832 account may be read to have a successive appearance of personages, one after the other. This is strengthened by the 1835 accounts mention of successive appearance. Further evidence of this in the 1832 account may be that Joseph was "filled with the spirit of God" before he mentions "the Lord".
Some have argued that the 8 uses of Lord in the 1832 account all refer to Jesus Christ.[33] There are at least three references that may be read otherwise:
A History of the life of Joseph Smith Jr. an account of his marvilous [sic] experience and of all the mighty acts which he doeth in the name of Jesus Christ the son of the living God of whom he beareth record and also an account of the rise of the Church of Christ in the eve of time according as the Lord brought forth and established by his hand.
A separation of "Christ" and "the Lord." This is able to be read with Christ or the Father as the Lord.
My mind became exceedingly distressed, for I became convicted of my sins, and by searching the scriptures I found that mankind did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatized from the true and living faith, and there was no society or denomination that was built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament.
Joseph may be referring to coming to the Lord (i.e., the Father) and the gospel of Christ.
The third plausible evidence of the Father as Lord is the ending of the account:
My soul was filled with love, and for many days I could rejoice with great joy. The Lord was with me, but I could find none that would believe the heavenly vision. Nevertheless, I pondered these things in my heart.
The reference here is vague enough that it cannot be conclusively read one way or the othe—especially with the just-cited mention of the Lord.
Since it can be concluded from the above documentary evidence that Joseph Smith did indeed make an oblique reference to the appearance of the Father in his 1832 history the question becomes—Why did the Prophet construct the 1832 narrative in the manner that he did (so as to exclude explicit mention of the Father's appearance)? A careful analysis of the 1832 First Vision text reveals that it was deliberately constructed on the framework of many scriptural citations. The apostle Stephen's view of both the Father and the Son is clearly utilized by the Prophet in one section of the 1832 text but, more importantly, Joseph Smith told the actual theophany portion of this narrative in language that very closely corresponds to the apostle Paul's vision of Jesus Christ (Acts 26).[34] .
On this reading, the Father is not explicitly mentioned as making an appearance in the theophany portion of the 1832 First Vision account because Joseph Smith patterned that part of his narrative after the vision of Jesus Christ experienced by the apostle Paul.
Paul did not report that he saw the Father alongside the Son, and so it is logical that this is the reason why Joseph Smith did not explicitly mention the Father's appearance in his text either. The Prophet's strong sense of connection with Paul's visionary experience is referred to by him right in his 1838 First Vision account. The context of this connection is the persecution experienced by both men for speaking publicly about a heavenly manifestation. Joseph Smith relates in his 1838 history that he was informed by a clergyman that his vision was "all of the devil." This piece of information may help to explain why the Prophet chose to couch his first known written account of his vision in heavy biblical language and imagery. He may have hoped that by doing this his story would have a better chance of being accepted amongst a populace that was steeped in biblical content.
The Gospel Topics Essay touching on the first vision touches on another way of looking at the evidence. It focuses on the awkward repetition of the word "Lord" and how this may have been Joseph's perhaps uneducated way of stating the order of appearance of the personages:
Embellishment. The second argument frequently made regarding the accounts of Joseph Smith’s First Vision is that he embellished his story over time. This argument focuses on two details: the number and identity of the heavenly beings Joseph Smith stated that he saw. Joseph’s First Vision accounts describe the heavenly beings with greater detail over time. The 1832 account says, “The Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord.” His 1838 account states, “I saw two Personages,” one of whom introduced the other as “My Beloved Son.” As a result, critics have argued that Joseph Smith started out reporting to have seen one being—“the Lord”—and ended up claiming to have seen both the Father and the Son.
There are other, more consistent ways of seeing the evidence. A basic harmony in the narrative across time must be acknowledged at the outset: three of the four accounts clearly state that two personages appeared to Joseph Smith in the First Vision. The outlier is Joseph Smith’s 1832 account, which can be read to refer to one or two personages. If read to refer to one heavenly being, it would likely be to the personage who forgave his sins. According to later accounts, the first divine personage told Joseph Smith to “hear” the second, Jesus Christ, who then delivered the main message, which included the message of forgiveness.10 Joseph Smith’s 1832 account, then, may have concentrated on Jesus Christ, the bearer of forgiveness.
Another way of reading the 1832 account is that Joseph Smith referred to two beings, both of whom he called “Lord.” The embellishment argument hinges on the assumption that the 1832 account describes the appearance of only one divine being. But the 1832 account does not say that only one being appeared. Note that the two references to “Lord” are separated in time: first “the Lord” opens the heavens; then Joseph Smith sees “the Lord.” This reading of the account is consistent with Joseph’s 1835 account, which has one personage appearing first, followed by another soon afterwards. The 1832 account, then, can reasonably be read to mean that Joseph Smith saw one being who then revealed another and that he referred to both of them as “the Lord”: “the Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord.”
Joseph’s increasingly specific descriptions can thus be compellingly read as evidence of increasing insight, accumulating over time, based on experience. In part, the differences between the 1832 account and the later accounts may have something to do with the differences between the written and the spoken word. The 1832 account represents the first time Joseph Smith attempted to write down his history. That same year, he wrote a friend that he felt imprisoned by “paper pen and Ink and a crooked broken scattered and imperfect Language.” He called the written word a “little narrow prison.” The expansiveness of the later accounts is more easily understood and even expected when we recognize that they were likely dictated accounts—an, easy, comfortable medium for Joseph Smith and one that allowed the words to flow more easily.[35]
Read the full article here.
It is worthwhile to note that the scribe for the material which directly precedes and follows after the 1832 First Vision narrative—Frederick G. Williams—never mentioned anything about Joseph Smith's story evolving over time and becoming more elaborate with the so-called 'addition' of the Father.
Williams was a resident of Quincy, Illinois when the First Vision account which explicitly refers to the Father was published in Nauvoo, Illinois on 1 April 1842. It is known that Williams was with the Prophet in Nauvoo shortly before his death on 10 October 1842 but during the intervening six months there is no known objection from Frederick to the content of the printed text. Why not? Williams was the person who wrote down the words in the introductory remarks of the 1832 document that talk of Joseph Smith receiving "the testimony from on high" during the First Vision. And it is known that Frederick was accompanying four LDS missionaries who, in November 1830, were teaching the citizens of Painesville, Ohio that Joseph Smith had seen "God" personally (see the 1830 statement about seeing "God").
Williams was a member of the First Presidency of the Church on 9 November 1835 when Joseph Smith was teaching a non-Mormon that there were two personages who appeared during the First Vision (see Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835). Frederick probably never drew attention to a so-called 'discrepancy' between what Joseph Smith taught in 1832, 1835, 1838, and 1842 because he knew that there wasn't one; he knew that the words of the Father spoken during the vision were referred to right in the text that he had written down in 1832.
Oliver Cowdery is another person who was in a position to know if the Prophet's First Vision story had changed over time by the addition of the Father. But he never mentioned any such 'discrepancy'. Cowdery had possession of the 1832 First Vision account when he wrote and published a series of Church history letters in December 1834 and February 1835 and so he was fully aware of the explicit mention of Christ's appearance and he also would have known of the introductory remark which refers to "the testimony from on high" being delivered during this event. Cowdery became the Associate or Assistant President of the entire Church on 5 December 1834 (Encyclopedia of Mormonism, 1653), and thus he would have been in the highest office of Church authority when the Prophet was teaching about one year later that two personages appeared during the First Vision (Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835).
Both Fredrick G. Williams and Oliver Cowdery had reason to feel animosity toward Joseph Smith and the Church since they were both excommunicated in the late 1830's. But neither of these men - even after their reinstatements into full fellowship - ever pointed to any 'creative editing' of the Prophet's First Vision story to sound more impressive and dramatic.
Critical sources |
|
Some have seen a discrepancy between the location of Deity in the Prophet's 1832 and 1838 First Vision accounts. The 1838 version says that the Prophet saw two Personages standing in the air above the earth, within his proximity. But the 1832 version is not so clear—it seems to locate Deity in heaven.
Details about Joseph Smith's First Vision experience are best interpreted by taking all of the extant accounts into consideration. A myopic focus on a limited number of historical documents can only lead to misunderstanding of the past and a twisted sense of the message that the author is trying to convey.
This so-called 'discrepancy' can be accounted for by the fact that Joseph Smith built his 1832 First Vision account using the framework of 47 biblical scriptures. And at this point in his manuscript he utilized Acts 7꞉55-56 to tell his story. It reads:
But [Stephen], being full of the Holy Ghost, looked up steadfastly into heaven, and saw the glory of God, and Jesus standing on the right hand of God.
And said, Behold, I see the heavens opened, and the Son of man standing on the right hand of God.
The Greek text that underlies the KJV translation says that Stephen looked into "heaven" (ouranos - 'the sky'; by extension: 'heaven'; also translated as 'air') and saw the "heavens" (the same Greek word - ouranos) opened. Thus, Stephen did not necessarily see Deity in their celestial abode - far beyond the confines of the earth - but rather standing above him in the air.
When Joseph Smith says in the 1832 First Vision account that he saw the Lord after the "heavens" (he uses the plural form) were opened he seems to be expressing the same idea that is found in the New Testament text.
Notice that the physical proximity of the Personages is established in the Prophet's 1835 recital: the pillar of fire can be physically seen in the air; the pillar of fire physically descends and rests upon Joseph; the pillar of fire has contact with physical objects that surround Joseph; two Personages are seen in the midst of this pillar of fire. Notice also that in the 1844 account the Prophet indicates that he could see with his natural eyesight the pillar "toward heaven", or up in the air. A glance at the 1840 account also shows that the phrase "in the heavens above" simply means "a considerable distance" up in the sky - it is not a reference to the celestial abode of Deity.
Critical sources |
|
The 1832 account of the First Vision does not portray the Lord as announcing that all the creeds were corrupt. These details do not show up until the 1838 account. Is this evidence that the Prophet's story evolved over time?
The claim that Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision story does not contain a divine injunction against joining any churches does not take evidence within the document itself into proper consideration. The information is implicit instead of explicit, but it is there nevertheless. This point cannot be legitimately used as evidence of an evolving storyline.
A quick look at the 1832 First Vision text reveals how untenable this claim is. Joseph Smith states that before he went into the woods to pray he had concluded in his own mind that "those of different denominations [which he was personally acquainted with]. . . did not adorn their profession by a holy walk and godly conversation agreeable to what [he] found contained in [the Bible] . . . . [There were] contentions and divisions [among them] . . . . [T]hey had apostatised from the true and living faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament."
Then, when Jesus Christ Himself made a personal appearance to Joseph in the grove, He informed the young boy that -
"the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good no not one they have turned aside from the gospel and keep not <my> commandments they draw near to me with their lips while their hearts are far from me and mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them acording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father"
To summarize:
How can critics possibly see this as anything other than a forceful and unambiguous indication on the Lord's part that joining any of the Christian denominations would be an unacceptable path for Joseph to take? Notice in the remainder of the 1832 text that Joseph says he felt great joy and love because of his experience and pondered the things which he had seen and heard during the vision . . . but during an interval of several years he did NOT join any church. Why?
As the 1832 text so plainly says—Joseph Smith believed that Christians had turned aside from the gospel; Jesus Christ confirmed that Christians had turned aside from the gospel; Joseph was therefore provided with a set of golden plates that contained writings which were "engrave[d] by . . . the servants of the living God." The 1832 account speaks three times of the "work" that God wanted Joseph Smith to do, while the 1838 account explicitly connects this "work" with the bringing forth of "the everlasting gospel." The 1842 First Vision account ties all of these themes together. There the Prophet relates: "I was expressly commanded to 'go not after them,' at the same time receiving a promise that the fulness of the gospel should at some future time be made known unto me."
Another indication from the 1832 document that Joseph Smith knew from the First Vision event that he should not join any of the churches can be found in something the Savior said to him. Jesus Christ explained that He was going to take action against the situation the world was currently in by "bring[ing] to pass that which hath been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles." What did this statement mean? In a canonized text written at approximately the same time as the 1832 First Vision account (September 1832) the following phraseology is found:
In other words, the Lord was telling Joseph Smith during the First Vision about the coming Restoration and so there would not be any need for him to join an existing church. This viewpoint is bolstered by several instances where the Prophet utilized the same phraseology used by the Lord during the First Vision to speak about the Restoration.
Critical sources |
|
Three of the primary sources that charge Joseph Smith with joining sectarian churches between 1820 and 1830 were produced in the latter part of the nineteenth century, over a half-century after the First Vision. None of the three are contemporary records; the earliest one was written 50 years after the First Vision took place.
We must note too that none of these sources confirms the others—they all discuss different denominations and different time frames. Thus, the stories are not mutually reinforcing.
Eyewitness reminiscences and contemporary records provide strong evidence that these claims are not valid and, therefore, do not reflect historical reality. The three sources are all late, and all from hostile voices.
Fayette Lapham claimed to have interviewed Joseph Smith Sr. in 1829-30, and published a report forty years later. In it, he reported:
About this time [1822, perhaps as late as 1824] he [Joseph, Jr.] became concerned as to his future state of existence, and was baptized, becoming thus a member of the Baptist Church.[42]
The Lapham source is secondhand at best—putting forward information that reportedly came from the Prophet's father. There are no records beyond this late, second-hand recollection to support this claim.
Joseph and Hiel Lewis were cousins of Emma Hale Smith; they would have been aged 21 and 11 respectively in 1828:
...while he, Smith, was in Harmony, Pa., translating his book....that he joined the M[ethodist] [Episocpal] church. He presented himself in a very serious and humble manner, and the minister, not suspecting evil, put his name on the class book, the absence of some of the official members, among whom was the undersigned, Joseph Lewis, who, when he learned what was done, took with him Joshua McKune, and had a talk with Smith. They told him plainly that such a character as he was a disgrace to the church, that he could not be a member of the church unless he broke off his sins by repentance, made public confession, renounced his fraudulent and hypocritical practices, and gave some evidence that he intended to reform and conduct himself somewhat nearer like a christian than he had done. They gave him his choice, to go before the class, and publicly ask to have his name stricken from the class book, or stand a disciplinary investigation. He chose the former, and immediately withdrew his name. So his name as a member of the class was on the book only three days.—It was the general opinion that his only object in joining the church was to bolster up his reputation and gain the sympathy and help of christians; that is, putting on the cloak of religion to serve the devil in.[43]
Note that Joseph did not inscribe himself, but the Methodist minister added Joseph's name to the class book. It is not surprising that Joseph might have attended Methodist services: Emma's family was involved in Methodism, she was related to Methodist ministers, and Joseph at this period was living on the Hale family's farm. The Hales had serious reservations about their new son-in-law, who claimed by this point to have the Book of Mormon plates in his possession. It would be natural for him to attend worship services with them if only to reassure them that he was not hostile to religion.
It is telling, though, that as soon as Joseph Lewis learned that Joseph had attended, he quickly took steps to disassociate the church from a person he saw as an imposter: note too that Lewis describes himself (rather than Joseph) as one "of the official members." A study of Methodist procedure makes it extremely unlikely that Joseph could have been a member of the Church, especially for only three days.
The Lewis source presents a scenario that was directly contradicted in print by an adult eyewitness who was a Methodist church officer. It is certainly possible that Joseph attended a Methodist meeting with his wife and in-laws: even in the Lewis' telling, however, he was quickly made to understand that he was not wanted, and he persisted in his own beliefs rather than continue with them.
| Main article: | Methodist membership procedures and Joseph Smith |
| See also: | Joseph became "partial to the Methodist sect" in 1820 |
S.F. Anderick (1887):
When Jo[seph Smith] joined the Presbyterian Church, in Palmyra village, it caused much talk and surprise, as he claimed to receive revelations from the Lord.[44]
As Dan Vogel notes, "Because Lucy Smith and three of her older children joined the Presbyterian Church, together with the possibility that Joseph Jr. may have attended some meetings with other family members, some observers may have assumed Joseph Jr. was also a member."[45] (Vogel notes that Lorenzo Saunders claimed in 1884 that he attended Sunday School with Joseph at the Presbyterian Church, and so that attendance (without formal membership) may be the source for this reminiscence.[46]
The Anderick source may simply be recalling an occasion when the young Prophet attended a church service with his Presbyterian mother and siblings.
The eyewitness sources that follow below indicate that up until the time that Joseph Smith announced the existence of the golden plates of the Book of Mormon to his family (23 September 1823) he was not formally attached to any church, but had instead publicly rejected all of them and manifested his desire NOT to join their ranks. Some are contemporaneous, others are later remembrances, but the hostile and friendly voices are clear that he had no denominational affiliation.
Pomeroy Tucker (a non-Mormon critic who knew Joseph Smith in Palmyra, New York) said that Joseph joined the Methodist probationary class in Palmyra but soon "withdrew from the class" without being converted; announcing that "all the churches [were] on a false foundation."[47] This information corresponds with historical details dated by Joseph Smith at around 1820.
Lucy Mack Smith:
Joseph Smith's mother recalled in her autobiography that shortly after her son Alvin died on 19 November 1823 Joseph "utterly refused" to attend church services with the intent to convert, and he made the specific request: "do not ask me to join them. I can take my Bible, and go into the woods, and learn more in two hours, than you can learn at meeting in two years, if you should go all the time."[48]
As can be seen by the continuing chronological sources which follow, Joseph Smith and his associates were teaching from 1825 to 1832 that the Prophet did not belong to any church between the years 1825 and 1827.
Josiah Stowell, Jr. (a non-Mormon):
I will give you a short history of what I know about Joseph Smith, Jr. I have been intimately acquainted with him about 2 years. He then was about 20 years old or thereabout. I also went to school with him one winter. He was a fine, likely young man and at that time did not profess religion.[49]
Peter Bauder:
In 1827 David Marks (a non-Mormon minister) went to Palmyra and Manchester, New York where he "made considerable inquiry respecting . . . [Joseph] Smith" and learned from "several persons in different places" that Joseph was "about 21 years [old]; that previous to his declaration of having found the plates he made no pretensions to religion."[50]
Observer and Telegraph (newspaper):
Four LDS men from New York state taught that at the time the angel appeared to Joseph Smith (22 September 1823) he "made no pretensions to religion of any kind."[52]
Palmyra Reflector (newspaper):
The editor of a Palmyra, New York newspaper claimed that he has been "credibly informed," and was "quite certain," that "the prophet . . . never made any serious pretensions to religion until his late pretended revelation"—meaning the Book of Mormon, which was made known among Palmyra's residents in the Fall of 1827.[53]
Orson Pratt:
Orson Pratt and Lyman Johnson taught on 8 April 1832 that "in 1827 a young man called Joseph Smith of the state of New York, of no denomination [i.e., not belonging to a church], but under conviction, inquired of the Lord . . . [and] an angel [appeared to him] . . . who gave information where the plates were deposited."[54] Pratt clarified in a much later statement that between 1820 and 1823 Joseph Smith "was not a member of any church."[55]
Thus, a great deal of contemporary evidence disproves the late, second hand claims.
Critical sources |
Primary Sources
|
One critical author states, "Joseph [Smith] added new elements to his later narratives that are not hinted at in his earlier ones. His first vision evolved from a forgiveness epiphany [1832 account] to a call from God the Father and Jesus Christ to restore the true order of things [1842 account]."
Taken altogether, the above information reveals that Joseph Smith considered his initial calling to have come directly from Deity in the Sacred Grove in 1820—not at some later time. The wording in the Prophet's 1832 First Vision account can be comfortably interpreted to mean that he understood this extraordinary event represented the beginning of a new gospel dispensation.
In Joseph Smith's 1832 account he plainly states that before the First Vision took place he was of the opinion that "mankind . . . had apostatized from the true and living faith, and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament." When the Prophet saw Jesus Christ face to face during the First Vision experience the Savior verified what Joseph had previously believed by saying, "the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good; no, not one. They have turned aside from the gospel and keep not my commandments" (emphasis added).
During the lifetime of Joseph Smith the word DISPENSATION was defined in a popular English dictionary in the following manner: "a system of principles and rites enjoined [or dispensed or bestowed]; as . . . the gospel dispensation; including . . . the scheme of redemption by Christ."[56] As noted above, Jesus Christ informed Joseph Smith that mankind had turned aside from the gospel and no longer kept His commandments. He then issued a directive straight to Joseph Smith by saying, "Walk in my statutes and keep my commandments" (emphasis added). This is clearly a new beginning; the Lord enjoined His ‘system of principles’ or ‘scheme of redemption’ upon Joseph Smith. This act qualifies—by definition—as a new dispensation of the gospel.
Was this early nineteenth-century dispensation of the gospel meant only for the benefit of Joseph Smith? In writing out the 1832 account the Prophet utilized some very specific wording when he said that "the world of mankind . . . . had apostatized" and he mourned for "the sins of the world." In his perspective "no society or denomination . . . built upon the gospel." And when the Lord spoke to Joseph during the vision He emphasized that this situation was on a universal scale saying, "the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good; no, not one." Thus, the 1832 account definitely describes a universal apostasy—and it makes no sense that the Savior would inaugurate a dispensation of His gospel only for the sake of one individual when innumerable humans were in need of salvation.
An entry found in the Encyclopedia of Mormonism agrees with the quotations provided above. It states with regard to the First Vision: "The Lord spoke face-to-face with Joseph and called him to service."[68]
Critical sources |
|
In light of the statements produced by Joseph Smith before he wrote the 1832 quotation of Jesus Christ in the Sacred Grove, it is not possible to uphold the claim that the Lord told the Prophet on that occasion that a Christian of any denomination automatically qualified for eternal life (in the LDS understanding of the term).
While it is true that the Lord is quoted in the 1832 First Vision account as saying "all those who believe on my name may have eternal life" it can be seen in an earlier revelation dated 7 March 1831 that those who "believe on [Christ's] name" must also "come unto [Him]" in order to "have everlasting life" (D&C 45꞉5).
The Lord does not state in the 1832 narrative that eternal life is available to members of every Christian church. Rather, He declares unambiguously in that account that "none" of the existing Christian denominations of the time were keeping His commandments; they had all turned aside from His gospel. From this piece of information alone, it is clear that eternal life could not be made available to them; they were categorized by the Lord as being in a state of "sin" (cf. Romans 5꞉21; Romans 6꞉22-23). In the 1832 text Jesus Christ says to Joseph Smith - "keep my commandments," and in connection with this it can be seen in a revelation dated March 1829 that the Lord informed the Prophet that he could only be granted "eternal life" if he was "firm in keeping the commandments" that Christ gave unto him (D&C 5꞉21-22; cf. D&C 14꞉7; D&C 18꞉8; D&C 30꞉8).
On 1 November 1831 the Lord affirmed to adherents of the LDS faith that there was "only [one] true and living church upon the face of the whole earth" (D&C 1꞉30). Earlier—in May 1831—He had spoken specifically to members of "the church that profess my name" (compare with the 1832 document wording) and indicated that only the faithful members of it who endured would "inherit eternal life" (D&C 50꞉4-5). Thus, the blessing of eternal life could not be obtained without complying with certain conditions.
Before Joseph Smith penned the Lord's words that are found in the 1832 First Vision text he clearly understood that:
The implication of this last point is that only one church can perform ordinances that will be considered valid in the sight of the Lord. And so a person can only be truly obedient to all of the Lord's commandments by holding membership in His one true Church. Joseph Smith indicated in the introductory remarks of the 1832 history that he had received priesthood authority, from a heavenly source, which enabled him to "administer . . . the commandments . . . and the ordinances".
Critical sources |
|
One discrepancy between the 1832 First Vision account and the official 1838 recital is that it portrays Jesus Christ as prophesying that He will return to earth quickly to destroy wicked mortals. The 1838 story makes no mention of the impending doom of this planet's depraved inhabitants.
The claim that there is a discrepancy between the 1832 and 1838 First Vision accounts on the point of the Second Coming and destruction of the wicked appears to be a desperate attempt at sowing discord. It is a charge without much substance. The Prophet's own statement about the omission of certain items can be legitimately utilized to account for several differences in the two documents.
This criticism loses its negative effect when it is weighed in the balance against the content of the relevant historical documents. In the 1832 account the Lord says:
mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them ac[c]ording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father.
There is, indeed, no reference to this specific prophecy in the First Vision portion of the 1838 document. However, Joseph Smith clearly states in that very narrative that Jesus Christ told him "many other things" during the First Vision that he decided not to write down at that time! Thus, an argument from silence (on the part of the critics) is utterly unconvincing. A close look at the remainder of the 1838 historical text reveals that the angel Moroni did, in fact, speak to Joseph Smith about prophecies of the Savior's return and the destruction of the wicked. The Prophet reports:
[The angel] first quoted part of the third chapter of Malachi and he quoted also the fourth or last chapter of the same prophecy though with a little variation from the way it reads in our Bibles. Instead of quoting the first verse as reads in our books he quoted it thus, 'For behold the day cometh that shall burn as an oven, and all the proud <yea> and all that do wickedly shall burn as stubble, for <they> that cometh shall burn them saith the Lord of hosts, that it shall leave them neither root nor branch.' And again he quoted the fifth verse thus, 'Behold I will reveal unto you the Priesthood by the hand of Elijah the prophet before the coming of the great and dreadful day of the Lord.' . . . . He also quoted the second chapter of Joel from the twenty eighth to the last verse. He also said that this was not yet fulfilled but was soon to be.
The 1832 and 1838 histories present the very same prophecy of the destruction of the wicked at the time of the Lord's Second Coming. The 1832 account portrays the Lord speaking it personally; the 1838 account portrays an angel relaying the words of the Lord as recorded in prophetic, biblical texts. Either way, the message is the same.
Critical sources |
|
Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision account does not explicitly say that he was persecuted for relating his spiritual manifestation to others. Some have claimed that this stands as evidence that the Prophet's story evolved over time—probably to add a sense of drama. However, the Prophet's 1832 history of the Restoration talks about persecution in very close proximity to the First Vision recital. The persecution is situated squarely between the First Vision experience and the angel Moroni visitations. The documentary evidence presented above demonstrates conclusively that Joseph Smith did not see anything wrong with telling the basic elements of his First Vision story and either giving a passing reference to other elements or leaving them out altogether. Regardless, it was still a record of the very same experience that took place at the Smith homestead near Palmyra, New York.
Joseph Smith made some remarks in his 1832 First Vision account that have a marked degree of relevance to the argument being put forward by his critics. In relation to the period of time between the First Vision and the appearance of the Book of Mormon angel he said,
Since it is explicitly stated by Joseph Smith that nobody believed his story, it would be unreasonable to assume that all of the responses to it were friendly in nature. In fact, the Prophet says right in this text that before the Book of Mormon angel visited him his family was persecuted and afflicted for some unspecified reason(s). He did not elaborate upon the nature of the "many persecutions" that took place against his family because—as far as this particular document was concerned—he had elected not to write down "many things which transpired."
The following documentary evidence from the 1838 First Vision account strengthens the argument that the 1832 text is referring to some type of persecution that took place because of Joseph's initial spiritual experience.
This 1838 description corresponds very well with the "many persecutions and afflictions" that are mentioned in the 1832 account. It also matches closely with the 1832 statements that nobody would believe Joseph's story and he reflected upon this adverse situation in his heart.
It should be pointed out that even though the 'persecution' theme is very pronounced in the 1838 account it is a piece of the story that was not always mentioned or emphasized in subsequent retelling (both published and verbal).
This last example is especially significant because it is an obvious reference to the Methodist minister who is spoken of in the 1838 History of the Church account. The 1844 rehearsal of events is less detailed but it is, nevertheless, the same exact story. The 1844 document clearly demonstrates that Joseph Smith did not always include an equal amount of story elements in his recitals of the First Vision. Critics of this manifestation should, therefore, not expect any such thing when they scrutinize the pertinent documents. If an element of the story was not known by one particular audience it cannot be automatically assumed that it was not known by another.
Online |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
The capitalized word "Angels" in Joseph Smith's diary entry for 14 November 1835 has given rise to two distinct criticisms by detractors of the faith, and one misguided conclusion by some Latter-day Saints.
The mention of "many angels" in the November 9, 1835 diary entry is a clarifying detail. The appearance of the Father and Son are clearly referenced separately from the mention of the "many angels." Since the visit of the Father and Son are acknowledged in the diary entry for the 9th the change from "first visitation of Angels" to "the First Vision" in the History of the Church entry is not a "falsification" of information.
Joseph Smith never actually referred to what we now call the "First Vision" by that name. Instead, he referred to it as the "first visitation of angels" or the "first communication." Joseph also referred to Moroni's visit as "another vision of angels."

The account that Joseph entered in his journal on 9 November 1835 was a detailed account which clearly describes two personages, as well as "many angels." The account that Joseph wrote just five days later in his journal on 14 November 1835 was a one line summary of the event, which he described as "the first visitation of Angels." Critics of the Church seem to believe that Joseph completely changed his story from "two personages" to "Angels" over the course of only five days. The truth is that Joseph referred to all of the personages that appeared to him as "angels."
This confusion regarding "angels" versus "personages" is illustrated in a critical "Mormoninfographic".[70] We have illustrated the error by comparing Joseph's journal entries on both days.
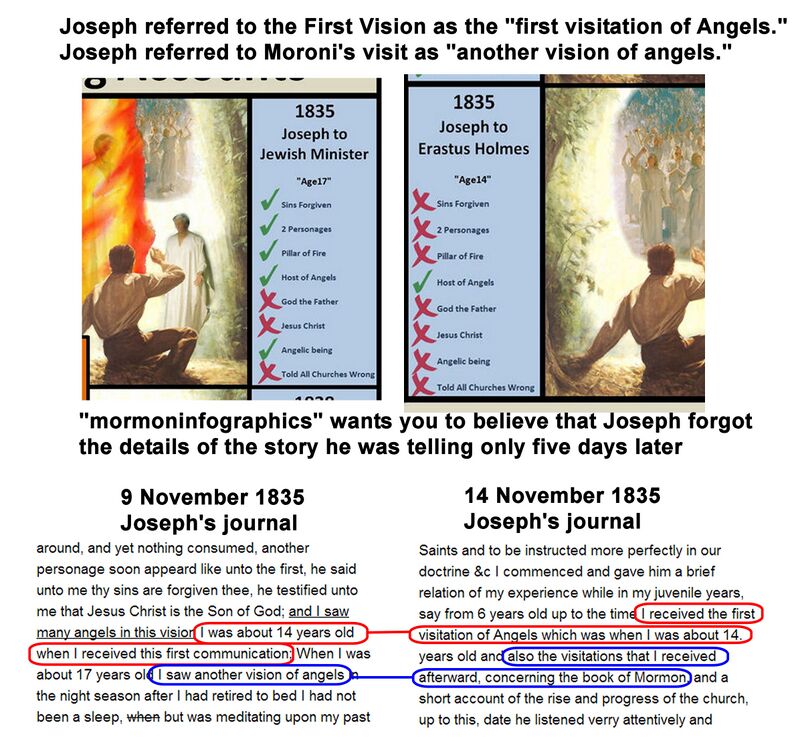

There were at the time people who went to the wood to pray after reading the Bible, and as a result received visions and epiphanies. The Encyclopedia of Mormonism (1992; 2007) noted that "[i]nitial skepticism toward Joseph Smith's testimony was understandable because others had made similar claims to receiving revelation from God."[71] Similarly, the Church's new narrative history Saints (2018) notes that after Joseph's vision when he spoke to the reverend about his vision that "[a]t first the preacher treated his words lightly. People claimed to have heavenly visions from time to time."[72] Visionaries are not that uncommon in environments where people are routinely open to the divine. Even the famous Charles Finney had one. Finney, after retiring to the woods to pray, described the experience:
Just at this moment I again thought I heard someone approach me, and I opened my eyes to see whether it were so. But right there the revelation of my pride of heart, as the great difficulty that stood in the way, was distinctly shown to me. An overwhelming sense of my wickedness in being ashamed to have a human being see me on my knees before God, took such powerful possession of me, that I cried at the top of my voice, and exclaimed that I would not leave that place if all the men on earth and all the devils in hell surrounded me. "What!" I said, "such a degraded sinner I am, on my knees confessing my sins to the great and holy God; and ashamed to have any human being, and a sinner like myself, find me on my knees endeavoring to make my peace with my offended God!" The sin appeared awful, infinite. It broke me down before the Lord.
Just at that point this passage of Scripture seemed to drop into my mind with a flood of light: "Then shall ye go and pray unto me, and I will hearken unto you. Then shall ye seek me and find me, when ye shall search for me with all your heart." I instantly seized hold of this with my heart. I had intellectually believed the Bible before; but never had the truth been in my mind that faith was a voluntary trust instead of an intellectual state. I was as conscious as I was of my existence, of trusting at that moment in God's veracity. Somehow I knew that that was a passage of Scripture, though I do not think I had ever read it. I knew that it was God's word, and God's voice, as it were, that spoke to me. I cried to Him, "Lord, I take Thee at Thy word. Now Thou knowest that I do search for Thee with all my heart, and that I have come here to pray to Thee; and Thou hast promised to hear me."
That seemed to settle the question that I could then, that day, perform my vow. The Spirit seemed to lay stress upon that idea in the text, "When you search for me with all your heart." The question of when, that is of the present time, seemed to fall heavily into my heart. I told the Lord that I should take Him at his word; that He could not lie; and that therefore I was sure that He heard my prayer, and that He would be found of me.
He then gave my many other promises, both from the Old and the New Testament, especially some most precious promises respecting our Lord Jesus Christ. I never can, in words, make any human being understand how precious and true those promises appeared to me. I took them one after the other as infallible truth, the assertions of God who could not lie. They did not seem so much to fall into my intellect as into my heart, to be put within the grasp of the voluntary powers of my mind; and I seized hold of them, appropriated them, and fastened upon them with the grasp of a drowning man.
I continued thus to pray, and to receive and appropriate promises for a long time, I know not how long. I prayed till my mind became so full that, before I was aware of it, I was on my feet and tripping up the ascent toward the road. The question of my being converted, had not so much as arisen to my thought; but as I went up, brushing through the leaves and bushes, I recollect saying with emphasis, "If I am ever converted, I will preach the Gospel."[73]
Although Finney doesn't claim to have seen any personages, he does describe a communication with God. Joseph Smith describes his experiences in much the same way as others in his environment did.
Keep in mind that Joseph prayed to find out if his sins had been forgiven. And he discovered that they had. This pleased him greatly. Why did he pray about this matter? The reason is that joining a church at that time often required that one explain one's standing with God to a preacher. We are dealing with Protestant sects. And conservative Protestants believe that one is saved (justified) at the moment one confesses Jesus Christ as Lord and Savior. So Joseph, as he faced the competing Protestant sects, was deeply concerned about his sins. One had to demonstrate to oneself and also convince a preacher that one had been saved—that is, justified. And there were many instances in which prayers were answered by visions in which the person learned that God had forgiven their sins.
The difference between Joseph's experience and many other accounts by visionaries, is that, in addition to being told that his sins were in fact forgiven, he was also told not to join any denomination. When he told that part of his visionary experience, it got him into big trouble with preachers. It was not the vision that was a problem for preachers, but his reporting that he should not join some sect.
So the fact is, contrary to our current way of telling his story, the First Vision was not the beginning of Joseph's call as Seer, Prophet, Revelator and Translator. His vision signaled the beginning of the restoration. It did not begin the work of the restoration.It steered him away from joining one of the competing denominations. It was Joseph's subsequent encounters with Moroni that made him a Seer, and eventually the founding Prophet of a fledgling Church, and not his initial vision, which was initially for him a private event about which he was reluctant to talk, though eventually he dictated some accounts that were found and published during our lifetime. Joseph told a few people about it, word got around, and this caused him much trouble with Protestant preachers.
Joseph eventually wrote the account of that early vision late in his life because rumors about it had circulated and caused him difficulty. But neither Joseph nor any of the other early Saints offered that vision as a reason for others to become Latter-day Saints during his lifetime. It was only much later that what we now call the First Vision began to take on a special importance for the Saints. One reason is that Americans soon did not live in a visionary environment. The great Charles Dickens, writing in England, explained why. He called Joseph Smith vision an absurdity—"seeing visions in the age of railways."
Wilford Woodruff came into the Church of Jesus Christ because he had known earlier in his life someone he believed was a prophet who had alerted him to the soon to be restoration of primitive Christianity. This remarkable story, which was included in the lesson manual on President Woodruff, illustrates the visionary world in which Joseph was raised. Though there were a few—one or two—instances in which the visionary reported encounters with two heavenly messengers, it was most often God the Son who they reported appearing to them.
But there have been and still are peoples not impacted by post-enlightenment skepticism about divine things who are open to visions and other dramatic encounters with the divine, though they often do not speak in public about such things, since they tend to see them as strictly private blessings and not something about which one ought to be gossiping and boasting.
The first missionaries in the Church used The Book of Mormon, not the First Vision, as a witness that the heavens were open, and that each individual, by applying the promise in Moroni 10:3-5, can receive a direct manifestation from Heavenly Father, through the Holy Ghost, that The Book of Mormon is true. After that testimony is gained, it follows that Joseph Smith is a true prophet, as he brought The Book of Mormon forth and restored the fullness of the Gospel under the direction of the Savior.
The fledgling Church of Christ began with the Book of Mormon, the witnesses to the plates, the restoration of priesthood keys, and not directly with what we call the First Vision, though that initial experience assisted in Joseph avoiding what could be perceived as damaging sectarian contamination. The historical record shows that Joseph never gave any attention to the creeds or arguments of quarreling preachers. This was the purpose served by the First Vision.
Some Christians accept Paul's vision while rejecting that of Joseph Smith for a variety of reasons. Richard Lloyd Anderson made the following comparisons.
Many Christians who comfortably accept Paul’s vision reject Joseph Smith’s. However, they aren’t consistent in their criticisms, for most arguments against Joseph Smith’s first vision would detract from Paul’s Damascus experience with equal force.
For instance, Joseph Smith’s credibility is attacked because the earliest known description of his vision wasn’t given until a dozen years after it happened. But Paul’s earliest known description of the Damascus appearance, found in 1 Corinthians 9꞉1, was recorded about two dozen years after his experience.
Critics love to dwell on supposed inconsistencies in Joseph Smith’s spontaneous accounts of his first vision. But people normally give shorter and longer accounts of their own vivid experiences when retelling them more than once. Joseph Smith was cautious about public explanations of his sacred experiences until the Church grew strong and could properly publicize what God had given him. Thus, his most detailed first vision account came after several others—when he began his formal history.
This, too, parallels Paul’s experience. His most detailed account of the vision on the road to Damascus is the last of several recorded. (See Acts 26:9–20.) And this is the only known instance in which he related the detail about the glorified Savior prophesying Paul’s work among the Gentiles. (See Acts 26:16–18.) Why would Paul include this previously unmentioned detail only on that occasion? Probably because he was speaking to a Gentile audience, rather than to a group of Jewish Christians. Both Paul and Joseph Smith had reasons for delaying full details of their visions until the proper time and place.[74]
Joseph Smith left several accounts of his First Vision. None of these accounts is identical with any other. As the main page discusses, some critics wish to argue that Joseph's vision accounts are mutually contradictory, and thus that there was no vision.
Latter-day Saints often point out that the Bible's accounts of Paul's vision on the road to Damascus appear to be contradictory. Yet, the Church's sectarian critics accept Paul's account as true despite the Bible containing apparently frank contradictions in its accounts. While accepting or explaining away these discrepancies, the critics nevertheless refuse to give Joseph Smith the same latitude. Members of the Church have long pointed out that this is a clear double standard, designed to bias the audience against Joseph from the beginning.
Perhaps because of the force of this argument, some critics have begun to argue that no contradiction exists between the versions of Paul's vision.
Author Richard Abanes wrote that contradictions in the stories of Paul's vision were
long ago resolved by scholars analyzing the Greek texts. The discrepancies in Paul's account involve modern ignorance of the Greek wording used.[75]
In support of this claim, Abanes cites W.E. Vine, Vine's Expository Dictionary of New Testament Words p. 544.
Despite Abanes' claim, Greek scholarship has not resolved this issue. In fact, his use of the scholarship is dated, he ignores contrary views, and does not seem to realize that the Bible text itself (including the Acts of the Apostles) violates his supposed 'rule' more often than it keeps it.
The two verses usually at issue are Acts 9꞉7 and Acts 22꞉9. For example, one Wikipedia editor claims that
"There is no conflict in the three accounts of Paul's vision if you read Acts 22:9 in any version other than the KJV. For instance, in the New American Standard Bible and the New International version, it says that Paul's companions did not "understand the voice"—that is hear what was uttered with understanding."[76]
| Bible version | Acts 9:7 | Acts 22:9 | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summary |
Heard voice, saw no one? |
Saw light, heard no voice? |
|
| KJV |
And the men which journeyed with him stood speechless, hearing a voice, but seeing no man. |
And they that were with me saw indeed the light, and were afraid; but they heard not the voice of him that spake to me. |
|
The work cited by Abanes is not a recent work of Greek scholarship—it was first published in 1940.[77] In the reference for ακούω, we read:
Thus, by this source, Abanes hopes to argue that there can be "no idea of any contradiction":
| Factor | Acts 9:7 | Acts 22:9 | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case |
partitive genitive |
accusative |
|
| Meaning |
One hears the sound |
One hears the message |
—|- |
We have seen Abanes appeal to a source that was more than sixty years old at the time of his writing. Have modern Greek scholars anything to add to our discussion?
Daniel Wallace (a non-LDS, conservative Christian scholar) wrote of this same issue:
...There seems to be a contradiction between this account [Acts 9:7] of Paul's conversion and his account of it in Acts 22, for there he says, "those who were with me..did not hear the voice..." However, in Acts 22:9 the verb ακούω takes an accusative direct object. On these two passages, Robertson states: '...it is perfectly proper to appeal to the distinction in the cases in the apparent contradiction....The accusative case (case of extent) accents the intellectual apprehension of the sound, while the genitive (specifying case) calls attention to the sound of the voice without accenting the sense.'...
The NIV [a conservative Bible translation, the New International Version] seems to follow this line of reasoning....[thus the differences in case] can be appealed to to harmonize these two accounts....(italics in original)[78]
Thus, Wallace is here dealing with the exact verses under discussion, and notes the exact argument which Abanes makes. Does he agree? Let us see:
On the other hand, it is doubtful that this is where the difference lay between the two cases used with ακούω in Hellenistic Greek: the N[ew] T[estament] (including the more literary writers) is filled with examples of ακούω + genitive indicating understanding[79]....as well as instances of ακούω + accusative where little or no comprehension takes place[80]}....The exceptions, in fact, are seemingly more numerous than the rule!
Thus, regardless of how one works through the accounts of Paul's conversion, an appeal to different cases probably ought not form any part of the solution (italics and bold italics in original).[81]
Thus, the New Testament itself does not agree with Abanes' reading. Far from supporting him, Greek scholarship argues against his solution—the Bible has more examples where his supposed "rule" is broken than when it is followed. (Even Acts itself contains three counterexamples!)
It would seem that this approach has been developed by those who wish to maintain the idea of biblical inerrancy in the face of the Greek evidence.
Critical sources |
|
Wiki links |
|
Online |
|
Video |
|
Navigators |
The various accounts of the First Vision tell a consistent story, though naturally they differ in emphasis and detail. Historians expect that when an individual retells an experience in multiple settings to different audiences over many years, each account will emphasize various aspects of the experience and contain unique details. Indeed, differences similar to those in the First Vision accounts exist in the multiple scriptural accounts of Paul’s vision on the road to Damascus and the Apostles’ experience on the Mount of Transfiguration.3 Yet despite the differences, a basic consistency remains across all the accounts of the First Vision. Some have mistakenly argued that any variation in the retelling of the story is evidence of fabrication. To the contrary, the rich historical record enables us to learn more about this remarkable event than we could if it were less well documented.
Author's source(s)
The author's source is assumed to be one of Joseph’s two 1835 journal entries which mention the First Vision. This particular instance would correlate with the 9 November 1835 journal entry.
Response
Author's source(s)
Joseph Smith’s 1832 history and Joseph Smith-History in the Pearl of Great Price.
Response
Author's source(s)
Tanner, ‘’Mormonism-Shadow or Reality?’’ 151-52.
Response
In 1834, Oliver Cowdery began publishing a history of the Church in installments in the pages of the Latter Day Saints’ Messenger and Advocate. The first installment talks of the religious excitement and events that ultimately led to Joseph Smith’s First Vision at age 14. However, in the subsequent installment published two months later, Oliver claims that he made a mistake, correcting Joseph’s age from 14 to 17 and failing to make any direct mention of the First Vision. Oliver instead tells the story of Moroni’s visit, thus making it appear that the religious excitement led to Moroni’s visit.
This curious account has been misunderstood by some to be evidence that the “first” vision that Joseph claimed was actually that of the angel Moroni and that Joseph invented the story of the First Vision of the Father and Son at a later time. However, Joseph wrote an account of his First Vision in 1832 in which he stated that he saw the Lord, and there is substantial evidence that Oliver had this document in his possession at the time that he wrote his history of the Church. This essay demonstrates the correlations between Joseph Smith’s 1832 First Vision account, Oliver’s 1834/1835 account, and Joseph’s 1835 journal entry on the same subject. It is clear that not only did Oliver have Joseph’s history in his possession but that he used Joseph’s 1832 account as a basis for his own account. This essay also shows that Oliver knew of the First Vision and attempted to obliquely refer to the event several times in his second installment before continuing with his narrative of Moroni’s visit.
Author's source(s)
Leviticus 19:26; 20:6, 27; Deuteronomy 18:10; Isaiah 19:3.
Response
Abner Cole wanted to mock the Book of Mormon in his newspaper (The Reflector). He was most probably motivated to do this because he had violated copyright law by printing portions of the Book of Mormon in his paper and the Prophet Joseph Smith forced him to stop his illegal activity. Cole’s mockery text was called the “Book of Pukei.” In this peculiar literary production the editor took many authentic elements of the story of the Book of Mormon’s origin and mixed them together with elements of speculation that had been floating around the community. Cole utilized the dialogue of one of the characters in his mockery text to call Joseph Smith an ignoramus, a criminal, and a servant of Satan. It is in this text that Joseph Smith is first connected with a man from Great Sodus Bay, New York, called “Walters the Magician” (probably Luman Walter).
The author notes that in 1826 Joseph was charged with being a “disorderly person” and “glass looker.” The author states that “glass looker” means “crystal ball user.”
Author's sources: Tanner, ‘’Mormonism-Shadow or Reality?’’ 32-49.
Life and Character |
|
Youth |
|
Revelations and the Church |
|
Prophetic Statements |
|
Society |
|
Plural marriage (polygamy) |
|
Death |
In 1825 Josiah Stowel sought out the young Joseph Smith, who had a reputation for being able to use his seer stone to locate lost objects, to help him to locate an ancient silver mine. After a few weeks of work, Joseph persuaded Stowel to give up the effort. In 1826, some of Stowel's relatives brought Joseph to court and accused him of "glasslooking" and being a "disorderly person." Several witnesses testified at the hearing.
Joseph was ultimately released without being fined and had no punishment imposed upon him. Years later, a bill from the judge was discovered which billed for court services.
Gordon Madsen summarized:
"The evidence thus far available about the 1826 trial before Justice Neely leads to the inescapable conclusion that Joseph Smith was acquitted." [1]
A review of all the relevant documents demonstrates that:
It was likely that the court hearing was initiated not so much from a concern about Joseph being a money digger, as concern that Joseph was having an influence on Josiah Stowel. Josiah Stowel was one of the first believers in Joseph Smith. His nephew was probably very concerned about that and was anxious to disrupt their relationship if possible. He did not succeed. The court hearing failed in its purpose, and was only resurrected decades later to accuse Joseph Smith of different crimes to a different people and culture.
Understanding the context of the case removes any threat it may have posed to Joseph's prophetic integrity.
In the spring of 1825 Josiah Stowell visited with Joseph Smith "on account of having heard that he possessed certain keys, by which he could discern things invisible to the natural eye." [2] Josiah Stowell wanted Joseph to help him in his quest to find treasure in an ancient silver mine. Joseph was reluctant, but Stowell persuaded Joseph to come by offering high wages. According to trial documents, Stowell says Joseph, using a seer stone, "Looked through stone and described Josiah Stowell's house and out houses, while at Palmyra at Sampson Stowell's correctly, that he had told about a painted tree with a man's hand painted upon it by means of said stone." [3]
Joseph and his father traveled to southern New York in November of 1825. This was after the crops were harvested and Joseph had finished his visit to the Hill Cumorah that year. They participated with Stowell and the company of workers in digging for the mine for less than a month. Finally Joseph persuaded him to stop. "After laboring for the old gentleman about a month, without success, Joseph prevailed upon him to cease his operations." [4]
Joseph continued to work in the area for Stowell and others. He boarded at the home of Isaac Hale and met Emma Hale, who was one "treasure" he got out of the enterprise.
In March of the next year, Stowell's sons or nephew (depending on which account you follow) brought charges against Joseph and he was taken before Justice Neely. The supposed trial record came from Miss Pearsall. "The record of the examination was torn from Neely's docket book by his niece, Emily Persall, and taken to Utah when she went to serve as a missionary under Episcopalian bishop Daniel S. Tuttle." [5] This will be identified as the Pearsall account although Neely possessed it after her death. It is interesting that the first published version of this record didn't appear until after Miss Pearsall had died.
William D. Purple took notes at the trial and tells us, "In February, 1826, the sons of Mr. Stowell, ...were greatly incensed against Smith, ...saw that the youthful seer had unlimited control over the illusions of their sire... They caused the arrest of Smith as a vagrant, without visible means of livelihood." [6]
Whereas the Pearsall account says: "Warrant issued upon oath of Peter G. Bridgman, [Josiah Stowell's nephew] who informed that one Joseph Smith of Bainbridge was a disorderly person and an imposter...brought before court March 20, 1826" [7]
So, we have what has been called "The 1826 Trial of Joseph Smith", even though the records show that this wasn't actually a trial. For many years LDS scholars Francis Kirkham, Hugh Nibley and others expressed serious doubts that such a trial had even taken place.
The court did not assess a fine against Joseph. There were bills made out by Judge Neely and Constable DeZeng, but these were for costs. Those bills were directed to the County for payment of witnesses, etc., not to Joseph.
Ensign (June 1994):
Highlights in the Prophet’s Life 20 Mar. 1826: Tried and acquitted on fanciful charge of being a "disorderly person," South Bainbridge, Chenango County, New York. New York law defined a disorderly person as, among other things, a vagrant or a seeker of "lost goods." The Prophet had been accused of both: the first charge was false and was made simply to cause trouble; Joseph’s use of a seer stone to see things that others could not see with the naked eye brought the second charge. Those who brought the charges were apparently concerned that Joseph might bilk his employer, Josiah Stowell, out of some money. Mr. Stowell’s testimony clearly said this was not so and that he trusted Joseph Smith. [8]
Hugh Nibley had serious doubts as to whether or not Joseph Smith was actually brought to trial in 1826, and he felt that the only real trial was in 1830. For the most part, Nibley felt that the "court record" didn't seem to be correct. The following quote is taken from Nibley's book "The Myth Makers:"
"if this court record is authentic it is the most damning evidence in existence against Joseph Smith."
It was easy to cast doubt on the reality of the 1826 hearing until the bills from Judge Albert Neely and Constable Philip De Zeng were found in 1971. These documents were removed from their purported site of discovery by Dr. Wesley Walters, a well-known anti-Mormon author.
Walters wrote, "Because the two 1826 bills had not only suffered from dampness, but had severe water damage as well, Mr. Poffarl hand-carried the documents to the Yale University's Beinecke Library, which has one of the best document preservation centers in the country." [9] The problem with this action is, once you have removed a document from a historical setting and then try to restore it to the same setting, you can't prove that you have not altered the document.
The actions of Walters and Poffarl compromised the documents. By having the documents removed and only returned under threat of a lawsuit by the County, it opened the possibility that they could be forged documents. They are generally considered to be authentic.
Since Wesley Walters has found some bills related to the trial, the critics now claim that the case is proven and that Nibley has proven their case for them. Nothing is further from the truth. First of all you need to look at the whole quote. Nibley was chastising Tuttle for not actually using the trial record that he had. He was questioning why he would do that if it was so important.
"You knew its immense value as a weapon against Joseph Smith if its authenticity could be established. And the only way to establish authenticity was to get hold of the record book from which the pages had been purportedly torn. After all, you had only Miss Pearsall's word for it that the book ever existed. Why didn't you immediately send he back to find the book or make every effort to get hold of I? Why didn't you "unearth" it, as they later said you did? . . . The authenticity of the record still rests entirely on the confidential testimony of Miss Pearsall to the Bishop. And who was Miss Pearsall? A zealous old maid, apparently: "a woman helper in our mission," who lived right in the Tuttle home and would do anything to assist her superior. The picture I get is that of a gossipy old housekeeper. If this court record is authentic, it is the most damning evidence in existence against Joseph Smith. Why, then, [speaking to Tuttle] was it not republished in your article in the Schaff-Herzog Encyclopedia of Religious Knowledge after 1891? . . . in 1906 Bishop Tuttle published his Reminiscences of a Missionary Bishop in which he blasts the Mormons as hotly as ever. . . yet in the final summary of his life's experiences he never mentions the story of the court record - his one claim to immortal fame and the gratitude of the human race if it were true!" (Nibley "The Myth Makers", 246)
The Pearsall account, which has never been produced, claims that the defendant was found guilty. The real point at issue is not whether or not there was a trial, but whether or not a record existed proving Joseph guilty of deceit. A document proving such guilt has not been found.
Critics of Joseph Smith's time ignored the 1826 court hearing:
The attraction of this event for a later generation of critics, however, lies in the fact that:
Many people of the 1800s did not see any differences between what later generations would label as "magic" and religiously-driven activities recorded in the Bible—such as Joseph's silver cup (see Genesis 44:2,5) in which 'he divineth' (which was also practiced by the surrounding pagans and referred to as hydromancy),[10] or the rod of Aaron and its divinely-driven power (Exodus 7:9-12).
The Bible records that Jacob used rods to cause Laban's cattle to produce spotted, and speckled offspring (see Genesis 30:37-39) — one can only imagine what the critics would say should Joseph Smith have attempted such a thing!
In Joseph Smith's own day other Christian leaders were involved in practices which today's critics would call 'occultic.' Quinn, for instance, observes that in "1825, a Massachusetts magazine noted with approval that a local clergyman used a forked divining rod.... Similarly, a Methodist minister wrote twenty-three years later that a fellow clergymen in New Jersey had used a divining rod up to the 1830s to locate buried treasure and the 'spirits [that] keep guard over buried coin'...." [11]
It is important to realize that every statement about "magic" or the "occult" by LDS authors is a negative one. Joseph and his contemporaries would likely have shocked and dismayed to be charged with practicing "magic." For them, such beliefs were simply how the world worked. Someone might make use of a compass without understanding the principles of magnetism. This mysterious, but apparently effective, device was useful even if its underlying mechanism was not understood. In a similar way, activities of the early 1800s or Biblical times which later generations would view skeptically were simply thought of as part of how the world worked.
But, it is a huge leap from this realization to charging that Joseph and his followers believed they were drawing power from anything but a divine or proper source.
We have five records of the 1826 hearing. These were published in eight documents.
1. Apr. 9, 1831 - A W. Benton in Evangelical Magazine and Gospel Advocate
2.Oct. 1835 - Oliver Cowdery in Latter-day Saints Messenger and Advocate
3.1842 letter from Joel K. Noble (not published until 1977)
4.Record torn from Judge Neely docket book by Miss Emily Pearsall (niece)
5. May 3, 1877 - W. D. Purple Chenango Union
It may be that Purple saw the publication in the Eclectic Magazine and that is why he published his account a few years later. There are no complete overlaps in the accounts; we will look at the similarities and differences.
Finally, we have the bills by Judge Neely and Constable Da Zeng which provide some additional useful details.
We don't have the actual record that Miss Pearsall had, but the claimed trail of events leads as follows:
It will be noticed with interest, that although Bishop Tuttle and others had access to the Pearsall account for several years it was not published until after her death. That combined with the fact that the torn leaves were never allowed to be examined, would cast some doubt on the completeness or accuracy of that which was published.
We know that the supposed "court record" obtained by Miss Pearsall can't be a court record at all.
This is the reason that the people stated for why they were putting forth this information.
Unsurprisingly, those who provided these accounts had an agenda. We are not looking at an event through the eyes of an unbiased observer, and most of that bias is directed against Joseph Smith.
If we look at the individuals bringing the charges, we have the following: Benton (1831): The Public Cowdery (1835): very officious person Noble (1842): Civil authority Marshall (1873): Peter G. Bridgman Purple (1877): sons of Mr. Stowell Tuttle (1883): Peter G. Bridgman Judge Neely: The Public
Note that the agreement of Marshall and Tuttle is misleading because they are essentially quoting the same source.
Whether it was Josiah Stowell's sons or his nephew Peter G. Bridgman, it seems to be close family members. We don't know why Peter G. Bridgman brought the charges, but it could easily have been because he was worried that his uncle was accepting Joseph Smith in his religious claims. Josiah did join the church organized by Joseph Smith and stayed faithful his whole life. As for Peter Bridgman, "Within a month after the trial he was licensed as an exhorter by the Methodists and within three years had helped establish the West Bainbridge Methodist Church. Upon his death in 1872 his fellow ministers characterized him as 'an ardent Methodist and any attack upon either the doctrines or the polity of the Methodist Episcopal Church, within his field of labor, was sure to be repelled by him with a vigorous hand." [12]
Is it possible that the trial of Joseph Smith was just one of his first attempts to apply a "vigorous hand?"
The charge is listed in the various accounts as:
Hugh Nibley indicated how it would be strange that he could be charged without visible means of livelihood, since he was being employed by Stowell and others.
The portion of the statute that would seem to apply was enacted by New York in 1813.
...all persons who not having wherewith to maintain themselves, live idle without employment, and also all persons who go about from door to door, or place themselves in the streets, highways or passages, to beg in the cities or towns where they respectively dwell, and all jugglers, and all persons pretending to have skill in physiognomy, palmistry, or like crafty science, or pretending to tell fortunes, or to discover where lost goods may be found; ... shall be deemed and adjudged disorderly persons.
What is a juggler? It used to be that a person skilled in sleight of hand was called a juggler, whereas today we would call them a "sleight of hand magician." Thus, a "juggler" was a con man; someone using his 'stage magic' talents to defraud. [13]
But what if you weren't pretending to discover lost goods? What if you actually had a gift where you "could discern things invisible to the natural eye" Could you then be judged guilty of this statute?
As far as the number of witnesses we have the following:
What is particularly interesting here is that Tuttle and Marshall are supposedly quoting from the same document. Marshall only quotes 5 witnesses, but at the end, the charges are listed for seven witnesses. The fee was 12-1/2 cents per witness. Eighty-seven and ½ cents divided by twelve ½ cents per witness, gives us seven witnesses. By combining the Purple and Pearsall accounts we can arrive at seven witnesses, and also a motive for not including all the witnesses or letting the record be examined. It is unknown why the constable would have listed twelve witnesses, unless that is the number he summoned to the proceedings. Seven would seem to be the correct number of those that testified.
Purple does add a witness that hadn't been included by Marshall or Tuttle: Joseph Smith, Sr. Maybe they didn't want to include the testimony of Joseph's father because his testimony was more religious in nature. He spoke of Joseph's "wonderful triumphs as a seer", that "both he and his son were mortified that this wonderful power which God had so miraculously given him should be used only in search of filthy lucre," and "he trusted that the Son of Righteousness would some day illumine the heart of the boy, and enable him to see His will concerning him." It is easy to see why this testimony wouldn't be included in a record where you are trying to show that Joseph Smith was a person trying to acquire work as a money digger. Which might be the reason the Tuttle and Marshall omitted the Joseph Smith Sr. testimony.
Noble's statement is hearsay, since there is no evidence that he actually attended this trial. Furthermore, his statement and Benton's statement can't be taken as an indication that Joseph was judged guilty. For example, in Joseph's 1830 trial he was acquitted. The court said that they "find nothing to condemn you, and therefore you are discharged." Then Mr Reid testifies, "They then proceeded to reprimand him severely, not because anything derogatory to his character in any shape had been proven against him by the host of witnesses that had testified during the trial." [14]
The verdict indicated by Marshall and Tuttle is questionable. It seems to be appended as an afterthought. Throughout the document Joseph is referred to as the "prisoner", then after the last testimony, we have one sentence in which he is named a defendant, "And thereupon the Court finds the defendant guilty." Here we have suddenly a declaratory statement that is completely out of character with the rest of the Pearsall document. Also, if this were actually a trial, Joseph wouldn't have testified against himself as the first witness.
Wesley P. Walters has demonstrated that this is not a trial. The Constable's charges of "19 cents attached to the mittimus marks it as the pre-trial 'commitment for want of bail' ...and not the post-trial 'warrant of commitment, on conviction, twenty-five cents." [15]
In the Tanners' anti-Mormon Salt Lake City Messenger, they stated, "Wesley P. Walters had convincingly demonstrated to us that we were dealing with 'an examination.' In a New Conductor Generalis, 1819, page 142, we learn that in an 'examination' the accused is not put under oath but that the witnesses are'" [16]
In all cases but one the witnesses were "sworn", whereas Joseph was examined. Judge Neeley's charges actually uses that precise terminology, "in examination of above cause". Therefore, since this wasn't a trial, one cannot have a guilty verdict.
Stowell joined the Church in 1830, and died in full fellowship, planning to join the Saints "in Zion."[17]
There are only three testimonies that are duplicated in both the Purple and Pearsall accounts. They are Joseph Smith, Josiah Stowel and Jonathan Thompson. In the Purple account Thompson said that he could not remember finding anything of value. He stated that Joseph claimed there was a treasure protected by sacrifice and that they had to be armed by fasting and prayer. They struck the treasure with a shovel. One man placed his hand on the treasure, but it gradually sunk out of reach. Joseph believed there was a lack of faith or devotion that caused the failure. They talked about getting the blood from a lamb and sprinkling it around.
Interestingly, the same witness in the Pearsall record says that Joseph indicated where the treasure was. He looked in the hat and told them how it was situated. An Indian had been killed and buried with the treasure. So this detail matches with the Purple account. The treasure kept settling away. Then Joseph talked about salt that could be found in Bainbridge and described money that Thompson had lost 16 years ago. Joseph described the man that had taken it and what happened to the money. There is nothing mentioned about sacrificing sheep or not having sufficient faith and so forth. The Pearsall record is supposedly a more complete written record, but it doesn't have the bleeding sheep, or fasting and prayer that characterizes the Purple account.
One biographical encyclopedia noted:
Josiah Stowell (sometimes spelled Stoal) was born in Winchester, New Hampshire, 22 March 1770, and later resided at his farm on the Susquehanna River, about 3.2 miles southwest of the village of South Bainbridge (now Afton). This village was part of the township of Bainbridge (now Afton), Chenango County, New York. In October 1825 Stowell was engaged in digging for reported Spanish treasure in the Ouaquaga (Ouaquagua) Mountains of Harmony, Susquehanna County, Pennsylvania. Hearing that Joseph Smith Jr. of Manchester, Ontario County, New York, had the ability to "discern things invisible to the natural eye," Mr. Stowell visited Joseph and employed him.
The men lodged at the home of Isaac Hale in Harmony. According to Hale, they dug from early November to about 17 November 1825, when successive failures caused them to withdraw to the Stowell farm. While at the Hale home, Joseph Smith had met Isaac's daughter, Emma. He continued to court her while he was employed in New York by Josiah Stowell and Joseph Knight Sr. After Joseph and Emma were married at South Bainbridge on 18 January 1827, Stowell gave the newlyweds a ride to Manchester, where they resided with Joseph's parents.
Stowell and Knight were both houseguests of the Smiths at Manchester on 21-22 September 1827, when Joseph Smith went to the Hill Cumorah and obtained the gold plates from Moroni. Stowell joined the Church in 1830 but did not go west with the Saints when they moved to Ohio in 1831. Josiah Stowell continued to express his belief in the Prophet and the Book of Mormon as indicated in a letter written by his son, Josiah Stowell Jr., to John S. Fullmer in February 1843. He also dictated a letter to the Prophet in Nauvoo on 19 December 1843 and told him of his desire "to come to Zion the next season"; however, conditions prevented his doing so. Josiah Stowell died in Smithboro, Tioga County, New York, on May 12, 1844. He is buried in the Smithboro Cemetery.[18]
Claims that Joseph was a "juggler," or "conjurer" were a common 19th century method of dismissing his prophetic claims via ad hominem. Modern-day claims about him being found to be a "con man" are simply the same attack with updated language, usually bolstered by a misunderstanding or misrepresentation of Joseph's 1826 court hearing.
Joseph's tendency to assume the best of others, even to his own repeated detriment, also argues for his sincerity. One might legitimately claim that Joseph was mistaken about his prophetic claims, but it will not do to claim that he was cynically, knowingly deceiving others for his own gain.
Claims about Joseph being found guilty of being a "con man" in court usually revolve around either a misunderstanding or misrepresentation of Joseph's 1826 court hearing:
| Main article: | 1826 trial for "glasslooking" |
Brant Gardner noted:
One very subtle but very important aspect of all of the dealings of the village seers is their relationship with their clients. The true cunning men and wise women were fixtures in the community. They received clients; they did not seek them out. In the cases reported about Sally Chase, her clients came to her. We have four descriptions of Joseph as this kind of village seer; and in each case, the client came to him with his problem....[T]hose who were searching for treasure invited the adept, but the cunning man or wise woman did not actively seek their employ.[19]
When Joseph's career is examined more broadly, there are other factors which argue for his sincerity. Arguably one character trait which gave Joseph repeated trouble was his willingness to trust others and give them the benefit of the doubt. His striking ability to accept people at face value, never doubting that their motives were as pure as his own, has many exemplars. The case of W.W. Phelps is one.
Phelps had betrayed Joseph and the Church during the Missouri persecutions, and contributed to Joseph's confinement in Liberty Jail. His signature was on the petition that resulted in the extermination order which led to the Saints' murder and dispossession. After receiving a penitent letter from Phelps, Joseph quickly responded
I must say that it is with no ordinary feelings I endeavor to write a few lines to you… I am rejoiced at the privilege granted me… when we read your letter—truly our hearts were melted into tenderness and compassion when we ascertained your resolves… It is true, that we have suffered much in consequence of your behavior… we say it is your privilege to be delivered from the powers of the adversary, be brought into the liberty of God's dear children, and again take your stand among the Saints of the Most High, and by diligence, humility, and love unfeigned, commend yourself to our God, and your God, and to the Church of Jesus Christ…
Believing your confession to be real, and your repentance genuine, I shall be happy once again to give you the right hand of fellowship, and rejoice over the returning prodigal…
"Come on, dear brother, since the war is past, For friends at first, are friends again at last."[20]
So it was that Joseph, while willing to do almost anything―from taking up arms, to petitioning presidents, to launching a campaign of disinformation―to protect the revealed Restoration and the Latter-day Saints, repeatedly opened himself to abuse and worse because of his apparent inability or unwillingness to think the worst of someone in advance of the evidence. Joseph assumed that all men were as purely motivated as he was. "It takes a con to know a con," and Joseph wasn’t a con.[21] If he had been cynically exploiting others, he would have tended to ascribe his own base motives of deception and taking advantage to others, and probably would have been more cautious. But, he did not. Elder B.H. Roberts, a seventy and historian, noted years later that:
[Joseph Smith had] a too implicit trust in [men's] protestations of repentance when overtaken in their sins; a too great tenacity in friendship for men he had once taken into his confidence after they had been proven unworthy of the friendship.…[22]
A prime example of this phenomenon is the case of John C. Bennett. Soon after Bennett's baptism in Nauvoo, Joseph received a letter reporting Bennett's abandonment of wife and children. Joseph knew from personal experience that "it is no uncommon thing for good men to be evil spoken against,"[23] and did nothing precipitous. The accusations against Bennett gained credence when Joseph learned of his attempts to persuade a young woman "that he intended to marry her." Joseph dispatched Hyrum Smith and William Law to make inquiries, and in early July 1841 he learned that Bennett had a wife and children living in the east. Non-LDS sources confirmed Bennett's infidelity: one noted that he "heard it from almost every person in town that [his wife] left him in consequence of his ill treatment of her home and his intimacy with other women." Another source reported that Bennett's wife "declared that she could no longer live with him…it would be the seventh family that he had parted during their union."[24]
When confronted with the evidence privately, Bennett confessed and promised to reform. He did not, though Joseph did not make his sins public until nearly a year later.[25]
| See also: | John C. Bennett |
Other examples of misplaced trust include George M. Hinckle, who sold Joseph out to the Missouri militia (resulting in his near-execution and his imprisonment in Liberty Jail) and William Law, who would help publish the Nauvoo Expositor, a newspaper which called for Joseph's death and contributed to the martyrdom.
Wiki links |
|
FAIR links |
|
Online |
|
Video |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
Early works that label Joseph a "juggler" or "conjurer"
Later works that use the modern terms "con man," "confidence man," or "con game"
|
Critical sources |
|
Response
Linda King Newell and Valeen Tippetts Avery, ‘’Mormon Enigma: Emma Hale Smith, Prophet’s Wife, “Elect Lady,” Polygamy’s Foe 1804-1879’’(Garden City, N.Y.: Doubleday, 1984); David Whitmer, ‘’An Address to All Belivers in Christ’’ (Richmond, Mo.: David Whitmer, 1887), 12.
These two instruments—the interpreters and the seer stone—were apparently interchangeable and worked in much the same way such that, in the course of time, Joseph Smith and his associates often used the term “Urim and Thummim” to refer to the single stone as well as the interpreters. In ancient times, Israelite priests used the Urim and Thummim to assist in receiving divine communications. Although commentators differ on the nature of the instrument, several ancient sources state that the instrument involved stones that lit up or were divinely illumin[at]ed. Latter-day Saints later understood the term “Urim and Thummim” to refer exclusively to the interpreters. Joseph Smith and others, however, seem to have understood the term more as a descriptive category of instruments for obtaining divine revelations and less as the name of a specific instrument.
The author claims that Joseph attempted to “join the Methodist Church in 1828, eight years after the Father and Son allegedly told him that all the churches were apostate….Why did he ignore God’s command to ‘join none of them’?”
Author's sources: Michael Marquardt and Wesley P. Walters, ‘’Inventing Mormonism: Tradition and the Historical Record’’ (Salt Lake City: Smith Research Associates, 1994), 55, 61, n. 49
Accounts |
|
Historical context |
|
Doctrinal impact |
Video published by the Church History Department.
Video from FAIR
Joseph's concern about religion started when he was twelve years old, close on the heels of the revival of 1817. In his 1832 account, Joseph notes that his concern about religion began at age 12 (1817-1818):
At about the age of twelve years my mind become seriously imprest with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul which led me to searching the scriptures believeing as I was taught, that they contained the word of God thus applying myself to them and my intimate acquaintance with those of different denominations led me to marvel excedingly for I discovered that they did not adorn instead of adorning their profession by a holy walk and Godly conversation agreeable to what I found contained in that sacred depository this was a grief to my Soul... (Joseph Smith's 1832 account of the First Vision)
Richard Bushman notes that this "would have been in late 1817 and early 1818, when the after-affects of the revival of 1816 and 1817 were still felt in Palmyra." [1]
Joseph Smith talked of observing, as a 14-year-old, "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion" in the Palmyra area during the Spring of 1820. Joseph notes that "It commenced with the Methodists, but soon became general among all the sects in that region of country." There is documented evidence of at least one Methodist camp meeting in the Palmyra area during that period, which only by chance happened to be mentioned in the local newspaper because of a specific death that seemed to be associated with it. In addition, there are newspaper articles talking of large-scale revival activity in the larger region surrounding Palmyra during the same general period when Joseph Smith said that it was taking place.
It is reasonable to assume based upon the facts that the Methodists had more than one camp meeting during this period. This could easily account for the religious excitement in Palmyra that, in Joseph's mind at age 14, began with the Methodists.
Joseph continues in his 1832 account: "[T]hus from the age of twelve years to fifteen I pondered many things in my heart concerning the sittuation of the world of mankind the contentions and divi[si]ons the wicke[d]ness and abominations and the darkness which pervaded the of the minds of mankind my mind become excedingly distressed for I become convicted of my sins." In July, 1819, several years after Joseph said his mind became "seriously imprest," a major Methodist conference was held near Palmyra:
[T]he Methodists of the Genesee Conference met for a week in Vienna (later Phelps), a village thirteen miles southeast of the Smith farm on the road to Geneva. About 110 ministers from a region stretching 500 miles from Detroit to the Catskills and from Canada to Pennsylvania met under the direction of Bishop R. R. Robert to receive instruction and set policy. If we are to judge from the experience at other conferences, the ministers preached between sessions to people who gathered from many miles around. It was a significant year for religion in the entire district. . . . The Geneva Presbytery, which included the churches in Joseph's immediate area, reported in February, 1820, that "during the past year more have been received into the communion of the Churches than perhaps in any former year." Methodists kept no records for individual congregations, but in 1821 they built a new meetinghouse in town. [2]

Some claim that there were no religious revivals in the Palmyra, New York area in 1820, contrary to Joseph Smith's claims that during that year there was "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion...indeed, the whole district of country seemed affected by it" Joseph Smith—History 1:5 Joseph Smith talked of observing, as a 14-year-old, "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion" in the Palmyra area during the Spring of 1820. Joseph notes that "It commenced with the Methodists, but soon became general among all the sects in that region of country."
Abundant evidence of religious excitement exists to substantiate Joseph’s account. This has been thoroughly summarized by Pearl of Great Price Central. Their analysis may be accessed by clicking on the hyperlinked text.
One should keep in mind that Joseph Smith never used the term "revival" in his description - he simply described it as "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion." To a 14 year old who had been concerned about religion starting at age 12 after the 1817 revival, the ongoing camp meetings in the town in which he lived would certainly qualify.

Critics of Joseph Smith claim that no revival is mentioned in the 1832 First Vision account because the actual word 'revival'—or something similar—is not found within the text. But they have failed to notice a distinct pattern of words that demonstrate a definite link between the various First Vision accounts.
When the September—November 1832 First Vision account is compared with subsequent recitals (especially 1838), and one partial previous rendition, it appears that they are all telling the same story: Prior to the First Vision event there were contentions and divisions among the different religious denominations in connection with a revival. It seems, therefore, that the Prophet's handwritten 1832 account does indeed make a passing reference to revival activity.
There are several other phrases in the Prophet's 1832 account that can be interpreted as references to revivals. For instance, Joseph Smith said that when he was "about the age of twelve years" (23 December 1817—23 December 1818) he became seriously concerned about the welfare of his soul. Why did these feelings arise at this point in time? Possibly because there was a Methodist camp-meeting/revival from June 19th through the 22nd, 1818 held in Palmyra, New York.[8]
Joseph Smith pointed to a time period "from the age of twelve years to fifteen" (i.e., between 23 December 1817 and 23 December 1821) when he –
Some of the themes enumerated above can be matched with the Prophet's other descriptions of things that happened during the revival activity of Palmyra and its vicinity. This matching of themes tends to support the argument that the 1832 text does indeed refer to revival activity.
The phrase "I cried unto the Lord for mercy" in Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision account also has a strong ring of revivalism to it. Rev. George Peck recounted the happenings at a Methodist camp meeting held on 4 July 1816 in Plymouth, New York. He said that "There was an unbroken roar of fervent supplication all over the ground, while the awful voice of the preacher resounded." One person then fell to the ground and cried for mercy.[9]
Wiki links |
|
Online |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Joseph Smith's stated motivation for praying to the Lord changes between the first known account of the First Vision (1832) and the official version of it (1838). The 1832 account emphasizes his desire for a forgiveness of sins, and the 1838 (official) account emphasizes his desire to know which church was right. Some critic claim that Joseph changed his story in later years.
The texts that are employed by critics to justify the charge of 'differing motivations' are as follows:
1832
1838
The words that precede the point at which Joseph Smith offers his prayer in the 1832 text demonstrate that the anti-Mormon claim about his motivation changing is not sustainable. These words read as follows (standardized for readability):
Historian Christopher Jones has observed that Joseph Smith's 1832 account (and indeed much of his other three accounts) are shaped as Methodist conversion narratives. Within Methodism (and indeed the broader religious culture of Joseph Smith's day), finding forgiveness of sins and joining the right Church rode in tandem. You receive forgiveness of sins by joining the right Church. If you don't follow the correct, "biblical" doctrine then you can't receive such forgiveness.[10] In the case of Joseph Smith, he receives forgiveness of sins and is told not to join any church with which he was acquainted at the time.
There are those who claim that Joseph Smith only claims to seek forgiveness of sins in his 1832 account. These critics ignore the larger historical context under which the 1832 account was written (documented by Jones) and also fail to take notice of scriptural passages quoted near the end of the account in which Christ echoes Matthew 15:8-9:
This clearly does not refer to young Joseph's seeking of a forgiveness of sins. It must refer to an apostasy and restoration of a Church—the true Church of Christ that Joseph had already proclaimed to restore as Doctrine and Covenants 1 (revealed in 1831) makes clear:
Some may counter that this only refers to corrupt people and not corrupt churches or religions. Going back to the passage from the 1832 account cited above, one reads "the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doth good no not one..." This phrase ('and none doeth good no not one') is echoed in a few scriptural passages (Psalm 53: 3; Romans 3: 10, 12; Moroni 7:17) but for our purposes we will highlight one of these occurrences in JST Psalm 14:2. The Church still describes this passage in its heading as lamenting "the loss of truth in the last days[.]" The passage "looks forward to the establishment of Zion." The italics represent edits made by Joseph Smith to the text:

Joseph Fielding McConkie said, 'The JST rendering of this Psalm reads like another account of the First Vision.'[11]
The late Matthew Brown suggested that Joseph's translation of Psalm 14 took place 'shortly after late July 1832.'[12] He even goes so far to say that 'the JST Psalm 14 text may have served as a prototype of sorts for the composition of the 1832 historical document.'[13]
The 1838–39 account’s mention of 'corrupt professors' seems to be reflected in the JST’s 'their teachers are workers of iniquity.' . . . JST Psalm 14:2-4 features 'all these who say they are [the Lord’s]' being rejected by the Lord due to them having 'gone aside,' 'become filthy,' and 'none of them…doing good.' And this is laid at the feet of their teachers who 'are workers of iniquity' [14] This use of Psalm 14 to be explanatory for Joseph's use of no one doing good is strengthened by the fact that Psalm 14 is quoted specifically earlier in the 1832 account ("And when I considered upon these things my heart exclaimed, 'Well hath the wise man said, It is a fool that saith in his heart there is no God.'")
Thus, to summarize again, those who don't do good are all people and this is caused by false teachers teaching incorrect doctrine.
The 1832 account emphasizes Joseph's want of forgiveness as a means to the end of restoring the true Church of Christ. This is completely in line with the rest of the accounts and thus the standard narrative of the First Vision and Joseph's motives in seeking such a vision as taught officially by the Church.
A longer version of this argument is made by Walker Wright and historian Don Bradley in a 2023 paper for BYU Studies.[15]
The First Vision has been a center of both faith and controversy. While millions of Latter-day Saints affirm it as the beginning of the Restoration, others see it as an ever-growing fish tale. The multiple accounts of the First Vision vary in detail, with Joseph Smith’s earliest written account (1832) lacking some of the elements found in his later accounts. However, some of these elements—particularly the appearance of God the Father as part of the First Vision experience—are laced throughout Joseph Smith’s translation of the Bible. These historical threads ultimately culminate in his translation of Psalm 14, which weaves together many of the elements supposedly lacking in Smith’s earliest account of the First Vision. But why bring these threads together in Psalm 14? What was its connection with his First Vision? A basic comparison of Psalm 14 with elements of the First Vision shows that elements of this psalm are found in the background of the vision, as Joseph Smith narrated it, and even in the words of Deity spoken within the vision itself.
It is clear from a consultation of the 1832 text that Joseph Smith's desire to be forgiven of his personal sins was NOT the only motivation for his prayer in the wilderness. He prayed (as he explicitly states) because of "all" of the things he mentions - including the desire to worship God in truth; according to His laws (which Joseph did not believe was the case among any of the Christians denominations that he knew of).
The 1832 textual pattern of (1) desire to prepare for eternity / worship God in truth and (2) desire for forgiveness of personal sins can be detected in subsequent First Vision recitals, demonstrating that there is no change in his declared motive over time. The confusion of the critics on this issue arises when they do not see exact matches in themes across documents or insist that every detail of the story be present in every text that relates it.
1832 (Smith)
1834 (Cowdery/Smith)
1835 (Smith)
1838 (Smith)
1840 (Pratt)
1842 (Smith)
1842 (Hyde)
Critical sources |
|
Critics claim that there is a contradiction between the 1832 account of Joseph Smith's First Vision and the rest of his first-hand accounts. They also claim that the same contradiction occurs internally in the 1838 account. It is alleged that Joseph Smith concluded prior to going to the grove of trees to pray that all the denominations on the earth were false. This supposedly contradicts the 1835 and 1838 accounts in which Joseph expresses doubt as to which Church was true prior to going to the grove.
In his 1832 history, Joseph Smith said:
I found [by searching the scriptures] that mankind did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatized from the true and living faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament
In his 1835 account, Joseph Smith said, "I knew not who [of the denominations] was right or who was wrong."
In his 1838 account of the Vision, Joseph writes:
The 1832 account then, according to some critics, contradicts the 1835 and 1838 account in that Joseph had already determined before seeing God and Jesus that there was no true Church and thus the only motive for going to the grove in the 1832 account would be to obtain a forgiveness of sins and not to find the true Church.
Author J.B. Haws describes the criticism as it relates to the 1838 account specifically:
Here is the essence of that trouble, as some have seen it. In Joseph’s 1838–39 dictated account (the account that would eventually find its way into the LDS Church’s canon as the official Joseph Smith—History), he described his youthful confusion about the competing religious sects that he encountered in these words: "In the midst of this war of words and tumult of opinions, I often said to myself: What is to be done? Who of all these parties are right; or, are they all wrong together?" (Joseph Smith History 1:10). According to this narrative, it seems that fourteen-year-old Joseph had already considered the possibility that all churches could be "wrong together." Yet only eight verses later (by the account’s current scriptural format), Joseph reported what seems like surprise in response to the divine injunction that he must join no church, "for they were all wrong"—and "it had never entered into [his] heart that all were wrong" (JS—H 1:18–19). But didn’t we just read that the "all were wrong" possibility had entered his heart in verse 10? Why such an apparently careless and contradictory oversight in the narrative?[16]
Critics claim that this is a contradiction and evidence that the First Vision story evolved over time.
Such a claim is a false dilemma, as we will now see.
Historian Christopher Jones has observed that Joseph Smith's 1832 account (and indeed much of his other three accounts) are shaped as Methodist conversion narratives. Within Methodism (and indeed the broader religious culture of Joseph Smith's day), finding forgiveness of sins and joining the right Church rode in tandem. You receive forgiveness of sins by joining the right Church. If you don't follow the correct, "biblical" doctrine then you can't receive such forgiveness.[17] In the case of Joseph Smith, he receives forgiveness of sins and is told not to join any church. Thus even if Joseph's main emphasis is forgiveness of sins in the 1832 account, that doesn't mean he's not talking about what Church is true.
Those critics who claim that Joseph is only speaking about the forgiveness of sins in the 1832 account are ignorant of the larger historical context under which the 1832 account was written (documented by Jones) and also fail to take notice of important scriptural passages quoted near the end of the account. Speaking about the condition of the world, Christ, speaking to Joseph, echoes Matthew 15:8-9:
'[T]hat which hath been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Apostles' might easily refer to an apostasy and restoration.
Some may counter that this only refers to corrupt people and not corrupt churches or religions. Going back to the passage from the 1832 account cited above, one reads "the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doth good no not one..." This phrase ('and none doeth good no not one') is echoed in a few scriptural passages (Psalm 53: 3; Romans 3: 10, 12; Moroni 7:17) but for our purposes we will highlight one of these occurrences in JST Psalm 14:2. The Church still describes this passage in its heading as lamenting "the loss of truth in the last days[.]" The passage "looks forward to the establishment of Zion." The italics represent edits made by Joseph Smith to the text:

Joseph Fielding McConkie said, 'The JST rendering of this Psalm reads like another account of the First Vision.'[18]
The late Matthew Brown suggested that Joseph's translation of Psalm 14 took place 'shortly after late July 1832.'[19] He even goes so far to say that 'the JST Psalm 14 text may have served as a prototype of sorts for the composition of the 1832 historical document.'[20]
"The 1838-39 account’s mention of 'corrupt professors' seems to be reflected in the JST’s 'their teachers are workers of iniquity.' . . . JST Psalm 14:2-4 features 'all these who say they are [the Lord’s]' being rejected by the Lord due to them having 'gone aside,' 'become filthy,' and 'none of them…doing good.' And this is laid at the feet of 'their teachers' who 'are workers of iniquity.'"[21] This use of Psalm 14 to be explanatory for Joseph's use of no one doing good is strengthened by the fact that Psalm 14 is quoted specifically earlier in the 1832 account ("And when I considered upon these things my heart exclaimed, 'Well hath the wise man said, It is a fool that saith in his heart there is no God.'")
Thus, to summarize again, those who don't do good are all people and this is caused by false teachers teaching incorrect doctrine. Under this understanding, the 1832 account of Joseph Smith's First Vision is giving implicit credence that Joseph was indeed seeking to know from God which Church to join because the teachers of other denominations had become corrupt.
Author Jim Bennet describes one approach that a person can take while seeking to reconcile this with their faith and that is to focus interpretation on the phrase "entered into my heart":
The key phrase is "entered into my heart."
We can have confidence in what Joseph means by this because it is not the only time he uses variations of this phrase. Here’s what he says about his experience reading James 1:5.
- Never did any passage of scripture come with more power to the heart of man than this did at this time to mine. It seemed to enter with great force into every feeling of my heart. [JSH 1:12, emphasis added]
This is a phrase Joseph uses to describe something more powerful than mere intellectual assent. He’s describing a spiritual experience, where the feelings of the heart complement and contribute to clarity of mind. It’s a concept that shows up in the Doctrine and Covenants, too:
- Yea, behold, I will tell you in your mind and in your heart, by the Holy Ghost, which shall come upon you and which shall dwell in your heart.
- Now, behold, this is the spirit of revelation; behold, this is the spirit by which Moses brought the children of Israel through the Red Sea on dry ground. [D&C 8:2-3, emphasis added]
Joseph had clearly considered the possibility all churches were in error in verse 10 (and in the 1832 account,) but the idea hadn’t really sunk in – i.e. entered into his heart – until after verse 18.
I think all of us have had this experience – things happen that we choose not to believe. Even when we have solid information, we don’t allow our intellectual knowledge to become wisdom and "enter into our hearts." He’s describing the very human process of denial, much like Amulek from the Book of Mormon, who once said of his own testimony, "I knew concerning these things, yet I would not know." (Alma 10:6)
Make up your mind, Amulek! Did you know or didn’t you know?! That’s a direct contradiction!
In the case of "Forgiveness of Sins v. Which Church is True,"... Joseph was preoccupied with what he needed to do to prepare to meet God. You see that in all of Joseph’s firsthand accounts.
"[M]y mind become seriously imprest with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul," he wrote in 1832. "I considered it of the first importance that I should be right, in matters that involve eternal consequ[e]nces;" he wrote in 1835. "My mind was called up to serious reflection and great uneasiness... my feelings were deep and often poignant... What is to be done?" he wrote in 1838. "I began to reflect upon the importance of being prepared for a future [i.e. eternal] state," he wrote in 1842. These are different words, to be sure, but there’s no mistaking the commonality of their underlying meaning. I believe that all these accounts show that Joseph’s deepest desire was to know what he had to do to be saved. That was the one and only item on his agenda in the Sacred Grove.
The question he asked, then, about which church he should join tells us about young Joseph’s theological assumptions. It’s clear in all accounts that salvation and church membership were inextricably linked in his mind. Even in 1832, where he doesn’t specify what question he asked the Lord before his sins were forgiven, he goes on at great length about his concern for the error he sees in all the churches.The possibility that a church might not be necessary doesn’t seem to occur to Joseph, nor would it have been likely to occur to anyone in the early 19th Century. Christ without a church in 1820? Who could imagine such heresy? Certainly not an illiterate farmboy who, at that point, had no inkling what the Lord had in store for him.
In Joseph’s mind, "which church is the right one" and "how can I get my sins forgiven" were variations on the same theme, and only minor variations at that. Rather than show inconsistency, the two accounts are remarkably united in their depiction of Joseph’s concern for his soul and his assumptions about what was necessary to save it.
So with that understanding, the apparent contradiction about whether or not he had decided that all the churches were wrong prior to praying becomes far less problematic. The 1832 account spends more time detailing the specific problems with all the churches than the 1838 account, indicating that Joseph still believed in the importance of joining a church to gain access to the Atonement. True, he doesn’t explicitly say that any church membership is necessary, but he didn’t have to – those reading his account in the 19th Century would have had the same assumptions, and neither Joseph nor his audience would have even considered the modern/post-modern idea of an effectual Christian life outside the boundaries of organized religion. Even if all the churches were wrong to one degree or another, surely Joseph would still have felt it necessary to join the best one... [22]
Speficially addressing the passages from JS History 1: 10 and 18, J.B. Haws wrote:
In a draft of Joseph Smith’s history that was written sometime in 1840–41 by scribe Howard Coray (but only essentially rediscovered in the Church’s archival holdings in 2005), the corresponding passage reads differently:
Joseph Smith—History 1:18–19
- I asked the Personages who stood above me in the light, which of all the sects was right (for at this time it had never entered into my heart that all were wrong)—and which I should join. I was answered that I must join none of them, for they were all wrong . . .
Howard Coray’s 1839–41 history (labeled Draft 3 in Histories, Volume 1 of The Joseph Smith Papers)
- I asked the Personages who stood in the light; Which of the sects were right. (for I supposed that one of them were so.) and which I should join. I was answered "join none of them; they are all are wrong . . ."
Coray’s version suggests that Joseph still "supposed"—still believed, still considered it most likely—that one of the sects was right, even if he had considered the possibility that such was not the case. Thanks to the careful editorial scrutiny of The Joseph Smith Papers scholars, it is apparent that Coray’s draft was written after the draft of Joseph Smith’s history (labeled Draft 2 in the handwriting of James Mulholland) that was eventually published in the Times and Seasons and then the Pearl of Great Price. The Joseph Smith Papers volume editors note that, "for whatever reason," Joseph Smith chose that Draft 2 (Mulholland) version for eventual publication, even though there is evidence to suggest that Coray transcribed as Joseph "read aloud from Draft 2 in the large manuscript volume, directing editorial changes as he read." With that background in mind, the parallel phrases above suggest an affinity of sentiment, such that the phrase "it had never entered into my heart" meant, essentially, "I [still] supposed one of them were [right]"—which reinforces the reading that Joseph held out hope in his heart that he would be pointed to the true denomination.[16]:99–100
Haws describes another way to view both the 1832 account and 1838 account:
One minor drawback in reading Joseph Smith’s history in its current scriptural format is that the verse divisions might inadvertently separate his thoughts too starkly. Because of that potential challenge, the second possibility proposed here is that the contradiction between verses 10 and 18 might simply be a question of antecedents in verse 10. Thus one final alternate reading (and reconciliation) of those verses becomes clearer in the paragraph format of the Draft 2 (Mulholland) manuscript version of Joseph Smith’s history. In what is now verse 9 in the Pearl of Great Price version, Joseph describes the furious activity of three named denominations: the Presbyterians, the Baptists, and the Methodists. Those were the major players in the religious competition that was all around him in that region of New York. And those three groups preached, importantly, distinct soteriological visions of Christianity. If, however, verse 10 is not seen as completely separate from verse 9, then we might understand Joseph’s questions as being much more specific.
Here is how the passage appears in Draft 2 (Mulholland) of Joseph Smith’s history:
- My mind at different times was greatly excited for the cry and tumult were so great and incessant. The Presbyterians were most decided against the Baptists and Methodists, and used all their powers of either reason or sophistry to prove their errors, or at least to make the people think they were in error. On the other hand the Baptists and Methodists in their turn were equally Zealous in endeavoring to establish their own tenets and disprove all others.
- In the midst of this war of words, and tumult of opinions, I often said to myself, what is to be done? Who of all these parties are right? Or are they all wrong together? and if any one of them be right which is it? And how shall I know it?
Read in that way, new attention to the determiners and pronouns might be in order. Which of all of these parties—that is, the Presbyterians, Baptists, or Methodists—is right? Or are they—Presbyterians, Baptists, Methodists— all wrong together? If any of them—Presbyterians, Baptists, Methodists—be right, which is it? It seems reasonable to conclude that Joseph wondered not about the possibility that there was no true religion on the earth, but only that the principal religions represented in his area might all be wrong. Hence, his crucial question—his "object in going to enquire of the Lord"— was "to know which of all the sects was right," and perhaps it was the subsequent instruction to join no sect anywhere ("for they were all wrong") that would have been surprising; in that case, this latter possibility was the one that had never entered into his heart.
Again, this is only suggested as one way to read the text—but it is one that also seems to fit with a telling line in the earliest known written account of the First Vision, one from 1832 that Joseph Smith partly dictated and partly wrote. The key is something he stated about personal familiarity:
In that 1832 history, Joseph wrote in his own hand:
- At about the age of twelve years my mind become seriously [impressed] with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul which led me to searching the scriptures believeing as I was taught, that they contained the word of God thus applying myself to them and my intimate acquaintance with those of differant denominations led me to marvel exceedingly for I discovered that <they did not adorn> instead of adorning their profession by a holy walk and Godly conversation agreeable to what I found contained in that sacred depository this was a grief to my Soul . . .
The fact that his conclusions were based on an "intimate acquaintance with those of differant denominations" should not be overlooked. His subsequent recollections do seem to reflect an expanded understanding of a broader apostasy: "by searching the scriptures I found that mand <mankind> did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatised from the true and liveing faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the new testament." Yet his choice of words ("no society or denomination") and his declaration that "I cried unto the Lord for mercy for there was none else to whom I could go and to obtain mercy" seem to reflect his discouragement with his local options and his growing assurance that only divine intervention could help him transcend that confusion.
It may, then, have been the sheer universality of the apostasy ("join none of them") that had not entered into his heart. It may have been Joseph Smith’s original hope and assumption, as expressed in the Howard Coray draft, that "one of them were" right, even if he had considered the theoretical possibility that the three denominations with which he had "intimate acquaintance" were all "wrong together" and that he would have to seek a religious home among another, less familiar one of "all the sects."[16]:101–102
If you had come to the conclusion that mankind has apostatized from the true faith, and you suddenly found Jesus standing in front of you, wouldn't you ask Him if any of those churches was the correct one? Or would you simply tell Him, "never mind, I already figured it out for myself"?
Could it be that Joseph simply misremembered? Why must one automatically have to be assumed that he was simply embellishing the story?
There are several interpretive possibilities for the supposed discrepancies between the accounts. Is it possible that Joseph Smith contradicted himself? Certainly. But it only remains just that: a possibility—one interpretive option among others. If we presume that Joseph was lying, our hostile reading will lead us to pick this option. If we grant that Joseph might be telling the truth, the other options will not be summarily rejected.
The answer to this apparent contradiction lies in a detailed examination of relevant texts. It is important to first compare Joseph Smith’s November 1832 text (which is in his own handwriting) with a newspaper article printed earlier that same year which refers to the Prophet’s inaugural religious experiences.
When both of these texts are taken into consideration the following storyline suggests itself: Joseph Smith had come to the conclusion, through personal scripture study, that none of the denominations WITH WHICH HE HAD AN INTIMATE ACQUAINTANCE was built upon the New Testament gospel. He prayed for guidance because he was "in doubt what his duty was." This doubt is obliquely referred to again in Oliver Cowdery’s February 1835 Messenger and Advocate partial First Vision recital where he said that because of the religious excitement the Prophet had "determination to know for himself of the certainty and reality of pure and holy religion."[24]
Doubt is present again in the Prophet’s November 1835 diary entry: "I knew not who was right or who was wrong and I considered it of the first importance that I should be right, in matters that involve eternal consequences."[25] So the conclusion this fourteen-year-old boy had reached through personal scripture study did not altogether solve his dilemma. In fact, in the May 1838 account he clarifies that because of his youth and inexperience in life he could not make an absolute decision with regard to this matter: "it was impossible for a person young as I was and so unacquainted with men and things to come to any certain conclusion who was right, and who was wrong"; "I often said to myself, what is to be done? Who of all these parties are right? Or, are they all wrong together? If any one of them be right which is it, and how shall I know it?"; "if any person needed wisdom from God I did, for how to act I did not know, and unless I could get more wisdom than I then had [I] would never know."
Orson Pratt’s 1840 First Vision account helps to explain why the ‘Joseph-decided-every-existing-church-was-wrong’ theory cannot possibly be valid. Elder Pratt reports, "He then reflected upon the immense number of doctrines now in the world which had given rise to many hundreds of different denominations. The great question to be decided in his mind was—if any one of these denominations be the Church of Christ, which one is it?" This expansive view is reflected in the Prophet’s 1838 account. There he states, "My object in going to enquire of the Lord was to know which of all the sects was right that I might know which to join. No sooner therefore did I get possession of myself, so as to be able to speak, than I asked the personages who stood above me in the light, which of all the sects was right (for at this time it had never entered into my heart that all were wrong) and which I should join."

In the 1832 account, Frederick G. Williams inserted the "in the 16th year of my age" above Joseph's text after Joseph had already written it. (See: "History, circa Summer 1832," The Joseph Smith Papers)

In Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision recital he said that he was "in the 16th year of [his] age" when the manifestation took place but in all other accounts in which he mentions his age, he was in his "fifteenth year."
The only First Vision account that provided a different age was the 1832 account written in Joseph Smith's own handwriting. In 1832, 12 years after the First Vision, Joseph wrote, "we were deprived of the bennifit of an education suffice it to say I was mearly instructid in reading and writing and the ground rules of Arithmatic which constuted my whole literary acquirements."
Although the portion of Joseph's 1832 history is in his own handwriting, the text insertion of "in the 16th year of my age" was in the handwriting of Frederick G. Williams, Joseph's scribe. It is likely that Joseph's dating schemes were slightly off when he dictated his age to Williams, many years afte the fact. There is nothing nefarious in Joseph Smith correcting his own slight mathematical miscalculations.
Two years later, Oliver Cowdery had Joseph's 1832 history in his possession when he began publishing history of the Church in late 1834 in the Latter-day Saints' Messenger and Advocate. Oliver clearly established Joseph's age as 14 ("the 15th year of his life") during the period of religious excitement (although Oliver ultimately never described the actual First Vision at this time). Once the date of the First Vision was correctly established it remained steady throughout all subsequent recitals as the "15th year" or "age 14."

The ages are not, as one critic states, "all over the place." [26] The only account produced by Joseph Smith that indicated a different age was the 1832 account (age 15 rather than 14, based upon a text insertion above the line by Frederick G. Williams after Joseph had already written his account). All remaining accounts indicate age 14 (the "15th" year).
In the 1832 account, Frederick G. Williams inserted the "in the 16th year of my age" above Joseph's text after Joseph had already written it. (See: "History, circa Summer 1832," The Joseph Smith Papers)

The 'one-year-off-the mark' dating anomaly of the 1832 First Vision account can best be understood by taking a look at all of the dates and time frame indicators that are provided within the document. It can then be seen that the farther back in time Joseph Smith goes, the more inexact his dating scheme becomes.
Notice that the date of the First Vision is an above-the-line insertion in the handwriting of Frederick G. Williams, meaning that it was not placed in the text initially but was added at a later time than the creation of the main text.
(17 years back in time)
(15 years back in time)
(12 years back in time)
(7 years back in time)
(5 years back in time)
We should carefully note that Joseph Smith correctly stated that he was "seventeen years of age" when the angel Moroni appeared to him on 22 September 1823, he got the time of that manifestation wrong by one year. A clue as to why this incorrect date was placed by the Prophet in this historical account can be found right in the 1832 document itself. Near the beginning of the narrative Joseph writes: "being in indigent circumstances [we] were obliged to labor hard for the support of a large family having nine children. And as it required the exertions of all that were able to render any assistance for the support of the family therefore we were deprived of the benefit of an education. Suffice it to say [that] I was merely instructed in reading and writing and the ground <rules> of arithmetic which constituted my whole literary acquirements". Elder Orson Pratt once asked rhetorical questions of the Prophet to illustrate his meager level of formal education: "Had you been to college? No. Had you studied in any seminary of learning? No. Did you know how to read? Yes. How to write? Yes. Did you understand much about arithmetic? No. About grammar? No. Did you understand all the branches of education which are generally taught in our common schools? No." (Journal of Discourses, 7:220-21). And when Elder Pratt wrote specifically about the First Vision he was even more specific about the level of the Prophet's math skills, saying that he had "a very limited understanding of the elementary rules of arithmetic." (Orson Pratt, An Interesting Account of Several Remarkable Visions [Edinburgh, Scotland: Ballantyne and Hughes, 1840],—-).
The 1832 history is not the only one where the Prophet made a dating mistake that was one year off the mark. He did the same thing when he created the 1838 Church history, but this time he got the year of his own brother's death wrong. He erroneously remembered that it was 1824 instead of 1823. The significant thing about this particular dating blunder is that four years after the Prophet recorded the initial information he came to the realization that it was not correct and had his scribe, Willard Richards, make the appropriate adjustment. Perhaps the problem with the date was brought to the Prophet's attention by a member of his own family after the information had been printed and made available for public perusal [publication in May 1842; correction in December 1842].
Initial Manuscript Record (2 May 1838)
Publication ( 15 March 1842 / 2 May 1842)
Post-Publication Manuscript Correction (2 December 1842)
A similar type of dating correction scenario, as mentioned above, may have taken place in connection with the 1832 history. Oliver Cowdery claimed that he had the Prophet's help in creating his December 1834 Church history article and despite the fact that he had the erroneously-dated 1832 document sitting in front of him [see paper on this subject] he provided the correct year for the Prophet's First Vision - "in the 15th year of his life" (i.e., between 23 December 1819 and 23 December 1820). And just nine months later the Prophet himself was telling a non-Mormon that the First Vision took place when he was "about 14 years old" (Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835).

An image from "mormoninfographics" is in circulation on the internet which mistakenly states that Joseph claimed that he was age 17 when the First Vision occurred. However, this was a misreading of Joseph Smith's 1835 journal entry, which clearly states that Joseph was age 14 at the time of the first vision, and age 17 at the time of Moroni's visit.

Is this evidence that this visionary tale evolved over time by becoming more dramatic and elaborate?
The 'struggle' motif is absent from the first known self-written account of the Prophet's visionary experience (1832) but it is also absent from his self-written Wentworth Letter account (1842). It is clear from the available documentary evidence that the Prophet did not feel constrained by the arbitrary rule of his modern critics that he must include every aspect of his First Vision story in every single retelling of it, and no reasonable person should be bothered that he doesn't.
The following timeline displays the 'struggle' material found in First Vision recitals that were produced during the Prophet's lifetime. The corresponding text from the 1832 document is also provided for purposes of comparison.
Several observations about the information presented below may prove useful.
September–November 1832
I cried unto the Lord for mercy. . . and while in the attitude of calling upon the Lord . . . a pillar of fire [or] light above the brightness of the sun at noonday came down from above and rested upon me and I was filled with the Spirit of God.
9 November 1835
I called on the Lord for the first time in the place above stated, or in other words, I made a fruitless attempt to pray. My tongue seemed to be swollen in my mouth, so that I could not utter. I heard a noise behind me like some one walking towards me. I strove again to pray, but could not. The noise of walking seemed to draw nearer. I sprang upon my feet and looked round, but saw no person or thing that was calculated to produce the noise of walking. I kneeled again, my mouth was opened and my tongue loosed. I called on the Lord in mighty prayer. A pillar of fire appeared above my head, which presently rested down upon me and filled me with unspeakable joy.
2 May 1838
I kneeled down and began to offer up the desires of my heart to God, I had scarcely done so, when immediately I was seized upon by some power which entirely overcame me and had such astonishing influence over me as to bind my tongue so that I could not speak. Thick darkness gathered around me and it seemed to me for a time as if I were doomed to sudden destruction. But exerting all my powers to call upon God to deliver me out of the power of this enemy which had seized upon me, and at the very moment when I was ready to sink into despair and abandon myself to destruction, not to an imaginary ruin but to the power of some actual being from the unseen world who had such a marvelous power as I had never before felt in any being, just at this moment of great alarm I saw a pillar of light exactly over my head above the brightness of the sun, which descended gradually until it fell upon me. It no sooner appeared than I found myself delivered from the enemy which held me bound.
September 1840
He therefore, retired to a secret place in a grove, but a short distance from his father's house, and knelt down, and began to call upon the Lord. At first, he was severely tempted by the powers of darkness, which endeavored to overcome him; but he continued to seek for deliverance, until darkness gave way from his mind, and he was enabled to pray in feverency of the spirit, and in faith. And while thus pouring out his soul, anxiously desiring an answer from God, he at length, saw a very bright and glorious light in the heavens above; which, at first, seemed to be a considerable distance. He continued praying, while the light appeared to be gradually descending towards him.
June 1841
He, therefore, retired to a secret place, in a grove, but a short distance from his father's house, and knelt down and began to call upon the Lord. At first, he was severely tempted by the powers of darkness, which endeavored to overcome him. The adversary benighted his mind with doubts, and brought to his soul all kinds of improper pictures and tried to hinder him in his efforts and the accomplishment of his goal. However, the overflowing mercy of God came to buoy him up, and gave new impulse and momentum to his dwindling strength. Soon the dark clouds disappeared, and light and peace filled his troubled heart. And again he called upon the Lord with renewed faith and spiritual strength. At this sacred moment his mind was caught away from the natural objects with which he was surrounded, and he was enwrapped in a heavenly vision.
1 March 1842
I retired to a secret place in a grove and began to call upon the Lord, while fervently engaged in supplication my mind was taken away from the objects with which I was surrounded, and I was enwrapped in a heavenly vision.
11 June 1843
he went into the grove & enquired of the Lord which of all the sects were right.
29 August 1843
I kneeled down, and prayed, saying, O Lord, what Church shall I join? Directly I saw a light.
24 May 1844
Went into the Wood to pray, kneels himself down, his tongue was close[d,] cleave[t]h to his roof—could utter not a word, felt easier after awhile—saw a fire toward heaven came near and nearer. . . . the fire drew nigher, rested upon the tree, enveloped him[, and] comforted [him].
Critical sources |
|
The theophany portion of the 1832 account does not specifically indicate that the Father appeared to Joseph Smith together with Jesus Christ. The relevant text (in its original form) reads as follows:
a piller of fire light above the brightness of the sun at noon day c[a]me down from above and rested upon me and I was filled with the spirit of god and the <Lord> opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord and he spake unto me saying Joseph <my son> thy sins are forgiven thee. go thy <way> walk in my statutes and keep my commandments behold I am the Lord of glory I was crucifyed for the world that all those who believe on my name may have Eternal life <behold> the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doeth good no not one they have turned asside from the gospel and keep not <my> commandments they draw near to me with their lips while their hearts are far from me and mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them acording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father.[29]
Even though the Savior makes a direct reference to the Father there is no indication in this portion of the 1832 document that God appeared to Joseph Smith alongside His Son.
This type of pattern is seen in the Book of Mormon, translated in 1829: The Book of Mormon begins (1 Nephi 1꞉8-10) with Lehi's vision of God on His throne. One [Christ] followed by twelve others descends from God to speak with Lehi—thus, Jesus and the Father are here both separate, and the role of Christ in giving instructions to the prophet while the Father looks on and approves is followed, just as it was in Joseph's First Vision. Here too, Lehi is described as praying to "the Lord," and yet has a vision of both God the Father and Christ.

There is a very significant phrase located in the introductory paragraph of the Prophet's historical narrative. There he indicates that the 1832 document is . . .
A History of the life of Joseph Smith Jr. an account of his marvilous experience and of all the mighty acts which he doeth in the name of Jesus Ch[r]ist the son of the living God of whom he beareth record and also an account of the rise of the church of Christ in the eve of time according as the Lord brough<t> [it] forth and established [it] by his hand <firstly> he receiving the testamony from on high secondly the ministering of Angels thirdly the reception of the holy Priesthood by the ministring of Aangels to adminster the letter of the Gospel—<—the Law and commandments as they were given unto him—>and the ordinencs, forthly a confirmation and reception of the high Priesthood after the holy order of the son of the living God.
This paragraph not only introduces the document with a heavy emphasis on the Son of God but it also chronologically outlines four inaugural events of the Restoration.
The significant phrase in the introductory paragraph is the one associated with the First Vision—"receiving the testimony from on high" (spelling standardized). When this phrase is placed in conjunction with the Prophet's 1835 and 1838 accounts of the First Vision it becomes obvious that the 1832 phraseology closely corresponds with the words spoken by God the Father when He introduced His Son in the Sacred Grove.
The Father's identification of Jesus Christ as His Son was His "testimony" of Him.
Critics have objected that—in their minds—the phrase "from on high" cannot be so easily equated with God the Father. But there is a sizable amount of corroborating evidence for this idea. Consider the following points of connection.
The Father's voice . . . came out of heaven [i.e., 'from on high'] and testified of His Beloved Son.
Joseph Smith stated, "the Lord God has spoken it; and we . . . have heard . . . the words of the glorious Majesty on high."
There are five New Testament scriptures (which Joseph Smith would have been familiar with from his work on the JST) that have distinct parallels to the First Vision story. Jesus Christ's Old World disciples heard the Father's voice come "from heaven" (Mt. 3:17; Mk. 1:11; Lk. 3:22; 2 Pt. 1:17-18) [i.e, 'from on high'] or "out of the cloud" (Mt. 17:5) [i.e., 'from on high'] and in each of these instances the Father testified of His Son and employed the same phraseology that Joseph Smith said He utilized during the First Vision
This chronological evidence points to the conclusion that Joseph Smith appears to have equated the voice "from on high" with God the Father both before and after he penned his 1832 First Vision account.
There is another line from the 1832 account that may be referring to two people:
I was filled with the spirit of God, and the Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord
It has been argued that the seperation of "Lord" into two may be referring to the Lord God [i.e., the Father] and the Lord Jesus Christ. Three pieces of evidence can be used to argue for this interpretation.
Some critics have taken issue with this evidence for the interpretation—claiming that since Psalm 110:1 was originally written in Hebrew with two different words for Lord (rendering "Lord" and "LORD" in all caps for the second mention) that the argument fails.[31]
Robert S. Boylan has responded by showing how Psalm 110:1 is the most quoted, echoed, and/or alluded to passage in the New Testament which Joseph would have been working on revising in his Inspired Translation of the Bible. He then shows that the revelations in Doctrine and Covenants leading up chronologically to the publication of the history containing the 1832 account of Joseph’s vision deliberately echo that verse (Doctrine and Covenants 20:24; 49:5-6; 76: 20, 23). If Joseph were familiar with that verse close to the publication of the account by way of the Old and/or New Testament and as echoed in his revelations published in the Doctrine and Covenants, it seems reasonable to assume that he could have used that verse as a template for rendering his account of events surrounding the First Vision.[32] This is even if one mention is capitalized and the other not. If the structure is deliberate and clear (and it appears so), then it seems odd to be upset that Joseph doesn't use capitals for the second "Lord" he writes about.
The 1832 account may be read to have a successive appearance of personages, one after the other. This is strengthened by the 1835 accounts mention of successive appearance. Further evidence of this in the 1832 account may be that Joseph was "filled with the spirit of God" before he mentions "the Lord".
Some have argued that the 8 uses of Lord in the 1832 account all refer to Jesus Christ.[33] There are at least three references that may be read otherwise:
A History of the life of Joseph Smith Jr. an account of his marvilous [sic] experience and of all the mighty acts which he doeth in the name of Jesus Christ the son of the living God of whom he beareth record and also an account of the rise of the Church of Christ in the eve of time according as the Lord brought forth and established by his hand.
A separation of "Christ" and "the Lord." This is able to be read with Christ or the Father as the Lord.
My mind became exceedingly distressed, for I became convicted of my sins, and by searching the scriptures I found that mankind did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatized from the true and living faith, and there was no society or denomination that was built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament.
Joseph may be referring to coming to the Lord (i.e., the Father) and the gospel of Christ.
The third plausible evidence of the Father as Lord is the ending of the account:
My soul was filled with love, and for many days I could rejoice with great joy. The Lord was with me, but I could find none that would believe the heavenly vision. Nevertheless, I pondered these things in my heart.
The reference here is vague enough that it cannot be conclusively read one way or the othe—especially with the just-cited mention of the Lord.
Since it can be concluded from the above documentary evidence that Joseph Smith did indeed make an oblique reference to the appearance of the Father in his 1832 history the question becomes—Why did the Prophet construct the 1832 narrative in the manner that he did (so as to exclude explicit mention of the Father's appearance)? A careful analysis of the 1832 First Vision text reveals that it was deliberately constructed on the framework of many scriptural citations. The apostle Stephen's view of both the Father and the Son is clearly utilized by the Prophet in one section of the 1832 text but, more importantly, Joseph Smith told the actual theophany portion of this narrative in language that very closely corresponds to the apostle Paul's vision of Jesus Christ (Acts 26).[34] .
On this reading, the Father is not explicitly mentioned as making an appearance in the theophany portion of the 1832 First Vision account because Joseph Smith patterned that part of his narrative after the vision of Jesus Christ experienced by the apostle Paul.
Paul did not report that he saw the Father alongside the Son, and so it is logical that this is the reason why Joseph Smith did not explicitly mention the Father's appearance in his text either. The Prophet's strong sense of connection with Paul's visionary experience is referred to by him right in his 1838 First Vision account. The context of this connection is the persecution experienced by both men for speaking publicly about a heavenly manifestation. Joseph Smith relates in his 1838 history that he was informed by a clergyman that his vision was "all of the devil." This piece of information may help to explain why the Prophet chose to couch his first known written account of his vision in heavy biblical language and imagery. He may have hoped that by doing this his story would have a better chance of being accepted amongst a populace that was steeped in biblical content.
The Gospel Topics Essay touching on the first vision touches on another way of looking at the evidence. It focuses on the awkward repetition of the word "Lord" and how this may have been Joseph's perhaps uneducated way of stating the order of appearance of the personages:
Embellishment. The second argument frequently made regarding the accounts of Joseph Smith’s First Vision is that he embellished his story over time. This argument focuses on two details: the number and identity of the heavenly beings Joseph Smith stated that he saw. Joseph’s First Vision accounts describe the heavenly beings with greater detail over time. The 1832 account says, “The Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord.” His 1838 account states, “I saw two Personages,” one of whom introduced the other as “My Beloved Son.” As a result, critics have argued that Joseph Smith started out reporting to have seen one being—“the Lord”—and ended up claiming to have seen both the Father and the Son.
There are other, more consistent ways of seeing the evidence. A basic harmony in the narrative across time must be acknowledged at the outset: three of the four accounts clearly state that two personages appeared to Joseph Smith in the First Vision. The outlier is Joseph Smith’s 1832 account, which can be read to refer to one or two personages. If read to refer to one heavenly being, it would likely be to the personage who forgave his sins. According to later accounts, the first divine personage told Joseph Smith to “hear” the second, Jesus Christ, who then delivered the main message, which included the message of forgiveness.10 Joseph Smith’s 1832 account, then, may have concentrated on Jesus Christ, the bearer of forgiveness.
Another way of reading the 1832 account is that Joseph Smith referred to two beings, both of whom he called “Lord.” The embellishment argument hinges on the assumption that the 1832 account describes the appearance of only one divine being. But the 1832 account does not say that only one being appeared. Note that the two references to “Lord” are separated in time: first “the Lord” opens the heavens; then Joseph Smith sees “the Lord.” This reading of the account is consistent with Joseph’s 1835 account, which has one personage appearing first, followed by another soon afterwards. The 1832 account, then, can reasonably be read to mean that Joseph Smith saw one being who then revealed another and that he referred to both of them as “the Lord”: “the Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord.”
Joseph’s increasingly specific descriptions can thus be compellingly read as evidence of increasing insight, accumulating over time, based on experience. In part, the differences between the 1832 account and the later accounts may have something to do with the differences between the written and the spoken word. The 1832 account represents the first time Joseph Smith attempted to write down his history. That same year, he wrote a friend that he felt imprisoned by “paper pen and Ink and a crooked broken scattered and imperfect Language.” He called the written word a “little narrow prison.” The expansiveness of the later accounts is more easily understood and even expected when we recognize that they were likely dictated accounts—an, easy, comfortable medium for Joseph Smith and one that allowed the words to flow more easily.[35]
Read the full article here.
It is worthwhile to note that the scribe for the material which directly precedes and follows after the 1832 First Vision narrative—Frederick G. Williams—never mentioned anything about Joseph Smith's story evolving over time and becoming more elaborate with the so-called 'addition' of the Father.
Williams was a resident of Quincy, Illinois when the First Vision account which explicitly refers to the Father was published in Nauvoo, Illinois on 1 April 1842. It is known that Williams was with the Prophet in Nauvoo shortly before his death on 10 October 1842 but during the intervening six months there is no known objection from Frederick to the content of the printed text. Why not? Williams was the person who wrote down the words in the introductory remarks of the 1832 document that talk of Joseph Smith receiving "the testimony from on high" during the First Vision. And it is known that Frederick was accompanying four LDS missionaries who, in November 1830, were teaching the citizens of Painesville, Ohio that Joseph Smith had seen "God" personally (see the 1830 statement about seeing "God").
Williams was a member of the First Presidency of the Church on 9 November 1835 when Joseph Smith was teaching a non-Mormon that there were two personages who appeared during the First Vision (see Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835). Frederick probably never drew attention to a so-called 'discrepancy' between what Joseph Smith taught in 1832, 1835, 1838, and 1842 because he knew that there wasn't one; he knew that the words of the Father spoken during the vision were referred to right in the text that he had written down in 1832.
Oliver Cowdery is another person who was in a position to know if the Prophet's First Vision story had changed over time by the addition of the Father. But he never mentioned any such 'discrepancy'. Cowdery had possession of the 1832 First Vision account when he wrote and published a series of Church history letters in December 1834 and February 1835 and so he was fully aware of the explicit mention of Christ's appearance and he also would have known of the introductory remark which refers to "the testimony from on high" being delivered during this event. Cowdery became the Associate or Assistant President of the entire Church on 5 December 1834 (Encyclopedia of Mormonism, 1653), and thus he would have been in the highest office of Church authority when the Prophet was teaching about one year later that two personages appeared during the First Vision (Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835).
Both Fredrick G. Williams and Oliver Cowdery had reason to feel animosity toward Joseph Smith and the Church since they were both excommunicated in the late 1830's. But neither of these men - even after their reinstatements into full fellowship - ever pointed to any 'creative editing' of the Prophet's First Vision story to sound more impressive and dramatic.
Critical sources |
|
Some have seen a discrepancy between the location of Deity in the Prophet's 1832 and 1838 First Vision accounts. The 1838 version says that the Prophet saw two Personages standing in the air above the earth, within his proximity. But the 1832 version is not so clear—it seems to locate Deity in heaven.
Details about Joseph Smith's First Vision experience are best interpreted by taking all of the extant accounts into consideration. A myopic focus on a limited number of historical documents can only lead to misunderstanding of the past and a twisted sense of the message that the author is trying to convey.
This so-called 'discrepancy' can be accounted for by the fact that Joseph Smith built his 1832 First Vision account using the framework of 47 biblical scriptures. And at this point in his manuscript he utilized Acts 7꞉55-56 to tell his story. It reads:
But [Stephen], being full of the Holy Ghost, looked up steadfastly into heaven, and saw the glory of God, and Jesus standing on the right hand of God.
And said, Behold, I see the heavens opened, and the Son of man standing on the right hand of God.
The Greek text that underlies the KJV translation says that Stephen looked into "heaven" (ouranos - 'the sky'; by extension: 'heaven'; also translated as 'air') and saw the "heavens" (the same Greek word - ouranos) opened. Thus, Stephen did not necessarily see Deity in their celestial abode - far beyond the confines of the earth - but rather standing above him in the air.
When Joseph Smith says in the 1832 First Vision account that he saw the Lord after the "heavens" (he uses the plural form) were opened he seems to be expressing the same idea that is found in the New Testament text.
Notice that the physical proximity of the Personages is established in the Prophet's 1835 recital: the pillar of fire can be physically seen in the air; the pillar of fire physically descends and rests upon Joseph; the pillar of fire has contact with physical objects that surround Joseph; two Personages are seen in the midst of this pillar of fire. Notice also that in the 1844 account the Prophet indicates that he could see with his natural eyesight the pillar "toward heaven", or up in the air. A glance at the 1840 account also shows that the phrase "in the heavens above" simply means "a considerable distance" up in the sky - it is not a reference to the celestial abode of Deity.
Critical sources |
|
The 1832 account of the First Vision does not portray the Lord as announcing that all the creeds were corrupt. These details do not show up until the 1838 account. Is this evidence that the Prophet's story evolved over time?
The claim that Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision story does not contain a divine injunction against joining any churches does not take evidence within the document itself into proper consideration. The information is implicit instead of explicit, but it is there nevertheless. This point cannot be legitimately used as evidence of an evolving storyline.
A quick look at the 1832 First Vision text reveals how untenable this claim is. Joseph Smith states that before he went into the woods to pray he had concluded in his own mind that "those of different denominations [which he was personally acquainted with]. . . did not adorn their profession by a holy walk and godly conversation agreeable to what [he] found contained in [the Bible] . . . . [There were] contentions and divisions [among them] . . . . [T]hey had apostatised from the true and living faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament."
Then, when Jesus Christ Himself made a personal appearance to Joseph in the grove, He informed the young boy that -
"the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good no not one they have turned aside from the gospel and keep not <my> commandments they draw near to me with their lips while their hearts are far from me and mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them acording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father"
To summarize:
How can critics possibly see this as anything other than a forceful and unambiguous indication on the Lord's part that joining any of the Christian denominations would be an unacceptable path for Joseph to take? Notice in the remainder of the 1832 text that Joseph says he felt great joy and love because of his experience and pondered the things which he had seen and heard during the vision . . . but during an interval of several years he did NOT join any church. Why?
As the 1832 text so plainly says—Joseph Smith believed that Christians had turned aside from the gospel; Jesus Christ confirmed that Christians had turned aside from the gospel; Joseph was therefore provided with a set of golden plates that contained writings which were "engrave[d] by . . . the servants of the living God." The 1832 account speaks three times of the "work" that God wanted Joseph Smith to do, while the 1838 account explicitly connects this "work" with the bringing forth of "the everlasting gospel." The 1842 First Vision account ties all of these themes together. There the Prophet relates: "I was expressly commanded to 'go not after them,' at the same time receiving a promise that the fulness of the gospel should at some future time be made known unto me."
Another indication from the 1832 document that Joseph Smith knew from the First Vision event that he should not join any of the churches can be found in something the Savior said to him. Jesus Christ explained that He was going to take action against the situation the world was currently in by "bring[ing] to pass that which hath been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles." What did this statement mean? In a canonized text written at approximately the same time as the 1832 First Vision account (September 1832) the following phraseology is found:
In other words, the Lord was telling Joseph Smith during the First Vision about the coming Restoration and so there would not be any need for him to join an existing church. This viewpoint is bolstered by several instances where the Prophet utilized the same phraseology used by the Lord during the First Vision to speak about the Restoration.
Critical sources |
|
Three of the primary sources that charge Joseph Smith with joining sectarian churches between 1820 and 1830 were produced in the latter part of the nineteenth century, over a half-century after the First Vision. None of the three are contemporary records; the earliest one was written 50 years after the First Vision took place.
We must note too that none of these sources confirms the others—they all discuss different denominations and different time frames. Thus, the stories are not mutually reinforcing.
Eyewitness reminiscences and contemporary records provide strong evidence that these claims are not valid and, therefore, do not reflect historical reality. The three sources are all late, and all from hostile voices.
Fayette Lapham claimed to have interviewed Joseph Smith Sr. in 1829-30, and published a report forty years later. In it, he reported:
About this time [1822, perhaps as late as 1824] he [Joseph, Jr.] became concerned as to his future state of existence, and was baptized, becoming thus a member of the Baptist Church.[42]
The Lapham source is secondhand at best—putting forward information that reportedly came from the Prophet's father. There are no records beyond this late, second-hand recollection to support this claim.
Joseph and Hiel Lewis were cousins of Emma Hale Smith; they would have been aged 21 and 11 respectively in 1828:
...while he, Smith, was in Harmony, Pa., translating his book....that he joined the M[ethodist] [Episocpal] church. He presented himself in a very serious and humble manner, and the minister, not suspecting evil, put his name on the class book, the absence of some of the official members, among whom was the undersigned, Joseph Lewis, who, when he learned what was done, took with him Joshua McKune, and had a talk with Smith. They told him plainly that such a character as he was a disgrace to the church, that he could not be a member of the church unless he broke off his sins by repentance, made public confession, renounced his fraudulent and hypocritical practices, and gave some evidence that he intended to reform and conduct himself somewhat nearer like a christian than he had done. They gave him his choice, to go before the class, and publicly ask to have his name stricken from the class book, or stand a disciplinary investigation. He chose the former, and immediately withdrew his name. So his name as a member of the class was on the book only three days.—It was the general opinion that his only object in joining the church was to bolster up his reputation and gain the sympathy and help of christians; that is, putting on the cloak of religion to serve the devil in.[43]
Note that Joseph did not inscribe himself, but the Methodist minister added Joseph's name to the class book. It is not surprising that Joseph might have attended Methodist services: Emma's family was involved in Methodism, she was related to Methodist ministers, and Joseph at this period was living on the Hale family's farm. The Hales had serious reservations about their new son-in-law, who claimed by this point to have the Book of Mormon plates in his possession. It would be natural for him to attend worship services with them if only to reassure them that he was not hostile to religion.
It is telling, though, that as soon as Joseph Lewis learned that Joseph had attended, he quickly took steps to disassociate the church from a person he saw as an imposter: note too that Lewis describes himself (rather than Joseph) as one "of the official members." A study of Methodist procedure makes it extremely unlikely that Joseph could have been a member of the Church, especially for only three days.
The Lewis source presents a scenario that was directly contradicted in print by an adult eyewitness who was a Methodist church officer. It is certainly possible that Joseph attended a Methodist meeting with his wife and in-laws: even in the Lewis' telling, however, he was quickly made to understand that he was not wanted, and he persisted in his own beliefs rather than continue with them.
| Main article: | Methodist membership procedures and Joseph Smith |
| See also: | Joseph became "partial to the Methodist sect" in 1820 |
S.F. Anderick (1887):
When Jo[seph Smith] joined the Presbyterian Church, in Palmyra village, it caused much talk and surprise, as he claimed to receive revelations from the Lord.[44]
As Dan Vogel notes, "Because Lucy Smith and three of her older children joined the Presbyterian Church, together with the possibility that Joseph Jr. may have attended some meetings with other family members, some observers may have assumed Joseph Jr. was also a member."[45] (Vogel notes that Lorenzo Saunders claimed in 1884 that he attended Sunday School with Joseph at the Presbyterian Church, and so that attendance (without formal membership) may be the source for this reminiscence.[46]
The Anderick source may simply be recalling an occasion when the young Prophet attended a church service with his Presbyterian mother and siblings.
The eyewitness sources that follow below indicate that up until the time that Joseph Smith announced the existence of the golden plates of the Book of Mormon to his family (23 September 1823) he was not formally attached to any church, but had instead publicly rejected all of them and manifested his desire NOT to join their ranks. Some are contemporaneous, others are later remembrances, but the hostile and friendly voices are clear that he had no denominational affiliation.
Pomeroy Tucker (a non-Mormon critic who knew Joseph Smith in Palmyra, New York) said that Joseph joined the Methodist probationary class in Palmyra but soon "withdrew from the class" without being converted; announcing that "all the churches [were] on a false foundation."[47] This information corresponds with historical details dated by Joseph Smith at around 1820.
Lucy Mack Smith:
Joseph Smith's mother recalled in her autobiography that shortly after her son Alvin died on 19 November 1823 Joseph "utterly refused" to attend church services with the intent to convert, and he made the specific request: "do not ask me to join them. I can take my Bible, and go into the woods, and learn more in two hours, than you can learn at meeting in two years, if you should go all the time."[48]
As can be seen by the continuing chronological sources which follow, Joseph Smith and his associates were teaching from 1825 to 1832 that the Prophet did not belong to any church between the years 1825 and 1827.
Josiah Stowell, Jr. (a non-Mormon):
I will give you a short history of what I know about Joseph Smith, Jr. I have been intimately acquainted with him about 2 years. He then was about 20 years old or thereabout. I also went to school with him one winter. He was a fine, likely young man and at that time did not profess religion.[49]
Peter Bauder:
In 1827 David Marks (a non-Mormon minister) went to Palmyra and Manchester, New York where he "made considerable inquiry respecting . . . [Joseph] Smith" and learned from "several persons in different places" that Joseph was "about 21 years [old]; that previous to his declaration of having found the plates he made no pretensions to religion."[50]
Observer and Telegraph (newspaper):
Four LDS men from New York state taught that at the time the angel appeared to Joseph Smith (22 September 1823) he "made no pretensions to religion of any kind."[52]
Palmyra Reflector (newspaper):
The editor of a Palmyra, New York newspaper claimed that he has been "credibly informed," and was "quite certain," that "the prophet . . . never made any serious pretensions to religion until his late pretended revelation"—meaning the Book of Mormon, which was made known among Palmyra's residents in the Fall of 1827.[53]
Orson Pratt:
Orson Pratt and Lyman Johnson taught on 8 April 1832 that "in 1827 a young man called Joseph Smith of the state of New York, of no denomination [i.e., not belonging to a church], but under conviction, inquired of the Lord . . . [and] an angel [appeared to him] . . . who gave information where the plates were deposited."[54] Pratt clarified in a much later statement that between 1820 and 1823 Joseph Smith "was not a member of any church."[55]
Thus, a great deal of contemporary evidence disproves the late, second hand claims.
Critical sources |
Primary Sources
|
One critical author states, "Joseph [Smith] added new elements to his later narratives that are not hinted at in his earlier ones. His first vision evolved from a forgiveness epiphany [1832 account] to a call from God the Father and Jesus Christ to restore the true order of things [1842 account]."
Taken altogether, the above information reveals that Joseph Smith considered his initial calling to have come directly from Deity in the Sacred Grove in 1820—not at some later time. The wording in the Prophet's 1832 First Vision account can be comfortably interpreted to mean that he understood this extraordinary event represented the beginning of a new gospel dispensation.
In Joseph Smith's 1832 account he plainly states that before the First Vision took place he was of the opinion that "mankind . . . had apostatized from the true and living faith, and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament." When the Prophet saw Jesus Christ face to face during the First Vision experience the Savior verified what Joseph had previously believed by saying, "the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good; no, not one. They have turned aside from the gospel and keep not my commandments" (emphasis added).
During the lifetime of Joseph Smith the word DISPENSATION was defined in a popular English dictionary in the following manner: "a system of principles and rites enjoined [or dispensed or bestowed]; as . . . the gospel dispensation; including . . . the scheme of redemption by Christ."[56] As noted above, Jesus Christ informed Joseph Smith that mankind had turned aside from the gospel and no longer kept His commandments. He then issued a directive straight to Joseph Smith by saying, "Walk in my statutes and keep my commandments" (emphasis added). This is clearly a new beginning; the Lord enjoined His ‘system of principles’ or ‘scheme of redemption’ upon Joseph Smith. This act qualifies—by definition—as a new dispensation of the gospel.
Was this early nineteenth-century dispensation of the gospel meant only for the benefit of Joseph Smith? In writing out the 1832 account the Prophet utilized some very specific wording when he said that "the world of mankind . . . . had apostatized" and he mourned for "the sins of the world." In his perspective "no society or denomination . . . built upon the gospel." And when the Lord spoke to Joseph during the vision He emphasized that this situation was on a universal scale saying, "the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good; no, not one." Thus, the 1832 account definitely describes a universal apostasy—and it makes no sense that the Savior would inaugurate a dispensation of His gospel only for the sake of one individual when innumerable humans were in need of salvation.
An entry found in the Encyclopedia of Mormonism agrees with the quotations provided above. It states with regard to the First Vision: "The Lord spoke face-to-face with Joseph and called him to service."[68]
Critical sources |
|
In light of the statements produced by Joseph Smith before he wrote the 1832 quotation of Jesus Christ in the Sacred Grove, it is not possible to uphold the claim that the Lord told the Prophet on that occasion that a Christian of any denomination automatically qualified for eternal life (in the LDS understanding of the term).
While it is true that the Lord is quoted in the 1832 First Vision account as saying "all those who believe on my name may have eternal life" it can be seen in an earlier revelation dated 7 March 1831 that those who "believe on [Christ's] name" must also "come unto [Him]" in order to "have everlasting life" (D&C 45꞉5).
The Lord does not state in the 1832 narrative that eternal life is available to members of every Christian church. Rather, He declares unambiguously in that account that "none" of the existing Christian denominations of the time were keeping His commandments; they had all turned aside from His gospel. From this piece of information alone, it is clear that eternal life could not be made available to them; they were categorized by the Lord as being in a state of "sin" (cf. Romans 5꞉21; Romans 6꞉22-23). In the 1832 text Jesus Christ says to Joseph Smith - "keep my commandments," and in connection with this it can be seen in a revelation dated March 1829 that the Lord informed the Prophet that he could only be granted "eternal life" if he was "firm in keeping the commandments" that Christ gave unto him (D&C 5꞉21-22; cf. D&C 14꞉7; D&C 18꞉8; D&C 30꞉8).
On 1 November 1831 the Lord affirmed to adherents of the LDS faith that there was "only [one] true and living church upon the face of the whole earth" (D&C 1꞉30). Earlier—in May 1831—He had spoken specifically to members of "the church that profess my name" (compare with the 1832 document wording) and indicated that only the faithful members of it who endured would "inherit eternal life" (D&C 50꞉4-5). Thus, the blessing of eternal life could not be obtained without complying with certain conditions.
Before Joseph Smith penned the Lord's words that are found in the 1832 First Vision text he clearly understood that:
The implication of this last point is that only one church can perform ordinances that will be considered valid in the sight of the Lord. And so a person can only be truly obedient to all of the Lord's commandments by holding membership in His one true Church. Joseph Smith indicated in the introductory remarks of the 1832 history that he had received priesthood authority, from a heavenly source, which enabled him to "administer . . . the commandments . . . and the ordinances".
Critical sources |
|
One discrepancy between the 1832 First Vision account and the official 1838 recital is that it portrays Jesus Christ as prophesying that He will return to earth quickly to destroy wicked mortals. The 1838 story makes no mention of the impending doom of this planet's depraved inhabitants.
The claim that there is a discrepancy between the 1832 and 1838 First Vision accounts on the point of the Second Coming and destruction of the wicked appears to be a desperate attempt at sowing discord. It is a charge without much substance. The Prophet's own statement about the omission of certain items can be legitimately utilized to account for several differences in the two documents.
This criticism loses its negative effect when it is weighed in the balance against the content of the relevant historical documents. In the 1832 account the Lord says:
mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them ac[c]ording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father.
There is, indeed, no reference to this specific prophecy in the First Vision portion of the 1838 document. However, Joseph Smith clearly states in that very narrative that Jesus Christ told him "many other things" during the First Vision that he decided not to write down at that time! Thus, an argument from silence (on the part of the critics) is utterly unconvincing. A close look at the remainder of the 1838 historical text reveals that the angel Moroni did, in fact, speak to Joseph Smith about prophecies of the Savior's return and the destruction of the wicked. The Prophet reports:
[The angel] first quoted part of the third chapter of Malachi and he quoted also the fourth or last chapter of the same prophecy though with a little variation from the way it reads in our Bibles. Instead of quoting the first verse as reads in our books he quoted it thus, 'For behold the day cometh that shall burn as an oven, and all the proud <yea> and all that do wickedly shall burn as stubble, for <they> that cometh shall burn them saith the Lord of hosts, that it shall leave them neither root nor branch.' And again he quoted the fifth verse thus, 'Behold I will reveal unto you the Priesthood by the hand of Elijah the prophet before the coming of the great and dreadful day of the Lord.' . . . . He also quoted the second chapter of Joel from the twenty eighth to the last verse. He also said that this was not yet fulfilled but was soon to be.
The 1832 and 1838 histories present the very same prophecy of the destruction of the wicked at the time of the Lord's Second Coming. The 1832 account portrays the Lord speaking it personally; the 1838 account portrays an angel relaying the words of the Lord as recorded in prophetic, biblical texts. Either way, the message is the same.
Critical sources |
|
Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision account does not explicitly say that he was persecuted for relating his spiritual manifestation to others. Some have claimed that this stands as evidence that the Prophet's story evolved over time—probably to add a sense of drama. However, the Prophet's 1832 history of the Restoration talks about persecution in very close proximity to the First Vision recital. The persecution is situated squarely between the First Vision experience and the angel Moroni visitations. The documentary evidence presented above demonstrates conclusively that Joseph Smith did not see anything wrong with telling the basic elements of his First Vision story and either giving a passing reference to other elements or leaving them out altogether. Regardless, it was still a record of the very same experience that took place at the Smith homestead near Palmyra, New York.
Joseph Smith made some remarks in his 1832 First Vision account that have a marked degree of relevance to the argument being put forward by his critics. In relation to the period of time between the First Vision and the appearance of the Book of Mormon angel he said,
Since it is explicitly stated by Joseph Smith that nobody believed his story, it would be unreasonable to assume that all of the responses to it were friendly in nature. In fact, the Prophet says right in this text that before the Book of Mormon angel visited him his family was persecuted and afflicted for some unspecified reason(s). He did not elaborate upon the nature of the "many persecutions" that took place against his family because—as far as this particular document was concerned—he had elected not to write down "many things which transpired."
The following documentary evidence from the 1838 First Vision account strengthens the argument that the 1832 text is referring to some type of persecution that took place because of Joseph's initial spiritual experience.
This 1838 description corresponds very well with the "many persecutions and afflictions" that are mentioned in the 1832 account. It also matches closely with the 1832 statements that nobody would believe Joseph's story and he reflected upon this adverse situation in his heart.
It should be pointed out that even though the 'persecution' theme is very pronounced in the 1838 account it is a piece of the story that was not always mentioned or emphasized in subsequent retelling (both published and verbal).
This last example is especially significant because it is an obvious reference to the Methodist minister who is spoken of in the 1838 History of the Church account. The 1844 rehearsal of events is less detailed but it is, nevertheless, the same exact story. The 1844 document clearly demonstrates that Joseph Smith did not always include an equal amount of story elements in his recitals of the First Vision. Critics of this manifestation should, therefore, not expect any such thing when they scrutinize the pertinent documents. If an element of the story was not known by one particular audience it cannot be automatically assumed that it was not known by another.
Online |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
The capitalized word "Angels" in Joseph Smith's diary entry for 14 November 1835 has given rise to two distinct criticisms by detractors of the faith, and one misguided conclusion by some Latter-day Saints.
The mention of "many angels" in the November 9, 1835 diary entry is a clarifying detail. The appearance of the Father and Son are clearly referenced separately from the mention of the "many angels." Since the visit of the Father and Son are acknowledged in the diary entry for the 9th the change from "first visitation of Angels" to "the First Vision" in the History of the Church entry is not a "falsification" of information.
Joseph Smith never actually referred to what we now call the "First Vision" by that name. Instead, he referred to it as the "first visitation of angels" or the "first communication." Joseph also referred to Moroni's visit as "another vision of angels."

The account that Joseph entered in his journal on 9 November 1835 was a detailed account which clearly describes two personages, as well as "many angels." The account that Joseph wrote just five days later in his journal on 14 November 1835 was a one line summary of the event, which he described as "the first visitation of Angels." Critics of the Church seem to believe that Joseph completely changed his story from "two personages" to "Angels" over the course of only five days. The truth is that Joseph referred to all of the personages that appeared to him as "angels."
This confusion regarding "angels" versus "personages" is illustrated in a critical "Mormoninfographic".[70] We have illustrated the error by comparing Joseph's journal entries on both days.


There were at the time people who went to the wood to pray after reading the Bible, and as a result received visions and epiphanies. The Encyclopedia of Mormonism (1992; 2007) noted that "[i]nitial skepticism toward Joseph Smith's testimony was understandable because others had made similar claims to receiving revelation from God."[71] Similarly, the Church's new narrative history Saints (2018) notes that after Joseph's vision when he spoke to the reverend about his vision that "[a]t first the preacher treated his words lightly. People claimed to have heavenly visions from time to time."[72] Visionaries are not that uncommon in environments where people are routinely open to the divine. Even the famous Charles Finney had one. Finney, after retiring to the woods to pray, described the experience:
Just at this moment I again thought I heard someone approach me, and I opened my eyes to see whether it were so. But right there the revelation of my pride of heart, as the great difficulty that stood in the way, was distinctly shown to me. An overwhelming sense of my wickedness in being ashamed to have a human being see me on my knees before God, took such powerful possession of me, that I cried at the top of my voice, and exclaimed that I would not leave that place if all the men on earth and all the devils in hell surrounded me. "What!" I said, "such a degraded sinner I am, on my knees confessing my sins to the great and holy God; and ashamed to have any human being, and a sinner like myself, find me on my knees endeavoring to make my peace with my offended God!" The sin appeared awful, infinite. It broke me down before the Lord.
Just at that point this passage of Scripture seemed to drop into my mind with a flood of light: "Then shall ye go and pray unto me, and I will hearken unto you. Then shall ye seek me and find me, when ye shall search for me with all your heart." I instantly seized hold of this with my heart. I had intellectually believed the Bible before; but never had the truth been in my mind that faith was a voluntary trust instead of an intellectual state. I was as conscious as I was of my existence, of trusting at that moment in God's veracity. Somehow I knew that that was a passage of Scripture, though I do not think I had ever read it. I knew that it was God's word, and God's voice, as it were, that spoke to me. I cried to Him, "Lord, I take Thee at Thy word. Now Thou knowest that I do search for Thee with all my heart, and that I have come here to pray to Thee; and Thou hast promised to hear me."
That seemed to settle the question that I could then, that day, perform my vow. The Spirit seemed to lay stress upon that idea in the text, "When you search for me with all your heart." The question of when, that is of the present time, seemed to fall heavily into my heart. I told the Lord that I should take Him at his word; that He could not lie; and that therefore I was sure that He heard my prayer, and that He would be found of me.
He then gave my many other promises, both from the Old and the New Testament, especially some most precious promises respecting our Lord Jesus Christ. I never can, in words, make any human being understand how precious and true those promises appeared to me. I took them one after the other as infallible truth, the assertions of God who could not lie. They did not seem so much to fall into my intellect as into my heart, to be put within the grasp of the voluntary powers of my mind; and I seized hold of them, appropriated them, and fastened upon them with the grasp of a drowning man.
I continued thus to pray, and to receive and appropriate promises for a long time, I know not how long. I prayed till my mind became so full that, before I was aware of it, I was on my feet and tripping up the ascent toward the road. The question of my being converted, had not so much as arisen to my thought; but as I went up, brushing through the leaves and bushes, I recollect saying with emphasis, "If I am ever converted, I will preach the Gospel."[73]
Although Finney doesn't claim to have seen any personages, he does describe a communication with God. Joseph Smith describes his experiences in much the same way as others in his environment did.
Keep in mind that Joseph prayed to find out if his sins had been forgiven. And he discovered that they had. This pleased him greatly. Why did he pray about this matter? The reason is that joining a church at that time often required that one explain one's standing with God to a preacher. We are dealing with Protestant sects. And conservative Protestants believe that one is saved (justified) at the moment one confesses Jesus Christ as Lord and Savior. So Joseph, as he faced the competing Protestant sects, was deeply concerned about his sins. One had to demonstrate to oneself and also convince a preacher that one had been saved—that is, justified. And there were many instances in which prayers were answered by visions in which the person learned that God had forgiven their sins.
The difference between Joseph's experience and many other accounts by visionaries, is that, in addition to being told that his sins were in fact forgiven, he was also told not to join any denomination. When he told that part of his visionary experience, it got him into big trouble with preachers. It was not the vision that was a problem for preachers, but his reporting that he should not join some sect.
So the fact is, contrary to our current way of telling his story, the First Vision was not the beginning of Joseph's call as Seer, Prophet, Revelator and Translator. His vision signaled the beginning of the restoration. It did not begin the work of the restoration.It steered him away from joining one of the competing denominations. It was Joseph's subsequent encounters with Moroni that made him a Seer, and eventually the founding Prophet of a fledgling Church, and not his initial vision, which was initially for him a private event about which he was reluctant to talk, though eventually he dictated some accounts that were found and published during our lifetime. Joseph told a few people about it, word got around, and this caused him much trouble with Protestant preachers.
Joseph eventually wrote the account of that early vision late in his life because rumors about it had circulated and caused him difficulty. But neither Joseph nor any of the other early Saints offered that vision as a reason for others to become Latter-day Saints during his lifetime. It was only much later that what we now call the First Vision began to take on a special importance for the Saints. One reason is that Americans soon did not live in a visionary environment. The great Charles Dickens, writing in England, explained why. He called Joseph Smith vision an absurdity—"seeing visions in the age of railways."
Wilford Woodruff came into the Church of Jesus Christ because he had known earlier in his life someone he believed was a prophet who had alerted him to the soon to be restoration of primitive Christianity. This remarkable story, which was included in the lesson manual on President Woodruff, illustrates the visionary world in which Joseph was raised. Though there were a few—one or two—instances in which the visionary reported encounters with two heavenly messengers, it was most often God the Son who they reported appearing to them.
But there have been and still are peoples not impacted by post-enlightenment skepticism about divine things who are open to visions and other dramatic encounters with the divine, though they often do not speak in public about such things, since they tend to see them as strictly private blessings and not something about which one ought to be gossiping and boasting.
The first missionaries in the Church used The Book of Mormon, not the First Vision, as a witness that the heavens were open, and that each individual, by applying the promise in Moroni 10:3-5, can receive a direct manifestation from Heavenly Father, through the Holy Ghost, that The Book of Mormon is true. After that testimony is gained, it follows that Joseph Smith is a true prophet, as he brought The Book of Mormon forth and restored the fullness of the Gospel under the direction of the Savior.
The fledgling Church of Christ began with the Book of Mormon, the witnesses to the plates, the restoration of priesthood keys, and not directly with what we call the First Vision, though that initial experience assisted in Joseph avoiding what could be perceived as damaging sectarian contamination. The historical record shows that Joseph never gave any attention to the creeds or arguments of quarreling preachers. This was the purpose served by the First Vision.
Some Christians accept Paul's vision while rejecting that of Joseph Smith for a variety of reasons. Richard Lloyd Anderson made the following comparisons.
Many Christians who comfortably accept Paul’s vision reject Joseph Smith’s. However, they aren’t consistent in their criticisms, for most arguments against Joseph Smith’s first vision would detract from Paul’s Damascus experience with equal force.
For instance, Joseph Smith’s credibility is attacked because the earliest known description of his vision wasn’t given until a dozen years after it happened. But Paul’s earliest known description of the Damascus appearance, found in 1 Corinthians 9꞉1, was recorded about two dozen years after his experience.
Critics love to dwell on supposed inconsistencies in Joseph Smith’s spontaneous accounts of his first vision. But people normally give shorter and longer accounts of their own vivid experiences when retelling them more than once. Joseph Smith was cautious about public explanations of his sacred experiences until the Church grew strong and could properly publicize what God had given him. Thus, his most detailed first vision account came after several others—when he began his formal history.
This, too, parallels Paul’s experience. His most detailed account of the vision on the road to Damascus is the last of several recorded. (See Acts 26:9–20.) And this is the only known instance in which he related the detail about the glorified Savior prophesying Paul’s work among the Gentiles. (See Acts 26:16–18.) Why would Paul include this previously unmentioned detail only on that occasion? Probably because he was speaking to a Gentile audience, rather than to a group of Jewish Christians. Both Paul and Joseph Smith had reasons for delaying full details of their visions until the proper time and place.[74]
Joseph Smith left several accounts of his First Vision. None of these accounts is identical with any other. As the main page discusses, some critics wish to argue that Joseph's vision accounts are mutually contradictory, and thus that there was no vision.
Latter-day Saints often point out that the Bible's accounts of Paul's vision on the road to Damascus appear to be contradictory. Yet, the Church's sectarian critics accept Paul's account as true despite the Bible containing apparently frank contradictions in its accounts. While accepting or explaining away these discrepancies, the critics nevertheless refuse to give Joseph Smith the same latitude. Members of the Church have long pointed out that this is a clear double standard, designed to bias the audience against Joseph from the beginning.
Perhaps because of the force of this argument, some critics have begun to argue that no contradiction exists between the versions of Paul's vision.
Author Richard Abanes wrote that contradictions in the stories of Paul's vision were
long ago resolved by scholars analyzing the Greek texts. The discrepancies in Paul's account involve modern ignorance of the Greek wording used.[75]
In support of this claim, Abanes cites W.E. Vine, Vine's Expository Dictionary of New Testament Words p. 544.
Despite Abanes' claim, Greek scholarship has not resolved this issue. In fact, his use of the scholarship is dated, he ignores contrary views, and does not seem to realize that the Bible text itself (including the Acts of the Apostles) violates his supposed 'rule' more often than it keeps it.
The two verses usually at issue are Acts 9꞉7 and Acts 22꞉9. For example, one Wikipedia editor claims that
"There is no conflict in the three accounts of Paul's vision if you read Acts 22:9 in any version other than the KJV. For instance, in the New American Standard Bible and the New International version, it says that Paul's companions did not "understand the voice"—that is hear what was uttered with understanding."[76]
| Bible version | Acts 9:7 | Acts 22:9 | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summary |
Heard voice, saw no one? |
Saw light, heard no voice? |
|
| KJV |
And the men which journeyed with him stood speechless, hearing a voice, but seeing no man. |
And they that were with me saw indeed the light, and were afraid; but they heard not the voice of him that spake to me. |
|
The work cited by Abanes is not a recent work of Greek scholarship—it was first published in 1940.[77] In the reference for ακούω, we read:
Thus, by this source, Abanes hopes to argue that there can be "no idea of any contradiction":
| Factor | Acts 9:7 | Acts 22:9 | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case |
partitive genitive |
accusative |
|
| Meaning |
One hears the sound |
One hears the message |
—|- |
We have seen Abanes appeal to a source that was more than sixty years old at the time of his writing. Have modern Greek scholars anything to add to our discussion?
Daniel Wallace (a non-LDS, conservative Christian scholar) wrote of this same issue:
...There seems to be a contradiction between this account [Acts 9:7] of Paul's conversion and his account of it in Acts 22, for there he says, "those who were with me..did not hear the voice..." However, in Acts 22:9 the verb ακούω takes an accusative direct object. On these two passages, Robertson states: '...it is perfectly proper to appeal to the distinction in the cases in the apparent contradiction....The accusative case (case of extent) accents the intellectual apprehension of the sound, while the genitive (specifying case) calls attention to the sound of the voice without accenting the sense.'...
The NIV [a conservative Bible translation, the New International Version] seems to follow this line of reasoning....[thus the differences in case] can be appealed to to harmonize these two accounts....(italics in original)[78]
Thus, Wallace is here dealing with the exact verses under discussion, and notes the exact argument which Abanes makes. Does he agree? Let us see:
On the other hand, it is doubtful that this is where the difference lay between the two cases used with ακούω in Hellenistic Greek: the N[ew] T[estament] (including the more literary writers) is filled with examples of ακούω + genitive indicating understanding[79]....as well as instances of ακούω + accusative where little or no comprehension takes place[80]}....The exceptions, in fact, are seemingly more numerous than the rule!
Thus, regardless of how one works through the accounts of Paul's conversion, an appeal to different cases probably ought not form any part of the solution (italics and bold italics in original).[81]
Thus, the New Testament itself does not agree with Abanes' reading. Far from supporting him, Greek scholarship argues against his solution—the Bible has more examples where his supposed "rule" is broken than when it is followed. (Even Acts itself contains three counterexamples!)
It would seem that this approach has been developed by those who wish to maintain the idea of biblical inerrancy in the face of the Greek evidence.
Critical sources |
|
Wiki links |
|
Online |
|
Video |
|
Navigators |
Accounts |
|
Historical context |
|
Doctrinal impact |
Video published by the Church History Department.
Video from FAIR
Joseph's concern about religion started when he was twelve years old, close on the heels of the revival of 1817. In his 1832 account, Joseph notes that his concern about religion began at age 12 (1817-1818):
At about the age of twelve years my mind become seriously imprest with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul which led me to searching the scriptures believeing as I was taught, that they contained the word of God thus applying myself to them and my intimate acquaintance with those of different denominations led me to marvel excedingly for I discovered that they did not adorn instead of adorning their profession by a holy walk and Godly conversation agreeable to what I found contained in that sacred depository this was a grief to my Soul... (Joseph Smith's 1832 account of the First Vision)
Richard Bushman notes that this "would have been in late 1817 and early 1818, when the after-affects of the revival of 1816 and 1817 were still felt in Palmyra." [1]
Joseph Smith talked of observing, as a 14-year-old, "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion" in the Palmyra area during the Spring of 1820. Joseph notes that "It commenced with the Methodists, but soon became general among all the sects in that region of country." There is documented evidence of at least one Methodist camp meeting in the Palmyra area during that period, which only by chance happened to be mentioned in the local newspaper because of a specific death that seemed to be associated with it. In addition, there are newspaper articles talking of large-scale revival activity in the larger region surrounding Palmyra during the same general period when Joseph Smith said that it was taking place.
It is reasonable to assume based upon the facts that the Methodists had more than one camp meeting during this period. This could easily account for the religious excitement in Palmyra that, in Joseph's mind at age 14, began with the Methodists.
Joseph continues in his 1832 account: "[T]hus from the age of twelve years to fifteen I pondered many things in my heart concerning the sittuation of the world of mankind the contentions and divi[si]ons the wicke[d]ness and abominations and the darkness which pervaded the of the minds of mankind my mind become excedingly distressed for I become convicted of my sins." In July, 1819, several years after Joseph said his mind became "seriously imprest," a major Methodist conference was held near Palmyra:
[T]he Methodists of the Genesee Conference met for a week in Vienna (later Phelps), a village thirteen miles southeast of the Smith farm on the road to Geneva. About 110 ministers from a region stretching 500 miles from Detroit to the Catskills and from Canada to Pennsylvania met under the direction of Bishop R. R. Robert to receive instruction and set policy. If we are to judge from the experience at other conferences, the ministers preached between sessions to people who gathered from many miles around. It was a significant year for religion in the entire district. . . . The Geneva Presbytery, which included the churches in Joseph's immediate area, reported in February, 1820, that "during the past year more have been received into the communion of the Churches than perhaps in any former year." Methodists kept no records for individual congregations, but in 1821 they built a new meetinghouse in town. [2]

Some claim that there were no religious revivals in the Palmyra, New York area in 1820, contrary to Joseph Smith's claims that during that year there was "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion...indeed, the whole district of country seemed affected by it" Joseph Smith—History 1:5 Joseph Smith talked of observing, as a 14-year-old, "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion" in the Palmyra area during the Spring of 1820. Joseph notes that "It commenced with the Methodists, but soon became general among all the sects in that region of country."
Abundant evidence of religious excitement exists to substantiate Joseph’s account. This has been thoroughly summarized by Pearl of Great Price Central. Their analysis may be accessed by clicking on the hyperlinked text.
One should keep in mind that Joseph Smith never used the term "revival" in his description - he simply described it as "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion." To a 14 year old who had been concerned about religion starting at age 12 after the 1817 revival, the ongoing camp meetings in the town in which he lived would certainly qualify.

Critics of Joseph Smith claim that no revival is mentioned in the 1832 First Vision account because the actual word 'revival'—or something similar—is not found within the text. But they have failed to notice a distinct pattern of words that demonstrate a definite link between the various First Vision accounts.
When the September—November 1832 First Vision account is compared with subsequent recitals (especially 1838), and one partial previous rendition, it appears that they are all telling the same story: Prior to the First Vision event there were contentions and divisions among the different religious denominations in connection with a revival. It seems, therefore, that the Prophet's handwritten 1832 account does indeed make a passing reference to revival activity.
There are several other phrases in the Prophet's 1832 account that can be interpreted as references to revivals. For instance, Joseph Smith said that when he was "about the age of twelve years" (23 December 1817—23 December 1818) he became seriously concerned about the welfare of his soul. Why did these feelings arise at this point in time? Possibly because there was a Methodist camp-meeting/revival from June 19th through the 22nd, 1818 held in Palmyra, New York.[8]
Joseph Smith pointed to a time period "from the age of twelve years to fifteen" (i.e., between 23 December 1817 and 23 December 1821) when he –
Some of the themes enumerated above can be matched with the Prophet's other descriptions of things that happened during the revival activity of Palmyra and its vicinity. This matching of themes tends to support the argument that the 1832 text does indeed refer to revival activity.
The phrase "I cried unto the Lord for mercy" in Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision account also has a strong ring of revivalism to it. Rev. George Peck recounted the happenings at a Methodist camp meeting held on 4 July 1816 in Plymouth, New York. He said that "There was an unbroken roar of fervent supplication all over the ground, while the awful voice of the preacher resounded." One person then fell to the ground and cried for mercy.[9]
Wiki links |
|
Online |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Joseph Smith's stated motivation for praying to the Lord changes between the first known account of the First Vision (1832) and the official version of it (1838). The 1832 account emphasizes his desire for a forgiveness of sins, and the 1838 (official) account emphasizes his desire to know which church was right. Some critic claim that Joseph changed his story in later years.
The texts that are employed by critics to justify the charge of 'differing motivations' are as follows:
1832
1838
The words that precede the point at which Joseph Smith offers his prayer in the 1832 text demonstrate that the anti-Mormon claim about his motivation changing is not sustainable. These words read as follows (standardized for readability):
Historian Christopher Jones has observed that Joseph Smith's 1832 account (and indeed much of his other three accounts) are shaped as Methodist conversion narratives. Within Methodism (and indeed the broader religious culture of Joseph Smith's day), finding forgiveness of sins and joining the right Church rode in tandem. You receive forgiveness of sins by joining the right Church. If you don't follow the correct, "biblical" doctrine then you can't receive such forgiveness.[10] In the case of Joseph Smith, he receives forgiveness of sins and is told not to join any church with which he was acquainted at the time.
There are those who claim that Joseph Smith only claims to seek forgiveness of sins in his 1832 account. These critics ignore the larger historical context under which the 1832 account was written (documented by Jones) and also fail to take notice of scriptural passages quoted near the end of the account in which Christ echoes Matthew 15:8-9:
This clearly does not refer to young Joseph's seeking of a forgiveness of sins. It must refer to an apostasy and restoration of a Church—the true Church of Christ that Joseph had already proclaimed to restore as Doctrine and Covenants 1 (revealed in 1831) makes clear:
Some may counter that this only refers to corrupt people and not corrupt churches or religions. Going back to the passage from the 1832 account cited above, one reads "the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doth good no not one..." This phrase ('and none doeth good no not one') is echoed in a few scriptural passages (Psalm 53: 3; Romans 3: 10, 12; Moroni 7:17) but for our purposes we will highlight one of these occurrences in JST Psalm 14:2. The Church still describes this passage in its heading as lamenting "the loss of truth in the last days[.]" The passage "looks forward to the establishment of Zion." The italics represent edits made by Joseph Smith to the text:

Joseph Fielding McConkie said, 'The JST rendering of this Psalm reads like another account of the First Vision.'[11]
The late Matthew Brown suggested that Joseph's translation of Psalm 14 took place 'shortly after late July 1832.'[12] He even goes so far to say that 'the JST Psalm 14 text may have served as a prototype of sorts for the composition of the 1832 historical document.'[13]
The 1838–39 account’s mention of 'corrupt professors' seems to be reflected in the JST’s 'their teachers are workers of iniquity.' . . . JST Psalm 14:2-4 features 'all these who say they are [the Lord’s]' being rejected by the Lord due to them having 'gone aside,' 'become filthy,' and 'none of them…doing good.' And this is laid at the feet of their teachers who 'are workers of iniquity' [14] This use of Psalm 14 to be explanatory for Joseph's use of no one doing good is strengthened by the fact that Psalm 14 is quoted specifically earlier in the 1832 account ("And when I considered upon these things my heart exclaimed, 'Well hath the wise man said, It is a fool that saith in his heart there is no God.'")
Thus, to summarize again, those who don't do good are all people and this is caused by false teachers teaching incorrect doctrine.
The 1832 account emphasizes Joseph's want of forgiveness as a means to the end of restoring the true Church of Christ. This is completely in line with the rest of the accounts and thus the standard narrative of the First Vision and Joseph's motives in seeking such a vision as taught officially by the Church.
A longer version of this argument is made by Walker Wright and historian Don Bradley in a 2023 paper for BYU Studies.[15]
The First Vision has been a center of both faith and controversy. While millions of Latter-day Saints affirm it as the beginning of the Restoration, others see it as an ever-growing fish tale. The multiple accounts of the First Vision vary in detail, with Joseph Smith’s earliest written account (1832) lacking some of the elements found in his later accounts. However, some of these elements—particularly the appearance of God the Father as part of the First Vision experience—are laced throughout Joseph Smith’s translation of the Bible. These historical threads ultimately culminate in his translation of Psalm 14, which weaves together many of the elements supposedly lacking in Smith’s earliest account of the First Vision. But why bring these threads together in Psalm 14? What was its connection with his First Vision? A basic comparison of Psalm 14 with elements of the First Vision shows that elements of this psalm are found in the background of the vision, as Joseph Smith narrated it, and even in the words of Deity spoken within the vision itself.
It is clear from a consultation of the 1832 text that Joseph Smith's desire to be forgiven of his personal sins was NOT the only motivation for his prayer in the wilderness. He prayed (as he explicitly states) because of "all" of the things he mentions - including the desire to worship God in truth; according to His laws (which Joseph did not believe was the case among any of the Christians denominations that he knew of).
The 1832 textual pattern of (1) desire to prepare for eternity / worship God in truth and (2) desire for forgiveness of personal sins can be detected in subsequent First Vision recitals, demonstrating that there is no change in his declared motive over time. The confusion of the critics on this issue arises when they do not see exact matches in themes across documents or insist that every detail of the story be present in every text that relates it.
1832 (Smith)
1834 (Cowdery/Smith)
1835 (Smith)
1838 (Smith)
1840 (Pratt)
1842 (Smith)
1842 (Hyde)
Critical sources |
|
Critics claim that there is a contradiction between the 1832 account of Joseph Smith's First Vision and the rest of his first-hand accounts. They also claim that the same contradiction occurs internally in the 1838 account. It is alleged that Joseph Smith concluded prior to going to the grove of trees to pray that all the denominations on the earth were false. This supposedly contradicts the 1835 and 1838 accounts in which Joseph expresses doubt as to which Church was true prior to going to the grove.
In his 1832 history, Joseph Smith said:
I found [by searching the scriptures] that mankind did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatized from the true and living faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament
In his 1835 account, Joseph Smith said, "I knew not who [of the denominations] was right or who was wrong."
In his 1838 account of the Vision, Joseph writes:
The 1832 account then, according to some critics, contradicts the 1835 and 1838 account in that Joseph had already determined before seeing God and Jesus that there was no true Church and thus the only motive for going to the grove in the 1832 account would be to obtain a forgiveness of sins and not to find the true Church.
Author J.B. Haws describes the criticism as it relates to the 1838 account specifically:
Here is the essence of that trouble, as some have seen it. In Joseph’s 1838–39 dictated account (the account that would eventually find its way into the LDS Church’s canon as the official Joseph Smith—History), he described his youthful confusion about the competing religious sects that he encountered in these words: "In the midst of this war of words and tumult of opinions, I often said to myself: What is to be done? Who of all these parties are right; or, are they all wrong together?" (Joseph Smith History 1:10). According to this narrative, it seems that fourteen-year-old Joseph had already considered the possibility that all churches could be "wrong together." Yet only eight verses later (by the account’s current scriptural format), Joseph reported what seems like surprise in response to the divine injunction that he must join no church, "for they were all wrong"—and "it had never entered into [his] heart that all were wrong" (JS—H 1:18–19). But didn’t we just read that the "all were wrong" possibility had entered his heart in verse 10? Why such an apparently careless and contradictory oversight in the narrative?[16]
Critics claim that this is a contradiction and evidence that the First Vision story evolved over time.
Such a claim is a false dilemma, as we will now see.
Historian Christopher Jones has observed that Joseph Smith's 1832 account (and indeed much of his other three accounts) are shaped as Methodist conversion narratives. Within Methodism (and indeed the broader religious culture of Joseph Smith's day), finding forgiveness of sins and joining the right Church rode in tandem. You receive forgiveness of sins by joining the right Church. If you don't follow the correct, "biblical" doctrine then you can't receive such forgiveness.[17] In the case of Joseph Smith, he receives forgiveness of sins and is told not to join any church. Thus even if Joseph's main emphasis is forgiveness of sins in the 1832 account, that doesn't mean he's not talking about what Church is true.
Those critics who claim that Joseph is only speaking about the forgiveness of sins in the 1832 account are ignorant of the larger historical context under which the 1832 account was written (documented by Jones) and also fail to take notice of important scriptural passages quoted near the end of the account. Speaking about the condition of the world, Christ, speaking to Joseph, echoes Matthew 15:8-9:
'[T]hat which hath been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Apostles' might easily refer to an apostasy and restoration.
Some may counter that this only refers to corrupt people and not corrupt churches or religions. Going back to the passage from the 1832 account cited above, one reads "the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doth good no not one..." This phrase ('and none doeth good no not one') is echoed in a few scriptural passages (Psalm 53: 3; Romans 3: 10, 12; Moroni 7:17) but for our purposes we will highlight one of these occurrences in JST Psalm 14:2. The Church still describes this passage in its heading as lamenting "the loss of truth in the last days[.]" The passage "looks forward to the establishment of Zion." The italics represent edits made by Joseph Smith to the text:

Joseph Fielding McConkie said, 'The JST rendering of this Psalm reads like another account of the First Vision.'[18]
The late Matthew Brown suggested that Joseph's translation of Psalm 14 took place 'shortly after late July 1832.'[19] He even goes so far to say that 'the JST Psalm 14 text may have served as a prototype of sorts for the composition of the 1832 historical document.'[20]
"The 1838-39 account’s mention of 'corrupt professors' seems to be reflected in the JST’s 'their teachers are workers of iniquity.' . . . JST Psalm 14:2-4 features 'all these who say they are [the Lord’s]' being rejected by the Lord due to them having 'gone aside,' 'become filthy,' and 'none of them…doing good.' And this is laid at the feet of 'their teachers' who 'are workers of iniquity.'"[21] This use of Psalm 14 to be explanatory for Joseph's use of no one doing good is strengthened by the fact that Psalm 14 is quoted specifically earlier in the 1832 account ("And when I considered upon these things my heart exclaimed, 'Well hath the wise man said, It is a fool that saith in his heart there is no God.'")
Thus, to summarize again, those who don't do good are all people and this is caused by false teachers teaching incorrect doctrine. Under this understanding, the 1832 account of Joseph Smith's First Vision is giving implicit credence that Joseph was indeed seeking to know from God which Church to join because the teachers of other denominations had become corrupt.
Author Jim Bennet describes one approach that a person can take while seeking to reconcile this with their faith and that is to focus interpretation on the phrase "entered into my heart":
The key phrase is "entered into my heart."
We can have confidence in what Joseph means by this because it is not the only time he uses variations of this phrase. Here’s what he says about his experience reading James 1:5.
- Never did any passage of scripture come with more power to the heart of man than this did at this time to mine. It seemed to enter with great force into every feeling of my heart. [JSH 1:12, emphasis added]
This is a phrase Joseph uses to describe something more powerful than mere intellectual assent. He’s describing a spiritual experience, where the feelings of the heart complement and contribute to clarity of mind. It’s a concept that shows up in the Doctrine and Covenants, too:
- Yea, behold, I will tell you in your mind and in your heart, by the Holy Ghost, which shall come upon you and which shall dwell in your heart.
- Now, behold, this is the spirit of revelation; behold, this is the spirit by which Moses brought the children of Israel through the Red Sea on dry ground. [D&C 8:2-3, emphasis added]
Joseph had clearly considered the possibility all churches were in error in verse 10 (and in the 1832 account,) but the idea hadn’t really sunk in – i.e. entered into his heart – until after verse 18.
I think all of us have had this experience – things happen that we choose not to believe. Even when we have solid information, we don’t allow our intellectual knowledge to become wisdom and "enter into our hearts." He’s describing the very human process of denial, much like Amulek from the Book of Mormon, who once said of his own testimony, "I knew concerning these things, yet I would not know." (Alma 10:6)
Make up your mind, Amulek! Did you know or didn’t you know?! That’s a direct contradiction!
In the case of "Forgiveness of Sins v. Which Church is True,"... Joseph was preoccupied with what he needed to do to prepare to meet God. You see that in all of Joseph’s firsthand accounts.
"[M]y mind become seriously imprest with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul," he wrote in 1832. "I considered it of the first importance that I should be right, in matters that involve eternal consequ[e]nces;" he wrote in 1835. "My mind was called up to serious reflection and great uneasiness... my feelings were deep and often poignant... What is to be done?" he wrote in 1838. "I began to reflect upon the importance of being prepared for a future [i.e. eternal] state," he wrote in 1842. These are different words, to be sure, but there’s no mistaking the commonality of their underlying meaning. I believe that all these accounts show that Joseph’s deepest desire was to know what he had to do to be saved. That was the one and only item on his agenda in the Sacred Grove.
The question he asked, then, about which church he should join tells us about young Joseph’s theological assumptions. It’s clear in all accounts that salvation and church membership were inextricably linked in his mind. Even in 1832, where he doesn’t specify what question he asked the Lord before his sins were forgiven, he goes on at great length about his concern for the error he sees in all the churches.The possibility that a church might not be necessary doesn’t seem to occur to Joseph, nor would it have been likely to occur to anyone in the early 19th Century. Christ without a church in 1820? Who could imagine such heresy? Certainly not an illiterate farmboy who, at that point, had no inkling what the Lord had in store for him.
In Joseph’s mind, "which church is the right one" and "how can I get my sins forgiven" were variations on the same theme, and only minor variations at that. Rather than show inconsistency, the two accounts are remarkably united in their depiction of Joseph’s concern for his soul and his assumptions about what was necessary to save it.
So with that understanding, the apparent contradiction about whether or not he had decided that all the churches were wrong prior to praying becomes far less problematic. The 1832 account spends more time detailing the specific problems with all the churches than the 1838 account, indicating that Joseph still believed in the importance of joining a church to gain access to the Atonement. True, he doesn’t explicitly say that any church membership is necessary, but he didn’t have to – those reading his account in the 19th Century would have had the same assumptions, and neither Joseph nor his audience would have even considered the modern/post-modern idea of an effectual Christian life outside the boundaries of organized religion. Even if all the churches were wrong to one degree or another, surely Joseph would still have felt it necessary to join the best one... [22]
Speficially addressing the passages from JS History 1: 10 and 18, J.B. Haws wrote:
In a draft of Joseph Smith’s history that was written sometime in 1840–41 by scribe Howard Coray (but only essentially rediscovered in the Church’s archival holdings in 2005), the corresponding passage reads differently:
Joseph Smith—History 1:18–19
- I asked the Personages who stood above me in the light, which of all the sects was right (for at this time it had never entered into my heart that all were wrong)—and which I should join. I was answered that I must join none of them, for they were all wrong . . .
Howard Coray’s 1839–41 history (labeled Draft 3 in Histories, Volume 1 of The Joseph Smith Papers)
- I asked the Personages who stood in the light; Which of the sects were right. (for I supposed that one of them were so.) and which I should join. I was answered "join none of them; they are all are wrong . . ."
Coray’s version suggests that Joseph still "supposed"—still believed, still considered it most likely—that one of the sects was right, even if he had considered the possibility that such was not the case. Thanks to the careful editorial scrutiny of The Joseph Smith Papers scholars, it is apparent that Coray’s draft was written after the draft of Joseph Smith’s history (labeled Draft 2 in the handwriting of James Mulholland) that was eventually published in the Times and Seasons and then the Pearl of Great Price. The Joseph Smith Papers volume editors note that, "for whatever reason," Joseph Smith chose that Draft 2 (Mulholland) version for eventual publication, even though there is evidence to suggest that Coray transcribed as Joseph "read aloud from Draft 2 in the large manuscript volume, directing editorial changes as he read." With that background in mind, the parallel phrases above suggest an affinity of sentiment, such that the phrase "it had never entered into my heart" meant, essentially, "I [still] supposed one of them were [right]"—which reinforces the reading that Joseph held out hope in his heart that he would be pointed to the true denomination.[16]:99–100
Haws describes another way to view both the 1832 account and 1838 account:
One minor drawback in reading Joseph Smith’s history in its current scriptural format is that the verse divisions might inadvertently separate his thoughts too starkly. Because of that potential challenge, the second possibility proposed here is that the contradiction between verses 10 and 18 might simply be a question of antecedents in verse 10. Thus one final alternate reading (and reconciliation) of those verses becomes clearer in the paragraph format of the Draft 2 (Mulholland) manuscript version of Joseph Smith’s history. In what is now verse 9 in the Pearl of Great Price version, Joseph describes the furious activity of three named denominations: the Presbyterians, the Baptists, and the Methodists. Those were the major players in the religious competition that was all around him in that region of New York. And those three groups preached, importantly, distinct soteriological visions of Christianity. If, however, verse 10 is not seen as completely separate from verse 9, then we might understand Joseph’s questions as being much more specific.
Here is how the passage appears in Draft 2 (Mulholland) of Joseph Smith’s history:
- My mind at different times was greatly excited for the cry and tumult were so great and incessant. The Presbyterians were most decided against the Baptists and Methodists, and used all their powers of either reason or sophistry to prove their errors, or at least to make the people think they were in error. On the other hand the Baptists and Methodists in their turn were equally Zealous in endeavoring to establish their own tenets and disprove all others.
- In the midst of this war of words, and tumult of opinions, I often said to myself, what is to be done? Who of all these parties are right? Or are they all wrong together? and if any one of them be right which is it? And how shall I know it?
Read in that way, new attention to the determiners and pronouns might be in order. Which of all of these parties—that is, the Presbyterians, Baptists, or Methodists—is right? Or are they—Presbyterians, Baptists, Methodists— all wrong together? If any of them—Presbyterians, Baptists, Methodists—be right, which is it? It seems reasonable to conclude that Joseph wondered not about the possibility that there was no true religion on the earth, but only that the principal religions represented in his area might all be wrong. Hence, his crucial question—his "object in going to enquire of the Lord"— was "to know which of all the sects was right," and perhaps it was the subsequent instruction to join no sect anywhere ("for they were all wrong") that would have been surprising; in that case, this latter possibility was the one that had never entered into his heart.
Again, this is only suggested as one way to read the text—but it is one that also seems to fit with a telling line in the earliest known written account of the First Vision, one from 1832 that Joseph Smith partly dictated and partly wrote. The key is something he stated about personal familiarity:
In that 1832 history, Joseph wrote in his own hand:
- At about the age of twelve years my mind become seriously [impressed] with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul which led me to searching the scriptures believeing as I was taught, that they contained the word of God thus applying myself to them and my intimate acquaintance with those of differant denominations led me to marvel exceedingly for I discovered that <they did not adorn> instead of adorning their profession by a holy walk and Godly conversation agreeable to what I found contained in that sacred depository this was a grief to my Soul . . .
The fact that his conclusions were based on an "intimate acquaintance with those of differant denominations" should not be overlooked. His subsequent recollections do seem to reflect an expanded understanding of a broader apostasy: "by searching the scriptures I found that mand <mankind> did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatised from the true and liveing faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the new testament." Yet his choice of words ("no society or denomination") and his declaration that "I cried unto the Lord for mercy for there was none else to whom I could go and to obtain mercy" seem to reflect his discouragement with his local options and his growing assurance that only divine intervention could help him transcend that confusion.
It may, then, have been the sheer universality of the apostasy ("join none of them") that had not entered into his heart. It may have been Joseph Smith’s original hope and assumption, as expressed in the Howard Coray draft, that "one of them were" right, even if he had considered the theoretical possibility that the three denominations with which he had "intimate acquaintance" were all "wrong together" and that he would have to seek a religious home among another, less familiar one of "all the sects."[16]:101–102
If you had come to the conclusion that mankind has apostatized from the true faith, and you suddenly found Jesus standing in front of you, wouldn't you ask Him if any of those churches was the correct one? Or would you simply tell Him, "never mind, I already figured it out for myself"?
Could it be that Joseph simply misremembered? Why must one automatically have to be assumed that he was simply embellishing the story?
There are several interpretive possibilities for the supposed discrepancies between the accounts. Is it possible that Joseph Smith contradicted himself? Certainly. But it only remains just that: a possibility—one interpretive option among others. If we presume that Joseph was lying, our hostile reading will lead us to pick this option. If we grant that Joseph might be telling the truth, the other options will not be summarily rejected.
The answer to this apparent contradiction lies in a detailed examination of relevant texts. It is important to first compare Joseph Smith’s November 1832 text (which is in his own handwriting) with a newspaper article printed earlier that same year which refers to the Prophet’s inaugural religious experiences.
When both of these texts are taken into consideration the following storyline suggests itself: Joseph Smith had come to the conclusion, through personal scripture study, that none of the denominations WITH WHICH HE HAD AN INTIMATE ACQUAINTANCE was built upon the New Testament gospel. He prayed for guidance because he was "in doubt what his duty was." This doubt is obliquely referred to again in Oliver Cowdery’s February 1835 Messenger and Advocate partial First Vision recital where he said that because of the religious excitement the Prophet had "determination to know for himself of the certainty and reality of pure and holy religion."[24]
Doubt is present again in the Prophet’s November 1835 diary entry: "I knew not who was right or who was wrong and I considered it of the first importance that I should be right, in matters that involve eternal consequences."[25] So the conclusion this fourteen-year-old boy had reached through personal scripture study did not altogether solve his dilemma. In fact, in the May 1838 account he clarifies that because of his youth and inexperience in life he could not make an absolute decision with regard to this matter: "it was impossible for a person young as I was and so unacquainted with men and things to come to any certain conclusion who was right, and who was wrong"; "I often said to myself, what is to be done? Who of all these parties are right? Or, are they all wrong together? If any one of them be right which is it, and how shall I know it?"; "if any person needed wisdom from God I did, for how to act I did not know, and unless I could get more wisdom than I then had [I] would never know."
Orson Pratt’s 1840 First Vision account helps to explain why the ‘Joseph-decided-every-existing-church-was-wrong’ theory cannot possibly be valid. Elder Pratt reports, "He then reflected upon the immense number of doctrines now in the world which had given rise to many hundreds of different denominations. The great question to be decided in his mind was—if any one of these denominations be the Church of Christ, which one is it?" This expansive view is reflected in the Prophet’s 1838 account. There he states, "My object in going to enquire of the Lord was to know which of all the sects was right that I might know which to join. No sooner therefore did I get possession of myself, so as to be able to speak, than I asked the personages who stood above me in the light, which of all the sects was right (for at this time it had never entered into my heart that all were wrong) and which I should join."

In the 1832 account, Frederick G. Williams inserted the "in the 16th year of my age" above Joseph's text after Joseph had already written it. (See: "History, circa Summer 1832," The Joseph Smith Papers)

In Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision recital he said that he was "in the 16th year of [his] age" when the manifestation took place but in all other accounts in which he mentions his age, he was in his "fifteenth year."
The only First Vision account that provided a different age was the 1832 account written in Joseph Smith's own handwriting. In 1832, 12 years after the First Vision, Joseph wrote, "we were deprived of the bennifit of an education suffice it to say I was mearly instructid in reading and writing and the ground rules of Arithmatic which constuted my whole literary acquirements."
Although the portion of Joseph's 1832 history is in his own handwriting, the text insertion of "in the 16th year of my age" was in the handwriting of Frederick G. Williams, Joseph's scribe. It is likely that Joseph's dating schemes were slightly off when he dictated his age to Williams, many years afte the fact. There is nothing nefarious in Joseph Smith correcting his own slight mathematical miscalculations.
Two years later, Oliver Cowdery had Joseph's 1832 history in his possession when he began publishing history of the Church in late 1834 in the Latter-day Saints' Messenger and Advocate. Oliver clearly established Joseph's age as 14 ("the 15th year of his life") during the period of religious excitement (although Oliver ultimately never described the actual First Vision at this time). Once the date of the First Vision was correctly established it remained steady throughout all subsequent recitals as the "15th year" or "age 14."

The ages are not, as one critic states, "all over the place." [26] The only account produced by Joseph Smith that indicated a different age was the 1832 account (age 15 rather than 14, based upon a text insertion above the line by Frederick G. Williams after Joseph had already written his account). All remaining accounts indicate age 14 (the "15th" year).
In the 1832 account, Frederick G. Williams inserted the "in the 16th year of my age" above Joseph's text after Joseph had already written it. (See: "History, circa Summer 1832," The Joseph Smith Papers)

The 'one-year-off-the mark' dating anomaly of the 1832 First Vision account can best be understood by taking a look at all of the dates and time frame indicators that are provided within the document. It can then be seen that the farther back in time Joseph Smith goes, the more inexact his dating scheme becomes.
Notice that the date of the First Vision is an above-the-line insertion in the handwriting of Frederick G. Williams, meaning that it was not placed in the text initially but was added at a later time than the creation of the main text.
(17 years back in time)
(15 years back in time)
(12 years back in time)
(7 years back in time)
(5 years back in time)
We should carefully note that Joseph Smith correctly stated that he was "seventeen years of age" when the angel Moroni appeared to him on 22 September 1823, he got the time of that manifestation wrong by one year. A clue as to why this incorrect date was placed by the Prophet in this historical account can be found right in the 1832 document itself. Near the beginning of the narrative Joseph writes: "being in indigent circumstances [we] were obliged to labor hard for the support of a large family having nine children. And as it required the exertions of all that were able to render any assistance for the support of the family therefore we were deprived of the benefit of an education. Suffice it to say [that] I was merely instructed in reading and writing and the ground <rules> of arithmetic which constituted my whole literary acquirements". Elder Orson Pratt once asked rhetorical questions of the Prophet to illustrate his meager level of formal education: "Had you been to college? No. Had you studied in any seminary of learning? No. Did you know how to read? Yes. How to write? Yes. Did you understand much about arithmetic? No. About grammar? No. Did you understand all the branches of education which are generally taught in our common schools? No." (Journal of Discourses, 7:220-21). And when Elder Pratt wrote specifically about the First Vision he was even more specific about the level of the Prophet's math skills, saying that he had "a very limited understanding of the elementary rules of arithmetic." (Orson Pratt, An Interesting Account of Several Remarkable Visions [Edinburgh, Scotland: Ballantyne and Hughes, 1840],—-).
The 1832 history is not the only one where the Prophet made a dating mistake that was one year off the mark. He did the same thing when he created the 1838 Church history, but this time he got the year of his own brother's death wrong. He erroneously remembered that it was 1824 instead of 1823. The significant thing about this particular dating blunder is that four years after the Prophet recorded the initial information he came to the realization that it was not correct and had his scribe, Willard Richards, make the appropriate adjustment. Perhaps the problem with the date was brought to the Prophet's attention by a member of his own family after the information had been printed and made available for public perusal [publication in May 1842; correction in December 1842].
Initial Manuscript Record (2 May 1838)
Publication ( 15 March 1842 / 2 May 1842)
Post-Publication Manuscript Correction (2 December 1842)
A similar type of dating correction scenario, as mentioned above, may have taken place in connection with the 1832 history. Oliver Cowdery claimed that he had the Prophet's help in creating his December 1834 Church history article and despite the fact that he had the erroneously-dated 1832 document sitting in front of him [see paper on this subject] he provided the correct year for the Prophet's First Vision - "in the 15th year of his life" (i.e., between 23 December 1819 and 23 December 1820). And just nine months later the Prophet himself was telling a non-Mormon that the First Vision took place when he was "about 14 years old" (Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835).

An image from "mormoninfographics" is in circulation on the internet which mistakenly states that Joseph claimed that he was age 17 when the First Vision occurred. However, this was a misreading of Joseph Smith's 1835 journal entry, which clearly states that Joseph was age 14 at the time of the first vision, and age 17 at the time of Moroni's visit.

Is this evidence that this visionary tale evolved over time by becoming more dramatic and elaborate?
The 'struggle' motif is absent from the first known self-written account of the Prophet's visionary experience (1832) but it is also absent from his self-written Wentworth Letter account (1842). It is clear from the available documentary evidence that the Prophet did not feel constrained by the arbitrary rule of his modern critics that he must include every aspect of his First Vision story in every single retelling of it, and no reasonable person should be bothered that he doesn't.
The following timeline displays the 'struggle' material found in First Vision recitals that were produced during the Prophet's lifetime. The corresponding text from the 1832 document is also provided for purposes of comparison.
Several observations about the information presented below may prove useful.
September–November 1832
I cried unto the Lord for mercy. . . and while in the attitude of calling upon the Lord . . . a pillar of fire [or] light above the brightness of the sun at noonday came down from above and rested upon me and I was filled with the Spirit of God.
9 November 1835
I called on the Lord for the first time in the place above stated, or in other words, I made a fruitless attempt to pray. My tongue seemed to be swollen in my mouth, so that I could not utter. I heard a noise behind me like some one walking towards me. I strove again to pray, but could not. The noise of walking seemed to draw nearer. I sprang upon my feet and looked round, but saw no person or thing that was calculated to produce the noise of walking. I kneeled again, my mouth was opened and my tongue loosed. I called on the Lord in mighty prayer. A pillar of fire appeared above my head, which presently rested down upon me and filled me with unspeakable joy.
2 May 1838
I kneeled down and began to offer up the desires of my heart to God, I had scarcely done so, when immediately I was seized upon by some power which entirely overcame me and had such astonishing influence over me as to bind my tongue so that I could not speak. Thick darkness gathered around me and it seemed to me for a time as if I were doomed to sudden destruction. But exerting all my powers to call upon God to deliver me out of the power of this enemy which had seized upon me, and at the very moment when I was ready to sink into despair and abandon myself to destruction, not to an imaginary ruin but to the power of some actual being from the unseen world who had such a marvelous power as I had never before felt in any being, just at this moment of great alarm I saw a pillar of light exactly over my head above the brightness of the sun, which descended gradually until it fell upon me. It no sooner appeared than I found myself delivered from the enemy which held me bound.
September 1840
He therefore, retired to a secret place in a grove, but a short distance from his father's house, and knelt down, and began to call upon the Lord. At first, he was severely tempted by the powers of darkness, which endeavored to overcome him; but he continued to seek for deliverance, until darkness gave way from his mind, and he was enabled to pray in feverency of the spirit, and in faith. And while thus pouring out his soul, anxiously desiring an answer from God, he at length, saw a very bright and glorious light in the heavens above; which, at first, seemed to be a considerable distance. He continued praying, while the light appeared to be gradually descending towards him.
June 1841
He, therefore, retired to a secret place, in a grove, but a short distance from his father's house, and knelt down and began to call upon the Lord. At first, he was severely tempted by the powers of darkness, which endeavored to overcome him. The adversary benighted his mind with doubts, and brought to his soul all kinds of improper pictures and tried to hinder him in his efforts and the accomplishment of his goal. However, the overflowing mercy of God came to buoy him up, and gave new impulse and momentum to his dwindling strength. Soon the dark clouds disappeared, and light and peace filled his troubled heart. And again he called upon the Lord with renewed faith and spiritual strength. At this sacred moment his mind was caught away from the natural objects with which he was surrounded, and he was enwrapped in a heavenly vision.
1 March 1842
I retired to a secret place in a grove and began to call upon the Lord, while fervently engaged in supplication my mind was taken away from the objects with which I was surrounded, and I was enwrapped in a heavenly vision.
11 June 1843
he went into the grove & enquired of the Lord which of all the sects were right.
29 August 1843
I kneeled down, and prayed, saying, O Lord, what Church shall I join? Directly I saw a light.
24 May 1844
Went into the Wood to pray, kneels himself down, his tongue was close[d,] cleave[t]h to his roof—could utter not a word, felt easier after awhile—saw a fire toward heaven came near and nearer. . . . the fire drew nigher, rested upon the tree, enveloped him[, and] comforted [him].
Critical sources |
|
The theophany portion of the 1832 account does not specifically indicate that the Father appeared to Joseph Smith together with Jesus Christ. The relevant text (in its original form) reads as follows:
a piller of fire light above the brightness of the sun at noon day c[a]me down from above and rested upon me and I was filled with the spirit of god and the <Lord> opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord and he spake unto me saying Joseph <my son> thy sins are forgiven thee. go thy <way> walk in my statutes and keep my commandments behold I am the Lord of glory I was crucifyed for the world that all those who believe on my name may have Eternal life <behold> the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doeth good no not one they have turned asside from the gospel and keep not <my> commandments they draw near to me with their lips while their hearts are far from me and mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them acording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father.[29]
Even though the Savior makes a direct reference to the Father there is no indication in this portion of the 1832 document that God appeared to Joseph Smith alongside His Son.
This type of pattern is seen in the Book of Mormon, translated in 1829: The Book of Mormon begins (1 Nephi 1꞉8-10) with Lehi's vision of God on His throne. One [Christ] followed by twelve others descends from God to speak with Lehi—thus, Jesus and the Father are here both separate, and the role of Christ in giving instructions to the prophet while the Father looks on and approves is followed, just as it was in Joseph's First Vision. Here too, Lehi is described as praying to "the Lord," and yet has a vision of both God the Father and Christ.

There is a very significant phrase located in the introductory paragraph of the Prophet's historical narrative. There he indicates that the 1832 document is . . .
A History of the life of Joseph Smith Jr. an account of his marvilous experience and of all the mighty acts which he doeth in the name of Jesus Ch[r]ist the son of the living God of whom he beareth record and also an account of the rise of the church of Christ in the eve of time according as the Lord brough<t> [it] forth and established [it] by his hand <firstly> he receiving the testamony from on high secondly the ministering of Angels thirdly the reception of the holy Priesthood by the ministring of Aangels to adminster the letter of the Gospel—<—the Law and commandments as they were given unto him—>and the ordinencs, forthly a confirmation and reception of the high Priesthood after the holy order of the son of the living God.
This paragraph not only introduces the document with a heavy emphasis on the Son of God but it also chronologically outlines four inaugural events of the Restoration.
The significant phrase in the introductory paragraph is the one associated with the First Vision—"receiving the testimony from on high" (spelling standardized). When this phrase is placed in conjunction with the Prophet's 1835 and 1838 accounts of the First Vision it becomes obvious that the 1832 phraseology closely corresponds with the words spoken by God the Father when He introduced His Son in the Sacred Grove.
The Father's identification of Jesus Christ as His Son was His "testimony" of Him.
Critics have objected that—in their minds—the phrase "from on high" cannot be so easily equated with God the Father. But there is a sizable amount of corroborating evidence for this idea. Consider the following points of connection.
The Father's voice . . . came out of heaven [i.e., 'from on high'] and testified of His Beloved Son.
Joseph Smith stated, "the Lord God has spoken it; and we . . . have heard . . . the words of the glorious Majesty on high."
There are five New Testament scriptures (which Joseph Smith would have been familiar with from his work on the JST) that have distinct parallels to the First Vision story. Jesus Christ's Old World disciples heard the Father's voice come "from heaven" (Mt. 3:17; Mk. 1:11; Lk. 3:22; 2 Pt. 1:17-18) [i.e, 'from on high'] or "out of the cloud" (Mt. 17:5) [i.e., 'from on high'] and in each of these instances the Father testified of His Son and employed the same phraseology that Joseph Smith said He utilized during the First Vision
This chronological evidence points to the conclusion that Joseph Smith appears to have equated the voice "from on high" with God the Father both before and after he penned his 1832 First Vision account.
There is another line from the 1832 account that may be referring to two people:
I was filled with the spirit of God, and the Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord
It has been argued that the seperation of "Lord" into two may be referring to the Lord God [i.e., the Father] and the Lord Jesus Christ. Three pieces of evidence can be used to argue for this interpretation.
Some critics have taken issue with this evidence for the interpretation—claiming that since Psalm 110:1 was originally written in Hebrew with two different words for Lord (rendering "Lord" and "LORD" in all caps for the second mention) that the argument fails.[31]
Robert S. Boylan has responded by showing how Psalm 110:1 is the most quoted, echoed, and/or alluded to passage in the New Testament which Joseph would have been working on revising in his Inspired Translation of the Bible. He then shows that the revelations in Doctrine and Covenants leading up chronologically to the publication of the history containing the 1832 account of Joseph’s vision deliberately echo that verse (Doctrine and Covenants 20:24; 49:5-6; 76: 20, 23). If Joseph were familiar with that verse close to the publication of the account by way of the Old and/or New Testament and as echoed in his revelations published in the Doctrine and Covenants, it seems reasonable to assume that he could have used that verse as a template for rendering his account of events surrounding the First Vision.[32] This is even if one mention is capitalized and the other not. If the structure is deliberate and clear (and it appears so), then it seems odd to be upset that Joseph doesn't use capitals for the second "Lord" he writes about.
The 1832 account may be read to have a successive appearance of personages, one after the other. This is strengthened by the 1835 accounts mention of successive appearance. Further evidence of this in the 1832 account may be that Joseph was "filled with the spirit of God" before he mentions "the Lord".
Some have argued that the 8 uses of Lord in the 1832 account all refer to Jesus Christ.[33] There are at least three references that may be read otherwise:
A History of the life of Joseph Smith Jr. an account of his marvilous [sic] experience and of all the mighty acts which he doeth in the name of Jesus Christ the son of the living God of whom he beareth record and also an account of the rise of the Church of Christ in the eve of time according as the Lord brought forth and established by his hand.
A separation of "Christ" and "the Lord." This is able to be read with Christ or the Father as the Lord.
My mind became exceedingly distressed, for I became convicted of my sins, and by searching the scriptures I found that mankind did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatized from the true and living faith, and there was no society or denomination that was built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament.
Joseph may be referring to coming to the Lord (i.e., the Father) and the gospel of Christ.
The third plausible evidence of the Father as Lord is the ending of the account:
My soul was filled with love, and for many days I could rejoice with great joy. The Lord was with me, but I could find none that would believe the heavenly vision. Nevertheless, I pondered these things in my heart.
The reference here is vague enough that it cannot be conclusively read one way or the othe—especially with the just-cited mention of the Lord.
Since it can be concluded from the above documentary evidence that Joseph Smith did indeed make an oblique reference to the appearance of the Father in his 1832 history the question becomes—Why did the Prophet construct the 1832 narrative in the manner that he did (so as to exclude explicit mention of the Father's appearance)? A careful analysis of the 1832 First Vision text reveals that it was deliberately constructed on the framework of many scriptural citations. The apostle Stephen's view of both the Father and the Son is clearly utilized by the Prophet in one section of the 1832 text but, more importantly, Joseph Smith told the actual theophany portion of this narrative in language that very closely corresponds to the apostle Paul's vision of Jesus Christ (Acts 26).[34] .
On this reading, the Father is not explicitly mentioned as making an appearance in the theophany portion of the 1832 First Vision account because Joseph Smith patterned that part of his narrative after the vision of Jesus Christ experienced by the apostle Paul.
Paul did not report that he saw the Father alongside the Son, and so it is logical that this is the reason why Joseph Smith did not explicitly mention the Father's appearance in his text either. The Prophet's strong sense of connection with Paul's visionary experience is referred to by him right in his 1838 First Vision account. The context of this connection is the persecution experienced by both men for speaking publicly about a heavenly manifestation. Joseph Smith relates in his 1838 history that he was informed by a clergyman that his vision was "all of the devil." This piece of information may help to explain why the Prophet chose to couch his first known written account of his vision in heavy biblical language and imagery. He may have hoped that by doing this his story would have a better chance of being accepted amongst a populace that was steeped in biblical content.
The Gospel Topics Essay touching on the first vision touches on another way of looking at the evidence. It focuses on the awkward repetition of the word "Lord" and how this may have been Joseph's perhaps uneducated way of stating the order of appearance of the personages:
Embellishment. The second argument frequently made regarding the accounts of Joseph Smith’s First Vision is that he embellished his story over time. This argument focuses on two details: the number and identity of the heavenly beings Joseph Smith stated that he saw. Joseph’s First Vision accounts describe the heavenly beings with greater detail over time. The 1832 account says, “The Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord.” His 1838 account states, “I saw two Personages,” one of whom introduced the other as “My Beloved Son.” As a result, critics have argued that Joseph Smith started out reporting to have seen one being—“the Lord”—and ended up claiming to have seen both the Father and the Son.
There are other, more consistent ways of seeing the evidence. A basic harmony in the narrative across time must be acknowledged at the outset: three of the four accounts clearly state that two personages appeared to Joseph Smith in the First Vision. The outlier is Joseph Smith’s 1832 account, which can be read to refer to one or two personages. If read to refer to one heavenly being, it would likely be to the personage who forgave his sins. According to later accounts, the first divine personage told Joseph Smith to “hear” the second, Jesus Christ, who then delivered the main message, which included the message of forgiveness.10 Joseph Smith’s 1832 account, then, may have concentrated on Jesus Christ, the bearer of forgiveness.
Another way of reading the 1832 account is that Joseph Smith referred to two beings, both of whom he called “Lord.” The embellishment argument hinges on the assumption that the 1832 account describes the appearance of only one divine being. But the 1832 account does not say that only one being appeared. Note that the two references to “Lord” are separated in time: first “the Lord” opens the heavens; then Joseph Smith sees “the Lord.” This reading of the account is consistent with Joseph’s 1835 account, which has one personage appearing first, followed by another soon afterwards. The 1832 account, then, can reasonably be read to mean that Joseph Smith saw one being who then revealed another and that he referred to both of them as “the Lord”: “the Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord.”
Joseph’s increasingly specific descriptions can thus be compellingly read as evidence of increasing insight, accumulating over time, based on experience. In part, the differences between the 1832 account and the later accounts may have something to do with the differences between the written and the spoken word. The 1832 account represents the first time Joseph Smith attempted to write down his history. That same year, he wrote a friend that he felt imprisoned by “paper pen and Ink and a crooked broken scattered and imperfect Language.” He called the written word a “little narrow prison.” The expansiveness of the later accounts is more easily understood and even expected when we recognize that they were likely dictated accounts—an, easy, comfortable medium for Joseph Smith and one that allowed the words to flow more easily.[35]
Read the full article here.
It is worthwhile to note that the scribe for the material which directly precedes and follows after the 1832 First Vision narrative—Frederick G. Williams—never mentioned anything about Joseph Smith's story evolving over time and becoming more elaborate with the so-called 'addition' of the Father.
Williams was a resident of Quincy, Illinois when the First Vision account which explicitly refers to the Father was published in Nauvoo, Illinois on 1 April 1842. It is known that Williams was with the Prophet in Nauvoo shortly before his death on 10 October 1842 but during the intervening six months there is no known objection from Frederick to the content of the printed text. Why not? Williams was the person who wrote down the words in the introductory remarks of the 1832 document that talk of Joseph Smith receiving "the testimony from on high" during the First Vision. And it is known that Frederick was accompanying four LDS missionaries who, in November 1830, were teaching the citizens of Painesville, Ohio that Joseph Smith had seen "God" personally (see the 1830 statement about seeing "God").
Williams was a member of the First Presidency of the Church on 9 November 1835 when Joseph Smith was teaching a non-Mormon that there were two personages who appeared during the First Vision (see Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835). Frederick probably never drew attention to a so-called 'discrepancy' between what Joseph Smith taught in 1832, 1835, 1838, and 1842 because he knew that there wasn't one; he knew that the words of the Father spoken during the vision were referred to right in the text that he had written down in 1832.
Oliver Cowdery is another person who was in a position to know if the Prophet's First Vision story had changed over time by the addition of the Father. But he never mentioned any such 'discrepancy'. Cowdery had possession of the 1832 First Vision account when he wrote and published a series of Church history letters in December 1834 and February 1835 and so he was fully aware of the explicit mention of Christ's appearance and he also would have known of the introductory remark which refers to "the testimony from on high" being delivered during this event. Cowdery became the Associate or Assistant President of the entire Church on 5 December 1834 (Encyclopedia of Mormonism, 1653), and thus he would have been in the highest office of Church authority when the Prophet was teaching about one year later that two personages appeared during the First Vision (Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835).
Both Fredrick G. Williams and Oliver Cowdery had reason to feel animosity toward Joseph Smith and the Church since they were both excommunicated in the late 1830's. But neither of these men - even after their reinstatements into full fellowship - ever pointed to any 'creative editing' of the Prophet's First Vision story to sound more impressive and dramatic.
Critical sources |
|
Some have seen a discrepancy between the location of Deity in the Prophet's 1832 and 1838 First Vision accounts. The 1838 version says that the Prophet saw two Personages standing in the air above the earth, within his proximity. But the 1832 version is not so clear—it seems to locate Deity in heaven.
Details about Joseph Smith's First Vision experience are best interpreted by taking all of the extant accounts into consideration. A myopic focus on a limited number of historical documents can only lead to misunderstanding of the past and a twisted sense of the message that the author is trying to convey.
This so-called 'discrepancy' can be accounted for by the fact that Joseph Smith built his 1832 First Vision account using the framework of 47 biblical scriptures. And at this point in his manuscript he utilized Acts 7꞉55-56 to tell his story. It reads:
But [Stephen], being full of the Holy Ghost, looked up steadfastly into heaven, and saw the glory of God, and Jesus standing on the right hand of God.
And said, Behold, I see the heavens opened, and the Son of man standing on the right hand of God.
The Greek text that underlies the KJV translation says that Stephen looked into "heaven" (ouranos - 'the sky'; by extension: 'heaven'; also translated as 'air') and saw the "heavens" (the same Greek word - ouranos) opened. Thus, Stephen did not necessarily see Deity in their celestial abode - far beyond the confines of the earth - but rather standing above him in the air.
When Joseph Smith says in the 1832 First Vision account that he saw the Lord after the "heavens" (he uses the plural form) were opened he seems to be expressing the same idea that is found in the New Testament text.
Notice that the physical proximity of the Personages is established in the Prophet's 1835 recital: the pillar of fire can be physically seen in the air; the pillar of fire physically descends and rests upon Joseph; the pillar of fire has contact with physical objects that surround Joseph; two Personages are seen in the midst of this pillar of fire. Notice also that in the 1844 account the Prophet indicates that he could see with his natural eyesight the pillar "toward heaven", or up in the air. A glance at the 1840 account also shows that the phrase "in the heavens above" simply means "a considerable distance" up in the sky - it is not a reference to the celestial abode of Deity.
Critical sources |
|
The 1832 account of the First Vision does not portray the Lord as announcing that all the creeds were corrupt. These details do not show up until the 1838 account. Is this evidence that the Prophet's story evolved over time?
The claim that Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision story does not contain a divine injunction against joining any churches does not take evidence within the document itself into proper consideration. The information is implicit instead of explicit, but it is there nevertheless. This point cannot be legitimately used as evidence of an evolving storyline.
A quick look at the 1832 First Vision text reveals how untenable this claim is. Joseph Smith states that before he went into the woods to pray he had concluded in his own mind that "those of different denominations [which he was personally acquainted with]. . . did not adorn their profession by a holy walk and godly conversation agreeable to what [he] found contained in [the Bible] . . . . [There were] contentions and divisions [among them] . . . . [T]hey had apostatised from the true and living faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament."
Then, when Jesus Christ Himself made a personal appearance to Joseph in the grove, He informed the young boy that -
"the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good no not one they have turned aside from the gospel and keep not <my> commandments they draw near to me with their lips while their hearts are far from me and mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them acording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father"
To summarize:
How can critics possibly see this as anything other than a forceful and unambiguous indication on the Lord's part that joining any of the Christian denominations would be an unacceptable path for Joseph to take? Notice in the remainder of the 1832 text that Joseph says he felt great joy and love because of his experience and pondered the things which he had seen and heard during the vision . . . but during an interval of several years he did NOT join any church. Why?
As the 1832 text so plainly says—Joseph Smith believed that Christians had turned aside from the gospel; Jesus Christ confirmed that Christians had turned aside from the gospel; Joseph was therefore provided with a set of golden plates that contained writings which were "engrave[d] by . . . the servants of the living God." The 1832 account speaks three times of the "work" that God wanted Joseph Smith to do, while the 1838 account explicitly connects this "work" with the bringing forth of "the everlasting gospel." The 1842 First Vision account ties all of these themes together. There the Prophet relates: "I was expressly commanded to 'go not after them,' at the same time receiving a promise that the fulness of the gospel should at some future time be made known unto me."
Another indication from the 1832 document that Joseph Smith knew from the First Vision event that he should not join any of the churches can be found in something the Savior said to him. Jesus Christ explained that He was going to take action against the situation the world was currently in by "bring[ing] to pass that which hath been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles." What did this statement mean? In a canonized text written at approximately the same time as the 1832 First Vision account (September 1832) the following phraseology is found:
In other words, the Lord was telling Joseph Smith during the First Vision about the coming Restoration and so there would not be any need for him to join an existing church. This viewpoint is bolstered by several instances where the Prophet utilized the same phraseology used by the Lord during the First Vision to speak about the Restoration.
Critical sources |
|
Three of the primary sources that charge Joseph Smith with joining sectarian churches between 1820 and 1830 were produced in the latter part of the nineteenth century, over a half-century after the First Vision. None of the three are contemporary records; the earliest one was written 50 years after the First Vision took place.
We must note too that none of these sources confirms the others—they all discuss different denominations and different time frames. Thus, the stories are not mutually reinforcing.
Eyewitness reminiscences and contemporary records provide strong evidence that these claims are not valid and, therefore, do not reflect historical reality. The three sources are all late, and all from hostile voices.
Fayette Lapham claimed to have interviewed Joseph Smith Sr. in 1829-30, and published a report forty years later. In it, he reported:
About this time [1822, perhaps as late as 1824] he [Joseph, Jr.] became concerned as to his future state of existence, and was baptized, becoming thus a member of the Baptist Church.[42]
The Lapham source is secondhand at best—putting forward information that reportedly came from the Prophet's father. There are no records beyond this late, second-hand recollection to support this claim.
Joseph and Hiel Lewis were cousins of Emma Hale Smith; they would have been aged 21 and 11 respectively in 1828:
...while he, Smith, was in Harmony, Pa., translating his book....that he joined the M[ethodist] [Episocpal] church. He presented himself in a very serious and humble manner, and the minister, not suspecting evil, put his name on the class book, the absence of some of the official members, among whom was the undersigned, Joseph Lewis, who, when he learned what was done, took with him Joshua McKune, and had a talk with Smith. They told him plainly that such a character as he was a disgrace to the church, that he could not be a member of the church unless he broke off his sins by repentance, made public confession, renounced his fraudulent and hypocritical practices, and gave some evidence that he intended to reform and conduct himself somewhat nearer like a christian than he had done. They gave him his choice, to go before the class, and publicly ask to have his name stricken from the class book, or stand a disciplinary investigation. He chose the former, and immediately withdrew his name. So his name as a member of the class was on the book only three days.—It was the general opinion that his only object in joining the church was to bolster up his reputation and gain the sympathy and help of christians; that is, putting on the cloak of religion to serve the devil in.[43]
Note that Joseph did not inscribe himself, but the Methodist minister added Joseph's name to the class book. It is not surprising that Joseph might have attended Methodist services: Emma's family was involved in Methodism, she was related to Methodist ministers, and Joseph at this period was living on the Hale family's farm. The Hales had serious reservations about their new son-in-law, who claimed by this point to have the Book of Mormon plates in his possession. It would be natural for him to attend worship services with them if only to reassure them that he was not hostile to religion.
It is telling, though, that as soon as Joseph Lewis learned that Joseph had attended, he quickly took steps to disassociate the church from a person he saw as an imposter: note too that Lewis describes himself (rather than Joseph) as one "of the official members." A study of Methodist procedure makes it extremely unlikely that Joseph could have been a member of the Church, especially for only three days.
The Lewis source presents a scenario that was directly contradicted in print by an adult eyewitness who was a Methodist church officer. It is certainly possible that Joseph attended a Methodist meeting with his wife and in-laws: even in the Lewis' telling, however, he was quickly made to understand that he was not wanted, and he persisted in his own beliefs rather than continue with them.
| Main article: | Methodist membership procedures and Joseph Smith |
| See also: | Joseph became "partial to the Methodist sect" in 1820 |
S.F. Anderick (1887):
When Jo[seph Smith] joined the Presbyterian Church, in Palmyra village, it caused much talk and surprise, as he claimed to receive revelations from the Lord.[44]
As Dan Vogel notes, "Because Lucy Smith and three of her older children joined the Presbyterian Church, together with the possibility that Joseph Jr. may have attended some meetings with other family members, some observers may have assumed Joseph Jr. was also a member."[45] (Vogel notes that Lorenzo Saunders claimed in 1884 that he attended Sunday School with Joseph at the Presbyterian Church, and so that attendance (without formal membership) may be the source for this reminiscence.[46]
The Anderick source may simply be recalling an occasion when the young Prophet attended a church service with his Presbyterian mother and siblings.
The eyewitness sources that follow below indicate that up until the time that Joseph Smith announced the existence of the golden plates of the Book of Mormon to his family (23 September 1823) he was not formally attached to any church, but had instead publicly rejected all of them and manifested his desire NOT to join their ranks. Some are contemporaneous, others are later remembrances, but the hostile and friendly voices are clear that he had no denominational affiliation.
Pomeroy Tucker (a non-Mormon critic who knew Joseph Smith in Palmyra, New York) said that Joseph joined the Methodist probationary class in Palmyra but soon "withdrew from the class" without being converted; announcing that "all the churches [were] on a false foundation."[47] This information corresponds with historical details dated by Joseph Smith at around 1820.
Lucy Mack Smith:
Joseph Smith's mother recalled in her autobiography that shortly after her son Alvin died on 19 November 1823 Joseph "utterly refused" to attend church services with the intent to convert, and he made the specific request: "do not ask me to join them. I can take my Bible, and go into the woods, and learn more in two hours, than you can learn at meeting in two years, if you should go all the time."[48]
As can be seen by the continuing chronological sources which follow, Joseph Smith and his associates were teaching from 1825 to 1832 that the Prophet did not belong to any church between the years 1825 and 1827.
Josiah Stowell, Jr. (a non-Mormon):
I will give you a short history of what I know about Joseph Smith, Jr. I have been intimately acquainted with him about 2 years. He then was about 20 years old or thereabout. I also went to school with him one winter. He was a fine, likely young man and at that time did not profess religion.[49]
Peter Bauder:
In 1827 David Marks (a non-Mormon minister) went to Palmyra and Manchester, New York where he "made considerable inquiry respecting . . . [Joseph] Smith" and learned from "several persons in different places" that Joseph was "about 21 years [old]; that previous to his declaration of having found the plates he made no pretensions to religion."[50]
Observer and Telegraph (newspaper):
Four LDS men from New York state taught that at the time the angel appeared to Joseph Smith (22 September 1823) he "made no pretensions to religion of any kind."[52]
Palmyra Reflector (newspaper):
The editor of a Palmyra, New York newspaper claimed that he has been "credibly informed," and was "quite certain," that "the prophet . . . never made any serious pretensions to religion until his late pretended revelation"—meaning the Book of Mormon, which was made known among Palmyra's residents in the Fall of 1827.[53]
Orson Pratt:
Orson Pratt and Lyman Johnson taught on 8 April 1832 that "in 1827 a young man called Joseph Smith of the state of New York, of no denomination [i.e., not belonging to a church], but under conviction, inquired of the Lord . . . [and] an angel [appeared to him] . . . who gave information where the plates were deposited."[54] Pratt clarified in a much later statement that between 1820 and 1823 Joseph Smith "was not a member of any church."[55]
Thus, a great deal of contemporary evidence disproves the late, second hand claims.
Critical sources |
Primary Sources
|
One critical author states, "Joseph [Smith] added new elements to his later narratives that are not hinted at in his earlier ones. His first vision evolved from a forgiveness epiphany [1832 account] to a call from God the Father and Jesus Christ to restore the true order of things [1842 account]."
Taken altogether, the above information reveals that Joseph Smith considered his initial calling to have come directly from Deity in the Sacred Grove in 1820—not at some later time. The wording in the Prophet's 1832 First Vision account can be comfortably interpreted to mean that he understood this extraordinary event represented the beginning of a new gospel dispensation.
In Joseph Smith's 1832 account he plainly states that before the First Vision took place he was of the opinion that "mankind . . . had apostatized from the true and living faith, and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament." When the Prophet saw Jesus Christ face to face during the First Vision experience the Savior verified what Joseph had previously believed by saying, "the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good; no, not one. They have turned aside from the gospel and keep not my commandments" (emphasis added).
During the lifetime of Joseph Smith the word DISPENSATION was defined in a popular English dictionary in the following manner: "a system of principles and rites enjoined [or dispensed or bestowed]; as . . . the gospel dispensation; including . . . the scheme of redemption by Christ."[56] As noted above, Jesus Christ informed Joseph Smith that mankind had turned aside from the gospel and no longer kept His commandments. He then issued a directive straight to Joseph Smith by saying, "Walk in my statutes and keep my commandments" (emphasis added). This is clearly a new beginning; the Lord enjoined His ‘system of principles’ or ‘scheme of redemption’ upon Joseph Smith. This act qualifies—by definition—as a new dispensation of the gospel.
Was this early nineteenth-century dispensation of the gospel meant only for the benefit of Joseph Smith? In writing out the 1832 account the Prophet utilized some very specific wording when he said that "the world of mankind . . . . had apostatized" and he mourned for "the sins of the world." In his perspective "no society or denomination . . . built upon the gospel." And when the Lord spoke to Joseph during the vision He emphasized that this situation was on a universal scale saying, "the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good; no, not one." Thus, the 1832 account definitely describes a universal apostasy—and it makes no sense that the Savior would inaugurate a dispensation of His gospel only for the sake of one individual when innumerable humans were in need of salvation.
An entry found in the Encyclopedia of Mormonism agrees with the quotations provided above. It states with regard to the First Vision: "The Lord spoke face-to-face with Joseph and called him to service."[68]
Critical sources |
|
In light of the statements produced by Joseph Smith before he wrote the 1832 quotation of Jesus Christ in the Sacred Grove, it is not possible to uphold the claim that the Lord told the Prophet on that occasion that a Christian of any denomination automatically qualified for eternal life (in the LDS understanding of the term).
While it is true that the Lord is quoted in the 1832 First Vision account as saying "all those who believe on my name may have eternal life" it can be seen in an earlier revelation dated 7 March 1831 that those who "believe on [Christ's] name" must also "come unto [Him]" in order to "have everlasting life" (D&C 45꞉5).
The Lord does not state in the 1832 narrative that eternal life is available to members of every Christian church. Rather, He declares unambiguously in that account that "none" of the existing Christian denominations of the time were keeping His commandments; they had all turned aside from His gospel. From this piece of information alone, it is clear that eternal life could not be made available to them; they were categorized by the Lord as being in a state of "sin" (cf. Romans 5꞉21; Romans 6꞉22-23). In the 1832 text Jesus Christ says to Joseph Smith - "keep my commandments," and in connection with this it can be seen in a revelation dated March 1829 that the Lord informed the Prophet that he could only be granted "eternal life" if he was "firm in keeping the commandments" that Christ gave unto him (D&C 5꞉21-22; cf. D&C 14꞉7; D&C 18꞉8; D&C 30꞉8).
On 1 November 1831 the Lord affirmed to adherents of the LDS faith that there was "only [one] true and living church upon the face of the whole earth" (D&C 1꞉30). Earlier—in May 1831—He had spoken specifically to members of "the church that profess my name" (compare with the 1832 document wording) and indicated that only the faithful members of it who endured would "inherit eternal life" (D&C 50꞉4-5). Thus, the blessing of eternal life could not be obtained without complying with certain conditions.
Before Joseph Smith penned the Lord's words that are found in the 1832 First Vision text he clearly understood that:
The implication of this last point is that only one church can perform ordinances that will be considered valid in the sight of the Lord. And so a person can only be truly obedient to all of the Lord's commandments by holding membership in His one true Church. Joseph Smith indicated in the introductory remarks of the 1832 history that he had received priesthood authority, from a heavenly source, which enabled him to "administer . . . the commandments . . . and the ordinances".
Critical sources |
|
One discrepancy between the 1832 First Vision account and the official 1838 recital is that it portrays Jesus Christ as prophesying that He will return to earth quickly to destroy wicked mortals. The 1838 story makes no mention of the impending doom of this planet's depraved inhabitants.
The claim that there is a discrepancy between the 1832 and 1838 First Vision accounts on the point of the Second Coming and destruction of the wicked appears to be a desperate attempt at sowing discord. It is a charge without much substance. The Prophet's own statement about the omission of certain items can be legitimately utilized to account for several differences in the two documents.
This criticism loses its negative effect when it is weighed in the balance against the content of the relevant historical documents. In the 1832 account the Lord says:
mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them ac[c]ording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father.
There is, indeed, no reference to this specific prophecy in the First Vision portion of the 1838 document. However, Joseph Smith clearly states in that very narrative that Jesus Christ told him "many other things" during the First Vision that he decided not to write down at that time! Thus, an argument from silence (on the part of the critics) is utterly unconvincing. A close look at the remainder of the 1838 historical text reveals that the angel Moroni did, in fact, speak to Joseph Smith about prophecies of the Savior's return and the destruction of the wicked. The Prophet reports:
[The angel] first quoted part of the third chapter of Malachi and he quoted also the fourth or last chapter of the same prophecy though with a little variation from the way it reads in our Bibles. Instead of quoting the first verse as reads in our books he quoted it thus, 'For behold the day cometh that shall burn as an oven, and all the proud <yea> and all that do wickedly shall burn as stubble, for <they> that cometh shall burn them saith the Lord of hosts, that it shall leave them neither root nor branch.' And again he quoted the fifth verse thus, 'Behold I will reveal unto you the Priesthood by the hand of Elijah the prophet before the coming of the great and dreadful day of the Lord.' . . . . He also quoted the second chapter of Joel from the twenty eighth to the last verse. He also said that this was not yet fulfilled but was soon to be.
The 1832 and 1838 histories present the very same prophecy of the destruction of the wicked at the time of the Lord's Second Coming. The 1832 account portrays the Lord speaking it personally; the 1838 account portrays an angel relaying the words of the Lord as recorded in prophetic, biblical texts. Either way, the message is the same.
Critical sources |
|
Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision account does not explicitly say that he was persecuted for relating his spiritual manifestation to others. Some have claimed that this stands as evidence that the Prophet's story evolved over time—probably to add a sense of drama. However, the Prophet's 1832 history of the Restoration talks about persecution in very close proximity to the First Vision recital. The persecution is situated squarely between the First Vision experience and the angel Moroni visitations. The documentary evidence presented above demonstrates conclusively that Joseph Smith did not see anything wrong with telling the basic elements of his First Vision story and either giving a passing reference to other elements or leaving them out altogether. Regardless, it was still a record of the very same experience that took place at the Smith homestead near Palmyra, New York.
Joseph Smith made some remarks in his 1832 First Vision account that have a marked degree of relevance to the argument being put forward by his critics. In relation to the period of time between the First Vision and the appearance of the Book of Mormon angel he said,
Since it is explicitly stated by Joseph Smith that nobody believed his story, it would be unreasonable to assume that all of the responses to it were friendly in nature. In fact, the Prophet says right in this text that before the Book of Mormon angel visited him his family was persecuted and afflicted for some unspecified reason(s). He did not elaborate upon the nature of the "many persecutions" that took place against his family because—as far as this particular document was concerned—he had elected not to write down "many things which transpired."
The following documentary evidence from the 1838 First Vision account strengthens the argument that the 1832 text is referring to some type of persecution that took place because of Joseph's initial spiritual experience.
This 1838 description corresponds very well with the "many persecutions and afflictions" that are mentioned in the 1832 account. It also matches closely with the 1832 statements that nobody would believe Joseph's story and he reflected upon this adverse situation in his heart.
It should be pointed out that even though the 'persecution' theme is very pronounced in the 1838 account it is a piece of the story that was not always mentioned or emphasized in subsequent retelling (both published and verbal).
This last example is especially significant because it is an obvious reference to the Methodist minister who is spoken of in the 1838 History of the Church account. The 1844 rehearsal of events is less detailed but it is, nevertheless, the same exact story. The 1844 document clearly demonstrates that Joseph Smith did not always include an equal amount of story elements in his recitals of the First Vision. Critics of this manifestation should, therefore, not expect any such thing when they scrutinize the pertinent documents. If an element of the story was not known by one particular audience it cannot be automatically assumed that it was not known by another.
Online |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
The capitalized word "Angels" in Joseph Smith's diary entry for 14 November 1835 has given rise to two distinct criticisms by detractors of the faith, and one misguided conclusion by some Latter-day Saints.
The mention of "many angels" in the November 9, 1835 diary entry is a clarifying detail. The appearance of the Father and Son are clearly referenced separately from the mention of the "many angels." Since the visit of the Father and Son are acknowledged in the diary entry for the 9th the change from "first visitation of Angels" to "the First Vision" in the History of the Church entry is not a "falsification" of information.
Joseph Smith never actually referred to what we now call the "First Vision" by that name. Instead, he referred to it as the "first visitation of angels" or the "first communication." Joseph also referred to Moroni's visit as "another vision of angels."

The account that Joseph entered in his journal on 9 November 1835 was a detailed account which clearly describes two personages, as well as "many angels." The account that Joseph wrote just five days later in his journal on 14 November 1835 was a one line summary of the event, which he described as "the first visitation of Angels." Critics of the Church seem to believe that Joseph completely changed his story from "two personages" to "Angels" over the course of only five days. The truth is that Joseph referred to all of the personages that appeared to him as "angels."
This confusion regarding "angels" versus "personages" is illustrated in a critical "Mormoninfographic".[70] We have illustrated the error by comparing Joseph's journal entries on both days.


There were at the time people who went to the wood to pray after reading the Bible, and as a result received visions and epiphanies. The Encyclopedia of Mormonism (1992; 2007) noted that "[i]nitial skepticism toward Joseph Smith's testimony was understandable because others had made similar claims to receiving revelation from God."[71] Similarly, the Church's new narrative history Saints (2018) notes that after Joseph's vision when he spoke to the reverend about his vision that "[a]t first the preacher treated his words lightly. People claimed to have heavenly visions from time to time."[72] Visionaries are not that uncommon in environments where people are routinely open to the divine. Even the famous Charles Finney had one. Finney, after retiring to the woods to pray, described the experience:
Just at this moment I again thought I heard someone approach me, and I opened my eyes to see whether it were so. But right there the revelation of my pride of heart, as the great difficulty that stood in the way, was distinctly shown to me. An overwhelming sense of my wickedness in being ashamed to have a human being see me on my knees before God, took such powerful possession of me, that I cried at the top of my voice, and exclaimed that I would not leave that place if all the men on earth and all the devils in hell surrounded me. "What!" I said, "such a degraded sinner I am, on my knees confessing my sins to the great and holy God; and ashamed to have any human being, and a sinner like myself, find me on my knees endeavoring to make my peace with my offended God!" The sin appeared awful, infinite. It broke me down before the Lord.
Just at that point this passage of Scripture seemed to drop into my mind with a flood of light: "Then shall ye go and pray unto me, and I will hearken unto you. Then shall ye seek me and find me, when ye shall search for me with all your heart." I instantly seized hold of this with my heart. I had intellectually believed the Bible before; but never had the truth been in my mind that faith was a voluntary trust instead of an intellectual state. I was as conscious as I was of my existence, of trusting at that moment in God's veracity. Somehow I knew that that was a passage of Scripture, though I do not think I had ever read it. I knew that it was God's word, and God's voice, as it were, that spoke to me. I cried to Him, "Lord, I take Thee at Thy word. Now Thou knowest that I do search for Thee with all my heart, and that I have come here to pray to Thee; and Thou hast promised to hear me."
That seemed to settle the question that I could then, that day, perform my vow. The Spirit seemed to lay stress upon that idea in the text, "When you search for me with all your heart." The question of when, that is of the present time, seemed to fall heavily into my heart. I told the Lord that I should take Him at his word; that He could not lie; and that therefore I was sure that He heard my prayer, and that He would be found of me.
He then gave my many other promises, both from the Old and the New Testament, especially some most precious promises respecting our Lord Jesus Christ. I never can, in words, make any human being understand how precious and true those promises appeared to me. I took them one after the other as infallible truth, the assertions of God who could not lie. They did not seem so much to fall into my intellect as into my heart, to be put within the grasp of the voluntary powers of my mind; and I seized hold of them, appropriated them, and fastened upon them with the grasp of a drowning man.
I continued thus to pray, and to receive and appropriate promises for a long time, I know not how long. I prayed till my mind became so full that, before I was aware of it, I was on my feet and tripping up the ascent toward the road. The question of my being converted, had not so much as arisen to my thought; but as I went up, brushing through the leaves and bushes, I recollect saying with emphasis, "If I am ever converted, I will preach the Gospel."[73]
Although Finney doesn't claim to have seen any personages, he does describe a communication with God. Joseph Smith describes his experiences in much the same way as others in his environment did.
Keep in mind that Joseph prayed to find out if his sins had been forgiven. And he discovered that they had. This pleased him greatly. Why did he pray about this matter? The reason is that joining a church at that time often required that one explain one's standing with God to a preacher. We are dealing with Protestant sects. And conservative Protestants believe that one is saved (justified) at the moment one confesses Jesus Christ as Lord and Savior. So Joseph, as he faced the competing Protestant sects, was deeply concerned about his sins. One had to demonstrate to oneself and also convince a preacher that one had been saved—that is, justified. And there were many instances in which prayers were answered by visions in which the person learned that God had forgiven their sins.
The difference between Joseph's experience and many other accounts by visionaries, is that, in addition to being told that his sins were in fact forgiven, he was also told not to join any denomination. When he told that part of his visionary experience, it got him into big trouble with preachers. It was not the vision that was a problem for preachers, but his reporting that he should not join some sect.
So the fact is, contrary to our current way of telling his story, the First Vision was not the beginning of Joseph's call as Seer, Prophet, Revelator and Translator. His vision signaled the beginning of the restoration. It did not begin the work of the restoration.It steered him away from joining one of the competing denominations. It was Joseph's subsequent encounters with Moroni that made him a Seer, and eventually the founding Prophet of a fledgling Church, and not his initial vision, which was initially for him a private event about which he was reluctant to talk, though eventually he dictated some accounts that were found and published during our lifetime. Joseph told a few people about it, word got around, and this caused him much trouble with Protestant preachers.
Joseph eventually wrote the account of that early vision late in his life because rumors about it had circulated and caused him difficulty. But neither Joseph nor any of the other early Saints offered that vision as a reason for others to become Latter-day Saints during his lifetime. It was only much later that what we now call the First Vision began to take on a special importance for the Saints. One reason is that Americans soon did not live in a visionary environment. The great Charles Dickens, writing in England, explained why. He called Joseph Smith vision an absurdity—"seeing visions in the age of railways."
Wilford Woodruff came into the Church of Jesus Christ because he had known earlier in his life someone he believed was a prophet who had alerted him to the soon to be restoration of primitive Christianity. This remarkable story, which was included in the lesson manual on President Woodruff, illustrates the visionary world in which Joseph was raised. Though there were a few—one or two—instances in which the visionary reported encounters with two heavenly messengers, it was most often God the Son who they reported appearing to them.
But there have been and still are peoples not impacted by post-enlightenment skepticism about divine things who are open to visions and other dramatic encounters with the divine, though they often do not speak in public about such things, since they tend to see them as strictly private blessings and not something about which one ought to be gossiping and boasting.
The first missionaries in the Church used The Book of Mormon, not the First Vision, as a witness that the heavens were open, and that each individual, by applying the promise in Moroni 10:3-5, can receive a direct manifestation from Heavenly Father, through the Holy Ghost, that The Book of Mormon is true. After that testimony is gained, it follows that Joseph Smith is a true prophet, as he brought The Book of Mormon forth and restored the fullness of the Gospel under the direction of the Savior.
The fledgling Church of Christ began with the Book of Mormon, the witnesses to the plates, the restoration of priesthood keys, and not directly with what we call the First Vision, though that initial experience assisted in Joseph avoiding what could be perceived as damaging sectarian contamination. The historical record shows that Joseph never gave any attention to the creeds or arguments of quarreling preachers. This was the purpose served by the First Vision.
Some Christians accept Paul's vision while rejecting that of Joseph Smith for a variety of reasons. Richard Lloyd Anderson made the following comparisons.
Many Christians who comfortably accept Paul’s vision reject Joseph Smith’s. However, they aren’t consistent in their criticisms, for most arguments against Joseph Smith’s first vision would detract from Paul’s Damascus experience with equal force.
For instance, Joseph Smith’s credibility is attacked because the earliest known description of his vision wasn’t given until a dozen years after it happened. But Paul’s earliest known description of the Damascus appearance, found in 1 Corinthians 9꞉1, was recorded about two dozen years after his experience.
Critics love to dwell on supposed inconsistencies in Joseph Smith’s spontaneous accounts of his first vision. But people normally give shorter and longer accounts of their own vivid experiences when retelling them more than once. Joseph Smith was cautious about public explanations of his sacred experiences until the Church grew strong and could properly publicize what God had given him. Thus, his most detailed first vision account came after several others—when he began his formal history.
This, too, parallels Paul’s experience. His most detailed account of the vision on the road to Damascus is the last of several recorded. (See Acts 26:9–20.) And this is the only known instance in which he related the detail about the glorified Savior prophesying Paul’s work among the Gentiles. (See Acts 26:16–18.) Why would Paul include this previously unmentioned detail only on that occasion? Probably because he was speaking to a Gentile audience, rather than to a group of Jewish Christians. Both Paul and Joseph Smith had reasons for delaying full details of their visions until the proper time and place.[74]
Joseph Smith left several accounts of his First Vision. None of these accounts is identical with any other. As the main page discusses, some critics wish to argue that Joseph's vision accounts are mutually contradictory, and thus that there was no vision.
Latter-day Saints often point out that the Bible's accounts of Paul's vision on the road to Damascus appear to be contradictory. Yet, the Church's sectarian critics accept Paul's account as true despite the Bible containing apparently frank contradictions in its accounts. While accepting or explaining away these discrepancies, the critics nevertheless refuse to give Joseph Smith the same latitude. Members of the Church have long pointed out that this is a clear double standard, designed to bias the audience against Joseph from the beginning.
Perhaps because of the force of this argument, some critics have begun to argue that no contradiction exists between the versions of Paul's vision.
Author Richard Abanes wrote that contradictions in the stories of Paul's vision were
long ago resolved by scholars analyzing the Greek texts. The discrepancies in Paul's account involve modern ignorance of the Greek wording used.[75]
In support of this claim, Abanes cites W.E. Vine, Vine's Expository Dictionary of New Testament Words p. 544.
Despite Abanes' claim, Greek scholarship has not resolved this issue. In fact, his use of the scholarship is dated, he ignores contrary views, and does not seem to realize that the Bible text itself (including the Acts of the Apostles) violates his supposed 'rule' more often than it keeps it.
The two verses usually at issue are Acts 9꞉7 and Acts 22꞉9. For example, one Wikipedia editor claims that
"There is no conflict in the three accounts of Paul's vision if you read Acts 22:9 in any version other than the KJV. For instance, in the New American Standard Bible and the New International version, it says that Paul's companions did not "understand the voice"—that is hear what was uttered with understanding."[76]
| Bible version | Acts 9:7 | Acts 22:9 | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summary |
Heard voice, saw no one? |
Saw light, heard no voice? |
|
| KJV |
And the men which journeyed with him stood speechless, hearing a voice, but seeing no man. |
And they that were with me saw indeed the light, and were afraid; but they heard not the voice of him that spake to me. |
|
The work cited by Abanes is not a recent work of Greek scholarship—it was first published in 1940.[77] In the reference for ακούω, we read:
Thus, by this source, Abanes hopes to argue that there can be "no idea of any contradiction":
| Factor | Acts 9:7 | Acts 22:9 | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case |
partitive genitive |
accusative |
|
| Meaning |
One hears the sound |
One hears the message |
—|- |
We have seen Abanes appeal to a source that was more than sixty years old at the time of his writing. Have modern Greek scholars anything to add to our discussion?
Daniel Wallace (a non-LDS, conservative Christian scholar) wrote of this same issue:
...There seems to be a contradiction between this account [Acts 9:7] of Paul's conversion and his account of it in Acts 22, for there he says, "those who were with me..did not hear the voice..." However, in Acts 22:9 the verb ακούω takes an accusative direct object. On these two passages, Robertson states: '...it is perfectly proper to appeal to the distinction in the cases in the apparent contradiction....The accusative case (case of extent) accents the intellectual apprehension of the sound, while the genitive (specifying case) calls attention to the sound of the voice without accenting the sense.'...
The NIV [a conservative Bible translation, the New International Version] seems to follow this line of reasoning....[thus the differences in case] can be appealed to to harmonize these two accounts....(italics in original)[78]
Thus, Wallace is here dealing with the exact verses under discussion, and notes the exact argument which Abanes makes. Does he agree? Let us see:
On the other hand, it is doubtful that this is where the difference lay between the two cases used with ακούω in Hellenistic Greek: the N[ew] T[estament] (including the more literary writers) is filled with examples of ακούω + genitive indicating understanding[79]....as well as instances of ακούω + accusative where little or no comprehension takes place[80]}....The exceptions, in fact, are seemingly more numerous than the rule!
Thus, regardless of how one works through the accounts of Paul's conversion, an appeal to different cases probably ought not form any part of the solution (italics and bold italics in original).[81]
Thus, the New Testament itself does not agree with Abanes' reading. Far from supporting him, Greek scholarship argues against his solution—the Bible has more examples where his supposed "rule" is broken than when it is followed. (Even Acts itself contains three counterexamples!)
It would seem that this approach has been developed by those who wish to maintain the idea of biblical inerrancy in the face of the Greek evidence.
Critical sources |
|
Wiki links |
|
Online |
|
Video |
|
Navigators |
Accounts |
|
Historical context |
|
Doctrinal impact |
Video published by the Church History Department.
Video from FAIR
Joseph's concern about religion started when he was twelve years old, close on the heels of the revival of 1817. In his 1832 account, Joseph notes that his concern about religion began at age 12 (1817-1818):
At about the age of twelve years my mind become seriously imprest with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul which led me to searching the scriptures believeing as I was taught, that they contained the word of God thus applying myself to them and my intimate acquaintance with those of different denominations led me to marvel excedingly for I discovered that they did not adorn instead of adorning their profession by a holy walk and Godly conversation agreeable to what I found contained in that sacred depository this was a grief to my Soul... (Joseph Smith's 1832 account of the First Vision)
Richard Bushman notes that this "would have been in late 1817 and early 1818, when the after-affects of the revival of 1816 and 1817 were still felt in Palmyra." [1]
Joseph Smith talked of observing, as a 14-year-old, "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion" in the Palmyra area during the Spring of 1820. Joseph notes that "It commenced with the Methodists, but soon became general among all the sects in that region of country." There is documented evidence of at least one Methodist camp meeting in the Palmyra area during that period, which only by chance happened to be mentioned in the local newspaper because of a specific death that seemed to be associated with it. In addition, there are newspaper articles talking of large-scale revival activity in the larger region surrounding Palmyra during the same general period when Joseph Smith said that it was taking place.
It is reasonable to assume based upon the facts that the Methodists had more than one camp meeting during this period. This could easily account for the religious excitement in Palmyra that, in Joseph's mind at age 14, began with the Methodists.
Joseph continues in his 1832 account: "[T]hus from the age of twelve years to fifteen I pondered many things in my heart concerning the sittuation of the world of mankind the contentions and divi[si]ons the wicke[d]ness and abominations and the darkness which pervaded the of the minds of mankind my mind become excedingly distressed for I become convicted of my sins." In July, 1819, several years after Joseph said his mind became "seriously imprest," a major Methodist conference was held near Palmyra:
[T]he Methodists of the Genesee Conference met for a week in Vienna (later Phelps), a village thirteen miles southeast of the Smith farm on the road to Geneva. About 110 ministers from a region stretching 500 miles from Detroit to the Catskills and from Canada to Pennsylvania met under the direction of Bishop R. R. Robert to receive instruction and set policy. If we are to judge from the experience at other conferences, the ministers preached between sessions to people who gathered from many miles around. It was a significant year for religion in the entire district. . . . The Geneva Presbytery, which included the churches in Joseph's immediate area, reported in February, 1820, that "during the past year more have been received into the communion of the Churches than perhaps in any former year." Methodists kept no records for individual congregations, but in 1821 they built a new meetinghouse in town. [2]

Some claim that there were no religious revivals in the Palmyra, New York area in 1820, contrary to Joseph Smith's claims that during that year there was "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion...indeed, the whole district of country seemed affected by it" Joseph Smith—History 1:5 Joseph Smith talked of observing, as a 14-year-old, "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion" in the Palmyra area during the Spring of 1820. Joseph notes that "It commenced with the Methodists, but soon became general among all the sects in that region of country."
Abundant evidence of religious excitement exists to substantiate Joseph’s account. This has been thoroughly summarized by Pearl of Great Price Central. Their analysis may be accessed by clicking on the hyperlinked text.
One should keep in mind that Joseph Smith never used the term "revival" in his description - he simply described it as "an unusual excitement on the subject of religion." To a 14 year old who had been concerned about religion starting at age 12 after the 1817 revival, the ongoing camp meetings in the town in which he lived would certainly qualify.

Critics of Joseph Smith claim that no revival is mentioned in the 1832 First Vision account because the actual word 'revival'—or something similar—is not found within the text. But they have failed to notice a distinct pattern of words that demonstrate a definite link between the various First Vision accounts.
When the September—November 1832 First Vision account is compared with subsequent recitals (especially 1838), and one partial previous rendition, it appears that they are all telling the same story: Prior to the First Vision event there were contentions and divisions among the different religious denominations in connection with a revival. It seems, therefore, that the Prophet's handwritten 1832 account does indeed make a passing reference to revival activity.
There are several other phrases in the Prophet's 1832 account that can be interpreted as references to revivals. For instance, Joseph Smith said that when he was "about the age of twelve years" (23 December 1817—23 December 1818) he became seriously concerned about the welfare of his soul. Why did these feelings arise at this point in time? Possibly because there was a Methodist camp-meeting/revival from June 19th through the 22nd, 1818 held in Palmyra, New York.[8]
Joseph Smith pointed to a time period "from the age of twelve years to fifteen" (i.e., between 23 December 1817 and 23 December 1821) when he –
Some of the themes enumerated above can be matched with the Prophet's other descriptions of things that happened during the revival activity of Palmyra and its vicinity. This matching of themes tends to support the argument that the 1832 text does indeed refer to revival activity.
The phrase "I cried unto the Lord for mercy" in Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision account also has a strong ring of revivalism to it. Rev. George Peck recounted the happenings at a Methodist camp meeting held on 4 July 1816 in Plymouth, New York. He said that "There was an unbroken roar of fervent supplication all over the ground, while the awful voice of the preacher resounded." One person then fell to the ground and cried for mercy.[9]
Wiki links |
|
Online |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
Joseph Smith's stated motivation for praying to the Lord changes between the first known account of the First Vision (1832) and the official version of it (1838). The 1832 account emphasizes his desire for a forgiveness of sins, and the 1838 (official) account emphasizes his desire to know which church was right. Some critic claim that Joseph changed his story in later years.
The texts that are employed by critics to justify the charge of 'differing motivations' are as follows:
1832
1838
The words that precede the point at which Joseph Smith offers his prayer in the 1832 text demonstrate that the anti-Mormon claim about his motivation changing is not sustainable. These words read as follows (standardized for readability):
Historian Christopher Jones has observed that Joseph Smith's 1832 account (and indeed much of his other three accounts) are shaped as Methodist conversion narratives. Within Methodism (and indeed the broader religious culture of Joseph Smith's day), finding forgiveness of sins and joining the right Church rode in tandem. You receive forgiveness of sins by joining the right Church. If you don't follow the correct, "biblical" doctrine then you can't receive such forgiveness.[10] In the case of Joseph Smith, he receives forgiveness of sins and is told not to join any church with which he was acquainted at the time.
There are those who claim that Joseph Smith only claims to seek forgiveness of sins in his 1832 account. These critics ignore the larger historical context under which the 1832 account was written (documented by Jones) and also fail to take notice of scriptural passages quoted near the end of the account in which Christ echoes Matthew 15:8-9:
This clearly does not refer to young Joseph's seeking of a forgiveness of sins. It must refer to an apostasy and restoration of a Church—the true Church of Christ that Joseph had already proclaimed to restore as Doctrine and Covenants 1 (revealed in 1831) makes clear:
Some may counter that this only refers to corrupt people and not corrupt churches or religions. Going back to the passage from the 1832 account cited above, one reads "the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doth good no not one..." This phrase ('and none doeth good no not one') is echoed in a few scriptural passages (Psalm 53: 3; Romans 3: 10, 12; Moroni 7:17) but for our purposes we will highlight one of these occurrences in JST Psalm 14:2. The Church still describes this passage in its heading as lamenting "the loss of truth in the last days[.]" The passage "looks forward to the establishment of Zion." The italics represent edits made by Joseph Smith to the text:

Joseph Fielding McConkie said, 'The JST rendering of this Psalm reads like another account of the First Vision.'[11]
The late Matthew Brown suggested that Joseph's translation of Psalm 14 took place 'shortly after late July 1832.'[12] He even goes so far to say that 'the JST Psalm 14 text may have served as a prototype of sorts for the composition of the 1832 historical document.'[13]
The 1838–39 account’s mention of 'corrupt professors' seems to be reflected in the JST’s 'their teachers are workers of iniquity.' . . . JST Psalm 14:2-4 features 'all these who say they are [the Lord’s]' being rejected by the Lord due to them having 'gone aside,' 'become filthy,' and 'none of them…doing good.' And this is laid at the feet of their teachers who 'are workers of iniquity' [14] This use of Psalm 14 to be explanatory for Joseph's use of no one doing good is strengthened by the fact that Psalm 14 is quoted specifically earlier in the 1832 account ("And when I considered upon these things my heart exclaimed, 'Well hath the wise man said, It is a fool that saith in his heart there is no God.'")
Thus, to summarize again, those who don't do good are all people and this is caused by false teachers teaching incorrect doctrine.
The 1832 account emphasizes Joseph's want of forgiveness as a means to the end of restoring the true Church of Christ. This is completely in line with the rest of the accounts and thus the standard narrative of the First Vision and Joseph's motives in seeking such a vision as taught officially by the Church.
A longer version of this argument is made by Walker Wright and historian Don Bradley in a 2023 paper for BYU Studies.[15]
The First Vision has been a center of both faith and controversy. While millions of Latter-day Saints affirm it as the beginning of the Restoration, others see it as an ever-growing fish tale. The multiple accounts of the First Vision vary in detail, with Joseph Smith’s earliest written account (1832) lacking some of the elements found in his later accounts. However, some of these elements—particularly the appearance of God the Father as part of the First Vision experience—are laced throughout Joseph Smith’s translation of the Bible. These historical threads ultimately culminate in his translation of Psalm 14, which weaves together many of the elements supposedly lacking in Smith’s earliest account of the First Vision. But why bring these threads together in Psalm 14? What was its connection with his First Vision? A basic comparison of Psalm 14 with elements of the First Vision shows that elements of this psalm are found in the background of the vision, as Joseph Smith narrated it, and even in the words of Deity spoken within the vision itself.
It is clear from a consultation of the 1832 text that Joseph Smith's desire to be forgiven of his personal sins was NOT the only motivation for his prayer in the wilderness. He prayed (as he explicitly states) because of "all" of the things he mentions - including the desire to worship God in truth; according to His laws (which Joseph did not believe was the case among any of the Christians denominations that he knew of).
The 1832 textual pattern of (1) desire to prepare for eternity / worship God in truth and (2) desire for forgiveness of personal sins can be detected in subsequent First Vision recitals, demonstrating that there is no change in his declared motive over time. The confusion of the critics on this issue arises when they do not see exact matches in themes across documents or insist that every detail of the story be present in every text that relates it.
1832 (Smith)
1834 (Cowdery/Smith)
1835 (Smith)
1838 (Smith)
1840 (Pratt)
1842 (Smith)
1842 (Hyde)
Critical sources |
|
Critics claim that there is a contradiction between the 1832 account of Joseph Smith's First Vision and the rest of his first-hand accounts. They also claim that the same contradiction occurs internally in the 1838 account. It is alleged that Joseph Smith concluded prior to going to the grove of trees to pray that all the denominations on the earth were false. This supposedly contradicts the 1835 and 1838 accounts in which Joseph expresses doubt as to which Church was true prior to going to the grove.
In his 1832 history, Joseph Smith said:
I found [by searching the scriptures] that mankind did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatized from the true and living faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament
In his 1835 account, Joseph Smith said, "I knew not who [of the denominations] was right or who was wrong."
In his 1838 account of the Vision, Joseph writes:
The 1832 account then, according to some critics, contradicts the 1835 and 1838 account in that Joseph had already determined before seeing God and Jesus that there was no true Church and thus the only motive for going to the grove in the 1832 account would be to obtain a forgiveness of sins and not to find the true Church.
Author J.B. Haws describes the criticism as it relates to the 1838 account specifically:
Here is the essence of that trouble, as some have seen it. In Joseph’s 1838–39 dictated account (the account that would eventually find its way into the LDS Church’s canon as the official Joseph Smith—History), he described his youthful confusion about the competing religious sects that he encountered in these words: "In the midst of this war of words and tumult of opinions, I often said to myself: What is to be done? Who of all these parties are right; or, are they all wrong together?" (Joseph Smith History 1:10). According to this narrative, it seems that fourteen-year-old Joseph had already considered the possibility that all churches could be "wrong together." Yet only eight verses later (by the account’s current scriptural format), Joseph reported what seems like surprise in response to the divine injunction that he must join no church, "for they were all wrong"—and "it had never entered into [his] heart that all were wrong" (JS—H 1:18–19). But didn’t we just read that the "all were wrong" possibility had entered his heart in verse 10? Why such an apparently careless and contradictory oversight in the narrative?[16]
Critics claim that this is a contradiction and evidence that the First Vision story evolved over time.
Such a claim is a false dilemma, as we will now see.
Historian Christopher Jones has observed that Joseph Smith's 1832 account (and indeed much of his other three accounts) are shaped as Methodist conversion narratives. Within Methodism (and indeed the broader religious culture of Joseph Smith's day), finding forgiveness of sins and joining the right Church rode in tandem. You receive forgiveness of sins by joining the right Church. If you don't follow the correct, "biblical" doctrine then you can't receive such forgiveness.[17] In the case of Joseph Smith, he receives forgiveness of sins and is told not to join any church. Thus even if Joseph's main emphasis is forgiveness of sins in the 1832 account, that doesn't mean he's not talking about what Church is true.
Those critics who claim that Joseph is only speaking about the forgiveness of sins in the 1832 account are ignorant of the larger historical context under which the 1832 account was written (documented by Jones) and also fail to take notice of important scriptural passages quoted near the end of the account. Speaking about the condition of the world, Christ, speaking to Joseph, echoes Matthew 15:8-9:
'[T]hat which hath been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Apostles' might easily refer to an apostasy and restoration.
Some may counter that this only refers to corrupt people and not corrupt churches or religions. Going back to the passage from the 1832 account cited above, one reads "the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doth good no not one..." This phrase ('and none doeth good no not one') is echoed in a few scriptural passages (Psalm 53: 3; Romans 3: 10, 12; Moroni 7:17) but for our purposes we will highlight one of these occurrences in JST Psalm 14:2. The Church still describes this passage in its heading as lamenting "the loss of truth in the last days[.]" The passage "looks forward to the establishment of Zion." The italics represent edits made by Joseph Smith to the text:

Joseph Fielding McConkie said, 'The JST rendering of this Psalm reads like another account of the First Vision.'[18]
The late Matthew Brown suggested that Joseph's translation of Psalm 14 took place 'shortly after late July 1832.'[19] He even goes so far to say that 'the JST Psalm 14 text may have served as a prototype of sorts for the composition of the 1832 historical document.'[20]
"The 1838-39 account’s mention of 'corrupt professors' seems to be reflected in the JST’s 'their teachers are workers of iniquity.' . . . JST Psalm 14:2-4 features 'all these who say they are [the Lord’s]' being rejected by the Lord due to them having 'gone aside,' 'become filthy,' and 'none of them…doing good.' And this is laid at the feet of 'their teachers' who 'are workers of iniquity.'"[21] This use of Psalm 14 to be explanatory for Joseph's use of no one doing good is strengthened by the fact that Psalm 14 is quoted specifically earlier in the 1832 account ("And when I considered upon these things my heart exclaimed, 'Well hath the wise man said, It is a fool that saith in his heart there is no God.'")
Thus, to summarize again, those who don't do good are all people and this is caused by false teachers teaching incorrect doctrine. Under this understanding, the 1832 account of Joseph Smith's First Vision is giving implicit credence that Joseph was indeed seeking to know from God which Church to join because the teachers of other denominations had become corrupt.
Author Jim Bennet describes one approach that a person can take while seeking to reconcile this with their faith and that is to focus interpretation on the phrase "entered into my heart":
The key phrase is "entered into my heart."
We can have confidence in what Joseph means by this because it is not the only time he uses variations of this phrase. Here’s what he says about his experience reading James 1:5.
- Never did any passage of scripture come with more power to the heart of man than this did at this time to mine. It seemed to enter with great force into every feeling of my heart. [JSH 1:12, emphasis added]
This is a phrase Joseph uses to describe something more powerful than mere intellectual assent. He’s describing a spiritual experience, where the feelings of the heart complement and contribute to clarity of mind. It’s a concept that shows up in the Doctrine and Covenants, too:
- Yea, behold, I will tell you in your mind and in your heart, by the Holy Ghost, which shall come upon you and which shall dwell in your heart.
- Now, behold, this is the spirit of revelation; behold, this is the spirit by which Moses brought the children of Israel through the Red Sea on dry ground. [D&C 8:2-3, emphasis added]
Joseph had clearly considered the possibility all churches were in error in verse 10 (and in the 1832 account,) but the idea hadn’t really sunk in – i.e. entered into his heart – until after verse 18.
I think all of us have had this experience – things happen that we choose not to believe. Even when we have solid information, we don’t allow our intellectual knowledge to become wisdom and "enter into our hearts." He’s describing the very human process of denial, much like Amulek from the Book of Mormon, who once said of his own testimony, "I knew concerning these things, yet I would not know." (Alma 10:6)
Make up your mind, Amulek! Did you know or didn’t you know?! That’s a direct contradiction!
In the case of "Forgiveness of Sins v. Which Church is True,"... Joseph was preoccupied with what he needed to do to prepare to meet God. You see that in all of Joseph’s firsthand accounts.
"[M]y mind become seriously imprest with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul," he wrote in 1832. "I considered it of the first importance that I should be right, in matters that involve eternal consequ[e]nces;" he wrote in 1835. "My mind was called up to serious reflection and great uneasiness... my feelings were deep and often poignant... What is to be done?" he wrote in 1838. "I began to reflect upon the importance of being prepared for a future [i.e. eternal] state," he wrote in 1842. These are different words, to be sure, but there’s no mistaking the commonality of their underlying meaning. I believe that all these accounts show that Joseph’s deepest desire was to know what he had to do to be saved. That was the one and only item on his agenda in the Sacred Grove.
The question he asked, then, about which church he should join tells us about young Joseph’s theological assumptions. It’s clear in all accounts that salvation and church membership were inextricably linked in his mind. Even in 1832, where he doesn’t specify what question he asked the Lord before his sins were forgiven, he goes on at great length about his concern for the error he sees in all the churches.The possibility that a church might not be necessary doesn’t seem to occur to Joseph, nor would it have been likely to occur to anyone in the early 19th Century. Christ without a church in 1820? Who could imagine such heresy? Certainly not an illiterate farmboy who, at that point, had no inkling what the Lord had in store for him.
In Joseph’s mind, "which church is the right one" and "how can I get my sins forgiven" were variations on the same theme, and only minor variations at that. Rather than show inconsistency, the two accounts are remarkably united in their depiction of Joseph’s concern for his soul and his assumptions about what was necessary to save it.
So with that understanding, the apparent contradiction about whether or not he had decided that all the churches were wrong prior to praying becomes far less problematic. The 1832 account spends more time detailing the specific problems with all the churches than the 1838 account, indicating that Joseph still believed in the importance of joining a church to gain access to the Atonement. True, he doesn’t explicitly say that any church membership is necessary, but he didn’t have to – those reading his account in the 19th Century would have had the same assumptions, and neither Joseph nor his audience would have even considered the modern/post-modern idea of an effectual Christian life outside the boundaries of organized religion. Even if all the churches were wrong to one degree or another, surely Joseph would still have felt it necessary to join the best one... [22]
Speficially addressing the passages from JS History 1: 10 and 18, J.B. Haws wrote:
In a draft of Joseph Smith’s history that was written sometime in 1840–41 by scribe Howard Coray (but only essentially rediscovered in the Church’s archival holdings in 2005), the corresponding passage reads differently:
Joseph Smith—History 1:18–19
- I asked the Personages who stood above me in the light, which of all the sects was right (for at this time it had never entered into my heart that all were wrong)—and which I should join. I was answered that I must join none of them, for they were all wrong . . .
Howard Coray’s 1839–41 history (labeled Draft 3 in Histories, Volume 1 of The Joseph Smith Papers)
- I asked the Personages who stood in the light; Which of the sects were right. (for I supposed that one of them were so.) and which I should join. I was answered "join none of them; they are all are wrong . . ."
Coray’s version suggests that Joseph still "supposed"—still believed, still considered it most likely—that one of the sects was right, even if he had considered the possibility that such was not the case. Thanks to the careful editorial scrutiny of The Joseph Smith Papers scholars, it is apparent that Coray’s draft was written after the draft of Joseph Smith’s history (labeled Draft 2 in the handwriting of James Mulholland) that was eventually published in the Times and Seasons and then the Pearl of Great Price. The Joseph Smith Papers volume editors note that, "for whatever reason," Joseph Smith chose that Draft 2 (Mulholland) version for eventual publication, even though there is evidence to suggest that Coray transcribed as Joseph "read aloud from Draft 2 in the large manuscript volume, directing editorial changes as he read." With that background in mind, the parallel phrases above suggest an affinity of sentiment, such that the phrase "it had never entered into my heart" meant, essentially, "I [still] supposed one of them were [right]"—which reinforces the reading that Joseph held out hope in his heart that he would be pointed to the true denomination.[16]:99–100
Haws describes another way to view both the 1832 account and 1838 account:
One minor drawback in reading Joseph Smith’s history in its current scriptural format is that the verse divisions might inadvertently separate his thoughts too starkly. Because of that potential challenge, the second possibility proposed here is that the contradiction between verses 10 and 18 might simply be a question of antecedents in verse 10. Thus one final alternate reading (and reconciliation) of those verses becomes clearer in the paragraph format of the Draft 2 (Mulholland) manuscript version of Joseph Smith’s history. In what is now verse 9 in the Pearl of Great Price version, Joseph describes the furious activity of three named denominations: the Presbyterians, the Baptists, and the Methodists. Those were the major players in the religious competition that was all around him in that region of New York. And those three groups preached, importantly, distinct soteriological visions of Christianity. If, however, verse 10 is not seen as completely separate from verse 9, then we might understand Joseph’s questions as being much more specific.
Here is how the passage appears in Draft 2 (Mulholland) of Joseph Smith’s history:
- My mind at different times was greatly excited for the cry and tumult were so great and incessant. The Presbyterians were most decided against the Baptists and Methodists, and used all their powers of either reason or sophistry to prove their errors, or at least to make the people think they were in error. On the other hand the Baptists and Methodists in their turn were equally Zealous in endeavoring to establish their own tenets and disprove all others.
- In the midst of this war of words, and tumult of opinions, I often said to myself, what is to be done? Who of all these parties are right? Or are they all wrong together? and if any one of them be right which is it? And how shall I know it?
Read in that way, new attention to the determiners and pronouns might be in order. Which of all of these parties—that is, the Presbyterians, Baptists, or Methodists—is right? Or are they—Presbyterians, Baptists, Methodists— all wrong together? If any of them—Presbyterians, Baptists, Methodists—be right, which is it? It seems reasonable to conclude that Joseph wondered not about the possibility that there was no true religion on the earth, but only that the principal religions represented in his area might all be wrong. Hence, his crucial question—his "object in going to enquire of the Lord"— was "to know which of all the sects was right," and perhaps it was the subsequent instruction to join no sect anywhere ("for they were all wrong") that would have been surprising; in that case, this latter possibility was the one that had never entered into his heart.
Again, this is only suggested as one way to read the text—but it is one that also seems to fit with a telling line in the earliest known written account of the First Vision, one from 1832 that Joseph Smith partly dictated and partly wrote. The key is something he stated about personal familiarity:
In that 1832 history, Joseph wrote in his own hand:
- At about the age of twelve years my mind become seriously [impressed] with regard to the all importent concerns of for the wellfare of my immortal Soul which led me to searching the scriptures believeing as I was taught, that they contained the word of God thus applying myself to them and my intimate acquaintance with those of differant denominations led me to marvel exceedingly for I discovered that <they did not adorn> instead of adorning their profession by a holy walk and Godly conversation agreeable to what I found contained in that sacred depository this was a grief to my Soul . . .
The fact that his conclusions were based on an "intimate acquaintance with those of differant denominations" should not be overlooked. His subsequent recollections do seem to reflect an expanded understanding of a broader apostasy: "by searching the scriptures I found that mand <mankind> did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatised from the true and liveing faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the new testament." Yet his choice of words ("no society or denomination") and his declaration that "I cried unto the Lord for mercy for there was none else to whom I could go and to obtain mercy" seem to reflect his discouragement with his local options and his growing assurance that only divine intervention could help him transcend that confusion.
It may, then, have been the sheer universality of the apostasy ("join none of them") that had not entered into his heart. It may have been Joseph Smith’s original hope and assumption, as expressed in the Howard Coray draft, that "one of them were" right, even if he had considered the theoretical possibility that the three denominations with which he had "intimate acquaintance" were all "wrong together" and that he would have to seek a religious home among another, less familiar one of "all the sects."[16]:101–102
If you had come to the conclusion that mankind has apostatized from the true faith, and you suddenly found Jesus standing in front of you, wouldn't you ask Him if any of those churches was the correct one? Or would you simply tell Him, "never mind, I already figured it out for myself"?
Could it be that Joseph simply misremembered? Why must one automatically have to be assumed that he was simply embellishing the story?
There are several interpretive possibilities for the supposed discrepancies between the accounts. Is it possible that Joseph Smith contradicted himself? Certainly. But it only remains just that: a possibility—one interpretive option among others. If we presume that Joseph was lying, our hostile reading will lead us to pick this option. If we grant that Joseph might be telling the truth, the other options will not be summarily rejected.
The answer to this apparent contradiction lies in a detailed examination of relevant texts. It is important to first compare Joseph Smith’s November 1832 text (which is in his own handwriting) with a newspaper article printed earlier that same year which refers to the Prophet’s inaugural religious experiences.
When both of these texts are taken into consideration the following storyline suggests itself: Joseph Smith had come to the conclusion, through personal scripture study, that none of the denominations WITH WHICH HE HAD AN INTIMATE ACQUAINTANCE was built upon the New Testament gospel. He prayed for guidance because he was "in doubt what his duty was." This doubt is obliquely referred to again in Oliver Cowdery’s February 1835 Messenger and Advocate partial First Vision recital where he said that because of the religious excitement the Prophet had "determination to know for himself of the certainty and reality of pure and holy religion."[24]
Doubt is present again in the Prophet’s November 1835 diary entry: "I knew not who was right or who was wrong and I considered it of the first importance that I should be right, in matters that involve eternal consequences."[25] So the conclusion this fourteen-year-old boy had reached through personal scripture study did not altogether solve his dilemma. In fact, in the May 1838 account he clarifies that because of his youth and inexperience in life he could not make an absolute decision with regard to this matter: "it was impossible for a person young as I was and so unacquainted with men and things to come to any certain conclusion who was right, and who was wrong"; "I often said to myself, what is to be done? Who of all these parties are right? Or, are they all wrong together? If any one of them be right which is it, and how shall I know it?"; "if any person needed wisdom from God I did, for how to act I did not know, and unless I could get more wisdom than I then had [I] would never know."
Orson Pratt’s 1840 First Vision account helps to explain why the ‘Joseph-decided-every-existing-church-was-wrong’ theory cannot possibly be valid. Elder Pratt reports, "He then reflected upon the immense number of doctrines now in the world which had given rise to many hundreds of different denominations. The great question to be decided in his mind was—if any one of these denominations be the Church of Christ, which one is it?" This expansive view is reflected in the Prophet’s 1838 account. There he states, "My object in going to enquire of the Lord was to know which of all the sects was right that I might know which to join. No sooner therefore did I get possession of myself, so as to be able to speak, than I asked the personages who stood above me in the light, which of all the sects was right (for at this time it had never entered into my heart that all were wrong) and which I should join."

In the 1832 account, Frederick G. Williams inserted the "in the 16th year of my age" above Joseph's text after Joseph had already written it. (See: "History, circa Summer 1832," The Joseph Smith Papers)

In Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision recital he said that he was "in the 16th year of [his] age" when the manifestation took place but in all other accounts in which he mentions his age, he was in his "fifteenth year."
The only First Vision account that provided a different age was the 1832 account written in Joseph Smith's own handwriting. In 1832, 12 years after the First Vision, Joseph wrote, "we were deprived of the bennifit of an education suffice it to say I was mearly instructid in reading and writing and the ground rules of Arithmatic which constuted my whole literary acquirements."
Although the portion of Joseph's 1832 history is in his own handwriting, the text insertion of "in the 16th year of my age" was in the handwriting of Frederick G. Williams, Joseph's scribe. It is likely that Joseph's dating schemes were slightly off when he dictated his age to Williams, many years afte the fact. There is nothing nefarious in Joseph Smith correcting his own slight mathematical miscalculations.
Two years later, Oliver Cowdery had Joseph's 1832 history in his possession when he began publishing history of the Church in late 1834 in the Latter-day Saints' Messenger and Advocate. Oliver clearly established Joseph's age as 14 ("the 15th year of his life") during the period of religious excitement (although Oliver ultimately never described the actual First Vision at this time). Once the date of the First Vision was correctly established it remained steady throughout all subsequent recitals as the "15th year" or "age 14."

The ages are not, as one critic states, "all over the place." [26] The only account produced by Joseph Smith that indicated a different age was the 1832 account (age 15 rather than 14, based upon a text insertion above the line by Frederick G. Williams after Joseph had already written his account). All remaining accounts indicate age 14 (the "15th" year).
In the 1832 account, Frederick G. Williams inserted the "in the 16th year of my age" above Joseph's text after Joseph had already written it. (See: "History, circa Summer 1832," The Joseph Smith Papers)

The 'one-year-off-the mark' dating anomaly of the 1832 First Vision account can best be understood by taking a look at all of the dates and time frame indicators that are provided within the document. It can then be seen that the farther back in time Joseph Smith goes, the more inexact his dating scheme becomes.
Notice that the date of the First Vision is an above-the-line insertion in the handwriting of Frederick G. Williams, meaning that it was not placed in the text initially but was added at a later time than the creation of the main text.
(17 years back in time)
(15 years back in time)
(12 years back in time)
(7 years back in time)
(5 years back in time)
We should carefully note that Joseph Smith correctly stated that he was "seventeen years of age" when the angel Moroni appeared to him on 22 September 1823, he got the time of that manifestation wrong by one year. A clue as to why this incorrect date was placed by the Prophet in this historical account can be found right in the 1832 document itself. Near the beginning of the narrative Joseph writes: "being in indigent circumstances [we] were obliged to labor hard for the support of a large family having nine children. And as it required the exertions of all that were able to render any assistance for the support of the family therefore we were deprived of the benefit of an education. Suffice it to say [that] I was merely instructed in reading and writing and the ground <rules> of arithmetic which constituted my whole literary acquirements". Elder Orson Pratt once asked rhetorical questions of the Prophet to illustrate his meager level of formal education: "Had you been to college? No. Had you studied in any seminary of learning? No. Did you know how to read? Yes. How to write? Yes. Did you understand much about arithmetic? No. About grammar? No. Did you understand all the branches of education which are generally taught in our common schools? No." (Journal of Discourses, 7:220-21). And when Elder Pratt wrote specifically about the First Vision he was even more specific about the level of the Prophet's math skills, saying that he had "a very limited understanding of the elementary rules of arithmetic." (Orson Pratt, An Interesting Account of Several Remarkable Visions [Edinburgh, Scotland: Ballantyne and Hughes, 1840],—-).
The 1832 history is not the only one where the Prophet made a dating mistake that was one year off the mark. He did the same thing when he created the 1838 Church history, but this time he got the year of his own brother's death wrong. He erroneously remembered that it was 1824 instead of 1823. The significant thing about this particular dating blunder is that four years after the Prophet recorded the initial information he came to the realization that it was not correct and had his scribe, Willard Richards, make the appropriate adjustment. Perhaps the problem with the date was brought to the Prophet's attention by a member of his own family after the information had been printed and made available for public perusal [publication in May 1842; correction in December 1842].
Initial Manuscript Record (2 May 1838)
Publication ( 15 March 1842 / 2 May 1842)
Post-Publication Manuscript Correction (2 December 1842)
A similar type of dating correction scenario, as mentioned above, may have taken place in connection with the 1832 history. Oliver Cowdery claimed that he had the Prophet's help in creating his December 1834 Church history article and despite the fact that he had the erroneously-dated 1832 document sitting in front of him [see paper on this subject] he provided the correct year for the Prophet's First Vision - "in the 15th year of his life" (i.e., between 23 December 1819 and 23 December 1820). And just nine months later the Prophet himself was telling a non-Mormon that the First Vision took place when he was "about 14 years old" (Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835).

An image from "mormoninfographics" is in circulation on the internet which mistakenly states that Joseph claimed that he was age 17 when the First Vision occurred. However, this was a misreading of Joseph Smith's 1835 journal entry, which clearly states that Joseph was age 14 at the time of the first vision, and age 17 at the time of Moroni's visit.

Is this evidence that this visionary tale evolved over time by becoming more dramatic and elaborate?
The 'struggle' motif is absent from the first known self-written account of the Prophet's visionary experience (1832) but it is also absent from his self-written Wentworth Letter account (1842). It is clear from the available documentary evidence that the Prophet did not feel constrained by the arbitrary rule of his modern critics that he must include every aspect of his First Vision story in every single retelling of it, and no reasonable person should be bothered that he doesn't.
The following timeline displays the 'struggle' material found in First Vision recitals that were produced during the Prophet's lifetime. The corresponding text from the 1832 document is also provided for purposes of comparison.
Several observations about the information presented below may prove useful.
September–November 1832
I cried unto the Lord for mercy. . . and while in the attitude of calling upon the Lord . . . a pillar of fire [or] light above the brightness of the sun at noonday came down from above and rested upon me and I was filled with the Spirit of God.
9 November 1835
I called on the Lord for the first time in the place above stated, or in other words, I made a fruitless attempt to pray. My tongue seemed to be swollen in my mouth, so that I could not utter. I heard a noise behind me like some one walking towards me. I strove again to pray, but could not. The noise of walking seemed to draw nearer. I sprang upon my feet and looked round, but saw no person or thing that was calculated to produce the noise of walking. I kneeled again, my mouth was opened and my tongue loosed. I called on the Lord in mighty prayer. A pillar of fire appeared above my head, which presently rested down upon me and filled me with unspeakable joy.
2 May 1838
I kneeled down and began to offer up the desires of my heart to God, I had scarcely done so, when immediately I was seized upon by some power which entirely overcame me and had such astonishing influence over me as to bind my tongue so that I could not speak. Thick darkness gathered around me and it seemed to me for a time as if I were doomed to sudden destruction. But exerting all my powers to call upon God to deliver me out of the power of this enemy which had seized upon me, and at the very moment when I was ready to sink into despair and abandon myself to destruction, not to an imaginary ruin but to the power of some actual being from the unseen world who had such a marvelous power as I had never before felt in any being, just at this moment of great alarm I saw a pillar of light exactly over my head above the brightness of the sun, which descended gradually until it fell upon me. It no sooner appeared than I found myself delivered from the enemy which held me bound.
September 1840
He therefore, retired to a secret place in a grove, but a short distance from his father's house, and knelt down, and began to call upon the Lord. At first, he was severely tempted by the powers of darkness, which endeavored to overcome him; but he continued to seek for deliverance, until darkness gave way from his mind, and he was enabled to pray in feverency of the spirit, and in faith. And while thus pouring out his soul, anxiously desiring an answer from God, he at length, saw a very bright and glorious light in the heavens above; which, at first, seemed to be a considerable distance. He continued praying, while the light appeared to be gradually descending towards him.
June 1841
He, therefore, retired to a secret place, in a grove, but a short distance from his father's house, and knelt down and began to call upon the Lord. At first, he was severely tempted by the powers of darkness, which endeavored to overcome him. The adversary benighted his mind with doubts, and brought to his soul all kinds of improper pictures and tried to hinder him in his efforts and the accomplishment of his goal. However, the overflowing mercy of God came to buoy him up, and gave new impulse and momentum to his dwindling strength. Soon the dark clouds disappeared, and light and peace filled his troubled heart. And again he called upon the Lord with renewed faith and spiritual strength. At this sacred moment his mind was caught away from the natural objects with which he was surrounded, and he was enwrapped in a heavenly vision.
1 March 1842
I retired to a secret place in a grove and began to call upon the Lord, while fervently engaged in supplication my mind was taken away from the objects with which I was surrounded, and I was enwrapped in a heavenly vision.
11 June 1843
he went into the grove & enquired of the Lord which of all the sects were right.
29 August 1843
I kneeled down, and prayed, saying, O Lord, what Church shall I join? Directly I saw a light.
24 May 1844
Went into the Wood to pray, kneels himself down, his tongue was close[d,] cleave[t]h to his roof—could utter not a word, felt easier after awhile—saw a fire toward heaven came near and nearer. . . . the fire drew nigher, rested upon the tree, enveloped him[, and] comforted [him].
Critical sources |
|
The theophany portion of the 1832 account does not specifically indicate that the Father appeared to Joseph Smith together with Jesus Christ. The relevant text (in its original form) reads as follows:
a piller of fire light above the brightness of the sun at noon day c[a]me down from above and rested upon me and I was filled with the spirit of god and the <Lord> opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord and he spake unto me saying Joseph <my son> thy sins are forgiven thee. go thy <way> walk in my statutes and keep my commandments behold I am the Lord of glory I was crucifyed for the world that all those who believe on my name may have Eternal life <behold> the world lieth in sin and at this time and none doeth good no not one they have turned asside from the gospel and keep not <my> commandments they draw near to me with their lips while their hearts are far from me and mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them acording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father.[29]
Even though the Savior makes a direct reference to the Father there is no indication in this portion of the 1832 document that God appeared to Joseph Smith alongside His Son.
This type of pattern is seen in the Book of Mormon, translated in 1829: The Book of Mormon begins (1 Nephi 1꞉8-10) with Lehi's vision of God on His throne. One [Christ] followed by twelve others descends from God to speak with Lehi—thus, Jesus and the Father are here both separate, and the role of Christ in giving instructions to the prophet while the Father looks on and approves is followed, just as it was in Joseph's First Vision. Here too, Lehi is described as praying to "the Lord," and yet has a vision of both God the Father and Christ.

There is a very significant phrase located in the introductory paragraph of the Prophet's historical narrative. There he indicates that the 1832 document is . . .
A History of the life of Joseph Smith Jr. an account of his marvilous experience and of all the mighty acts which he doeth in the name of Jesus Ch[r]ist the son of the living God of whom he beareth record and also an account of the rise of the church of Christ in the eve of time according as the Lord brough<t> [it] forth and established [it] by his hand <firstly> he receiving the testamony from on high secondly the ministering of Angels thirdly the reception of the holy Priesthood by the ministring of Aangels to adminster the letter of the Gospel—<—the Law and commandments as they were given unto him—>and the ordinencs, forthly a confirmation and reception of the high Priesthood after the holy order of the son of the living God.
This paragraph not only introduces the document with a heavy emphasis on the Son of God but it also chronologically outlines four inaugural events of the Restoration.
The significant phrase in the introductory paragraph is the one associated with the First Vision—"receiving the testimony from on high" (spelling standardized). When this phrase is placed in conjunction with the Prophet's 1835 and 1838 accounts of the First Vision it becomes obvious that the 1832 phraseology closely corresponds with the words spoken by God the Father when He introduced His Son in the Sacred Grove.
The Father's identification of Jesus Christ as His Son was His "testimony" of Him.
Critics have objected that—in their minds—the phrase "from on high" cannot be so easily equated with God the Father. But there is a sizable amount of corroborating evidence for this idea. Consider the following points of connection.
The Father's voice . . . came out of heaven [i.e., 'from on high'] and testified of His Beloved Son.
Joseph Smith stated, "the Lord God has spoken it; and we . . . have heard . . . the words of the glorious Majesty on high."
There are five New Testament scriptures (which Joseph Smith would have been familiar with from his work on the JST) that have distinct parallels to the First Vision story. Jesus Christ's Old World disciples heard the Father's voice come "from heaven" (Mt. 3:17; Mk. 1:11; Lk. 3:22; 2 Pt. 1:17-18) [i.e, 'from on high'] or "out of the cloud" (Mt. 17:5) [i.e., 'from on high'] and in each of these instances the Father testified of His Son and employed the same phraseology that Joseph Smith said He utilized during the First Vision
This chronological evidence points to the conclusion that Joseph Smith appears to have equated the voice "from on high" with God the Father both before and after he penned his 1832 First Vision account.
There is another line from the 1832 account that may be referring to two people:
I was filled with the spirit of God, and the Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord
It has been argued that the seperation of "Lord" into two may be referring to the Lord God [i.e., the Father] and the Lord Jesus Christ. Three pieces of evidence can be used to argue for this interpretation.
Some critics have taken issue with this evidence for the interpretation—claiming that since Psalm 110:1 was originally written in Hebrew with two different words for Lord (rendering "Lord" and "LORD" in all caps for the second mention) that the argument fails.[31]
Robert S. Boylan has responded by showing how Psalm 110:1 is the most quoted, echoed, and/or alluded to passage in the New Testament which Joseph would have been working on revising in his Inspired Translation of the Bible. He then shows that the revelations in Doctrine and Covenants leading up chronologically to the publication of the history containing the 1832 account of Joseph’s vision deliberately echo that verse (Doctrine and Covenants 20:24; 49:5-6; 76: 20, 23). If Joseph were familiar with that verse close to the publication of the account by way of the Old and/or New Testament and as echoed in his revelations published in the Doctrine and Covenants, it seems reasonable to assume that he could have used that verse as a template for rendering his account of events surrounding the First Vision.[32] This is even if one mention is capitalized and the other not. If the structure is deliberate and clear (and it appears so), then it seems odd to be upset that Joseph doesn't use capitals for the second "Lord" he writes about.
The 1832 account may be read to have a successive appearance of personages, one after the other. This is strengthened by the 1835 accounts mention of successive appearance. Further evidence of this in the 1832 account may be that Joseph was "filled with the spirit of God" before he mentions "the Lord".
Some have argued that the 8 uses of Lord in the 1832 account all refer to Jesus Christ.[33] There are at least three references that may be read otherwise:
A History of the life of Joseph Smith Jr. an account of his marvilous [sic] experience and of all the mighty acts which he doeth in the name of Jesus Christ the son of the living God of whom he beareth record and also an account of the rise of the Church of Christ in the eve of time according as the Lord brought forth and established by his hand.
A separation of "Christ" and "the Lord." This is able to be read with Christ or the Father as the Lord.
My mind became exceedingly distressed, for I became convicted of my sins, and by searching the scriptures I found that mankind did not come unto the Lord but that they had apostatized from the true and living faith, and there was no society or denomination that was built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament.
Joseph may be referring to coming to the Lord (i.e., the Father) and the gospel of Christ.
The third plausible evidence of the Father as Lord is the ending of the account:
My soul was filled with love, and for many days I could rejoice with great joy. The Lord was with me, but I could find none that would believe the heavenly vision. Nevertheless, I pondered these things in my heart.
The reference here is vague enough that it cannot be conclusively read one way or the othe—especially with the just-cited mention of the Lord.
Since it can be concluded from the above documentary evidence that Joseph Smith did indeed make an oblique reference to the appearance of the Father in his 1832 history the question becomes—Why did the Prophet construct the 1832 narrative in the manner that he did (so as to exclude explicit mention of the Father's appearance)? A careful analysis of the 1832 First Vision text reveals that it was deliberately constructed on the framework of many scriptural citations. The apostle Stephen's view of both the Father and the Son is clearly utilized by the Prophet in one section of the 1832 text but, more importantly, Joseph Smith told the actual theophany portion of this narrative in language that very closely corresponds to the apostle Paul's vision of Jesus Christ (Acts 26).[34] .
On this reading, the Father is not explicitly mentioned as making an appearance in the theophany portion of the 1832 First Vision account because Joseph Smith patterned that part of his narrative after the vision of Jesus Christ experienced by the apostle Paul.
Paul did not report that he saw the Father alongside the Son, and so it is logical that this is the reason why Joseph Smith did not explicitly mention the Father's appearance in his text either. The Prophet's strong sense of connection with Paul's visionary experience is referred to by him right in his 1838 First Vision account. The context of this connection is the persecution experienced by both men for speaking publicly about a heavenly manifestation. Joseph Smith relates in his 1838 history that he was informed by a clergyman that his vision was "all of the devil." This piece of information may help to explain why the Prophet chose to couch his first known written account of his vision in heavy biblical language and imagery. He may have hoped that by doing this his story would have a better chance of being accepted amongst a populace that was steeped in biblical content.
The Gospel Topics Essay touching on the first vision touches on another way of looking at the evidence. It focuses on the awkward repetition of the word "Lord" and how this may have been Joseph's perhaps uneducated way of stating the order of appearance of the personages:
Embellishment. The second argument frequently made regarding the accounts of Joseph Smith’s First Vision is that he embellished his story over time. This argument focuses on two details: the number and identity of the heavenly beings Joseph Smith stated that he saw. Joseph’s First Vision accounts describe the heavenly beings with greater detail over time. The 1832 account says, “The Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord.” His 1838 account states, “I saw two Personages,” one of whom introduced the other as “My Beloved Son.” As a result, critics have argued that Joseph Smith started out reporting to have seen one being—“the Lord”—and ended up claiming to have seen both the Father and the Son.
There are other, more consistent ways of seeing the evidence. A basic harmony in the narrative across time must be acknowledged at the outset: three of the four accounts clearly state that two personages appeared to Joseph Smith in the First Vision. The outlier is Joseph Smith’s 1832 account, which can be read to refer to one or two personages. If read to refer to one heavenly being, it would likely be to the personage who forgave his sins. According to later accounts, the first divine personage told Joseph Smith to “hear” the second, Jesus Christ, who then delivered the main message, which included the message of forgiveness.10 Joseph Smith’s 1832 account, then, may have concentrated on Jesus Christ, the bearer of forgiveness.
Another way of reading the 1832 account is that Joseph Smith referred to two beings, both of whom he called “Lord.” The embellishment argument hinges on the assumption that the 1832 account describes the appearance of only one divine being. But the 1832 account does not say that only one being appeared. Note that the two references to “Lord” are separated in time: first “the Lord” opens the heavens; then Joseph Smith sees “the Lord.” This reading of the account is consistent with Joseph’s 1835 account, which has one personage appearing first, followed by another soon afterwards. The 1832 account, then, can reasonably be read to mean that Joseph Smith saw one being who then revealed another and that he referred to both of them as “the Lord”: “the Lord opened the heavens upon me and I saw the Lord.”
Joseph’s increasingly specific descriptions can thus be compellingly read as evidence of increasing insight, accumulating over time, based on experience. In part, the differences between the 1832 account and the later accounts may have something to do with the differences between the written and the spoken word. The 1832 account represents the first time Joseph Smith attempted to write down his history. That same year, he wrote a friend that he felt imprisoned by “paper pen and Ink and a crooked broken scattered and imperfect Language.” He called the written word a “little narrow prison.” The expansiveness of the later accounts is more easily understood and even expected when we recognize that they were likely dictated accounts—an, easy, comfortable medium for Joseph Smith and one that allowed the words to flow more easily.[35]
Read the full article here.
It is worthwhile to note that the scribe for the material which directly precedes and follows after the 1832 First Vision narrative—Frederick G. Williams—never mentioned anything about Joseph Smith's story evolving over time and becoming more elaborate with the so-called 'addition' of the Father.
Williams was a resident of Quincy, Illinois when the First Vision account which explicitly refers to the Father was published in Nauvoo, Illinois on 1 April 1842. It is known that Williams was with the Prophet in Nauvoo shortly before his death on 10 October 1842 but during the intervening six months there is no known objection from Frederick to the content of the printed text. Why not? Williams was the person who wrote down the words in the introductory remarks of the 1832 document that talk of Joseph Smith receiving "the testimony from on high" during the First Vision. And it is known that Frederick was accompanying four LDS missionaries who, in November 1830, were teaching the citizens of Painesville, Ohio that Joseph Smith had seen "God" personally (see the 1830 statement about seeing "God").
Williams was a member of the First Presidency of the Church on 9 November 1835 when Joseph Smith was teaching a non-Mormon that there were two personages who appeared during the First Vision (see Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835). Frederick probably never drew attention to a so-called 'discrepancy' between what Joseph Smith taught in 1832, 1835, 1838, and 1842 because he knew that there wasn't one; he knew that the words of the Father spoken during the vision were referred to right in the text that he had written down in 1832.
Oliver Cowdery is another person who was in a position to know if the Prophet's First Vision story had changed over time by the addition of the Father. But he never mentioned any such 'discrepancy'. Cowdery had possession of the 1832 First Vision account when he wrote and published a series of Church history letters in December 1834 and February 1835 and so he was fully aware of the explicit mention of Christ's appearance and he also would have known of the introductory remark which refers to "the testimony from on high" being delivered during this event. Cowdery became the Associate or Assistant President of the entire Church on 5 December 1834 (Encyclopedia of Mormonism, 1653), and thus he would have been in the highest office of Church authority when the Prophet was teaching about one year later that two personages appeared during the First Vision (Joseph Smith diary, 9 November 1835).
Both Fredrick G. Williams and Oliver Cowdery had reason to feel animosity toward Joseph Smith and the Church since they were both excommunicated in the late 1830's. But neither of these men - even after their reinstatements into full fellowship - ever pointed to any 'creative editing' of the Prophet's First Vision story to sound more impressive and dramatic.
Critical sources |
|
Some have seen a discrepancy between the location of Deity in the Prophet's 1832 and 1838 First Vision accounts. The 1838 version says that the Prophet saw two Personages standing in the air above the earth, within his proximity. But the 1832 version is not so clear—it seems to locate Deity in heaven.
Details about Joseph Smith's First Vision experience are best interpreted by taking all of the extant accounts into consideration. A myopic focus on a limited number of historical documents can only lead to misunderstanding of the past and a twisted sense of the message that the author is trying to convey.
This so-called 'discrepancy' can be accounted for by the fact that Joseph Smith built his 1832 First Vision account using the framework of 47 biblical scriptures. And at this point in his manuscript he utilized Acts 7꞉55-56 to tell his story. It reads:
But [Stephen], being full of the Holy Ghost, looked up steadfastly into heaven, and saw the glory of God, and Jesus standing on the right hand of God.
And said, Behold, I see the heavens opened, and the Son of man standing on the right hand of God.
The Greek text that underlies the KJV translation says that Stephen looked into "heaven" (ouranos - 'the sky'; by extension: 'heaven'; also translated as 'air') and saw the "heavens" (the same Greek word - ouranos) opened. Thus, Stephen did not necessarily see Deity in their celestial abode - far beyond the confines of the earth - but rather standing above him in the air.
When Joseph Smith says in the 1832 First Vision account that he saw the Lord after the "heavens" (he uses the plural form) were opened he seems to be expressing the same idea that is found in the New Testament text.
Notice that the physical proximity of the Personages is established in the Prophet's 1835 recital: the pillar of fire can be physically seen in the air; the pillar of fire physically descends and rests upon Joseph; the pillar of fire has contact with physical objects that surround Joseph; two Personages are seen in the midst of this pillar of fire. Notice also that in the 1844 account the Prophet indicates that he could see with his natural eyesight the pillar "toward heaven", or up in the air. A glance at the 1840 account also shows that the phrase "in the heavens above" simply means "a considerable distance" up in the sky - it is not a reference to the celestial abode of Deity.
Critical sources |
|
The 1832 account of the First Vision does not portray the Lord as announcing that all the creeds were corrupt. These details do not show up until the 1838 account. Is this evidence that the Prophet's story evolved over time?
The claim that Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision story does not contain a divine injunction against joining any churches does not take evidence within the document itself into proper consideration. The information is implicit instead of explicit, but it is there nevertheless. This point cannot be legitimately used as evidence of an evolving storyline.
A quick look at the 1832 First Vision text reveals how untenable this claim is. Joseph Smith states that before he went into the woods to pray he had concluded in his own mind that "those of different denominations [which he was personally acquainted with]. . . did not adorn their profession by a holy walk and godly conversation agreeable to what [he] found contained in [the Bible] . . . . [There were] contentions and divisions [among them] . . . . [T]hey had apostatised from the true and living faith and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament."
Then, when Jesus Christ Himself made a personal appearance to Joseph in the grove, He informed the young boy that -
"the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good no not one they have turned aside from the gospel and keep not <my> commandments they draw near to me with their lips while their hearts are far from me and mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them acording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father"
To summarize:
How can critics possibly see this as anything other than a forceful and unambiguous indication on the Lord's part that joining any of the Christian denominations would be an unacceptable path for Joseph to take? Notice in the remainder of the 1832 text that Joseph says he felt great joy and love because of his experience and pondered the things which he had seen and heard during the vision . . . but during an interval of several years he did NOT join any church. Why?
As the 1832 text so plainly says—Joseph Smith believed that Christians had turned aside from the gospel; Jesus Christ confirmed that Christians had turned aside from the gospel; Joseph was therefore provided with a set of golden plates that contained writings which were "engrave[d] by . . . the servants of the living God." The 1832 account speaks three times of the "work" that God wanted Joseph Smith to do, while the 1838 account explicitly connects this "work" with the bringing forth of "the everlasting gospel." The 1842 First Vision account ties all of these themes together. There the Prophet relates: "I was expressly commanded to 'go not after them,' at the same time receiving a promise that the fulness of the gospel should at some future time be made known unto me."
Another indication from the 1832 document that Joseph Smith knew from the First Vision event that he should not join any of the churches can be found in something the Savior said to him. Jesus Christ explained that He was going to take action against the situation the world was currently in by "bring[ing] to pass that which hath been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles." What did this statement mean? In a canonized text written at approximately the same time as the 1832 First Vision account (September 1832) the following phraseology is found:
In other words, the Lord was telling Joseph Smith during the First Vision about the coming Restoration and so there would not be any need for him to join an existing church. This viewpoint is bolstered by several instances where the Prophet utilized the same phraseology used by the Lord during the First Vision to speak about the Restoration.
Critical sources |
|
Three of the primary sources that charge Joseph Smith with joining sectarian churches between 1820 and 1830 were produced in the latter part of the nineteenth century, over a half-century after the First Vision. None of the three are contemporary records; the earliest one was written 50 years after the First Vision took place.
We must note too that none of these sources confirms the others—they all discuss different denominations and different time frames. Thus, the stories are not mutually reinforcing.
Eyewitness reminiscences and contemporary records provide strong evidence that these claims are not valid and, therefore, do not reflect historical reality. The three sources are all late, and all from hostile voices.
Fayette Lapham claimed to have interviewed Joseph Smith Sr. in 1829-30, and published a report forty years later. In it, he reported:
About this time [1822, perhaps as late as 1824] he [Joseph, Jr.] became concerned as to his future state of existence, and was baptized, becoming thus a member of the Baptist Church.[42]
The Lapham source is secondhand at best—putting forward information that reportedly came from the Prophet's father. There are no records beyond this late, second-hand recollection to support this claim.
Joseph and Hiel Lewis were cousins of Emma Hale Smith; they would have been aged 21 and 11 respectively in 1828:
...while he, Smith, was in Harmony, Pa., translating his book....that he joined the M[ethodist] [Episocpal] church. He presented himself in a very serious and humble manner, and the minister, not suspecting evil, put his name on the class book, the absence of some of the official members, among whom was the undersigned, Joseph Lewis, who, when he learned what was done, took with him Joshua McKune, and had a talk with Smith. They told him plainly that such a character as he was a disgrace to the church, that he could not be a member of the church unless he broke off his sins by repentance, made public confession, renounced his fraudulent and hypocritical practices, and gave some evidence that he intended to reform and conduct himself somewhat nearer like a christian than he had done. They gave him his choice, to go before the class, and publicly ask to have his name stricken from the class book, or stand a disciplinary investigation. He chose the former, and immediately withdrew his name. So his name as a member of the class was on the book only three days.—It was the general opinion that his only object in joining the church was to bolster up his reputation and gain the sympathy and help of christians; that is, putting on the cloak of religion to serve the devil in.[43]
Note that Joseph did not inscribe himself, but the Methodist minister added Joseph's name to the class book. It is not surprising that Joseph might have attended Methodist services: Emma's family was involved in Methodism, she was related to Methodist ministers, and Joseph at this period was living on the Hale family's farm. The Hales had serious reservations about their new son-in-law, who claimed by this point to have the Book of Mormon plates in his possession. It would be natural for him to attend worship services with them if only to reassure them that he was not hostile to religion.
It is telling, though, that as soon as Joseph Lewis learned that Joseph had attended, he quickly took steps to disassociate the church from a person he saw as an imposter: note too that Lewis describes himself (rather than Joseph) as one "of the official members." A study of Methodist procedure makes it extremely unlikely that Joseph could have been a member of the Church, especially for only three days.
The Lewis source presents a scenario that was directly contradicted in print by an adult eyewitness who was a Methodist church officer. It is certainly possible that Joseph attended a Methodist meeting with his wife and in-laws: even in the Lewis' telling, however, he was quickly made to understand that he was not wanted, and he persisted in his own beliefs rather than continue with them.
| Main article: | Methodist membership procedures and Joseph Smith |
| See also: | Joseph became "partial to the Methodist sect" in 1820 |
S.F. Anderick (1887):
When Jo[seph Smith] joined the Presbyterian Church, in Palmyra village, it caused much talk and surprise, as he claimed to receive revelations from the Lord.[44]
As Dan Vogel notes, "Because Lucy Smith and three of her older children joined the Presbyterian Church, together with the possibility that Joseph Jr. may have attended some meetings with other family members, some observers may have assumed Joseph Jr. was also a member."[45] (Vogel notes that Lorenzo Saunders claimed in 1884 that he attended Sunday School with Joseph at the Presbyterian Church, and so that attendance (without formal membership) may be the source for this reminiscence.[46]
The Anderick source may simply be recalling an occasion when the young Prophet attended a church service with his Presbyterian mother and siblings.
The eyewitness sources that follow below indicate that up until the time that Joseph Smith announced the existence of the golden plates of the Book of Mormon to his family (23 September 1823) he was not formally attached to any church, but had instead publicly rejected all of them and manifested his desire NOT to join their ranks. Some are contemporaneous, others are later remembrances, but the hostile and friendly voices are clear that he had no denominational affiliation.
Pomeroy Tucker (a non-Mormon critic who knew Joseph Smith in Palmyra, New York) said that Joseph joined the Methodist probationary class in Palmyra but soon "withdrew from the class" without being converted; announcing that "all the churches [were] on a false foundation."[47] This information corresponds with historical details dated by Joseph Smith at around 1820.
Lucy Mack Smith:
Joseph Smith's mother recalled in her autobiography that shortly after her son Alvin died on 19 November 1823 Joseph "utterly refused" to attend church services with the intent to convert, and he made the specific request: "do not ask me to join them. I can take my Bible, and go into the woods, and learn more in two hours, than you can learn at meeting in two years, if you should go all the time."[48]
As can be seen by the continuing chronological sources which follow, Joseph Smith and his associates were teaching from 1825 to 1832 that the Prophet did not belong to any church between the years 1825 and 1827.
Josiah Stowell, Jr. (a non-Mormon):
I will give you a short history of what I know about Joseph Smith, Jr. I have been intimately acquainted with him about 2 years. He then was about 20 years old or thereabout. I also went to school with him one winter. He was a fine, likely young man and at that time did not profess religion.[49]
Peter Bauder:
In 1827 David Marks (a non-Mormon minister) went to Palmyra and Manchester, New York where he "made considerable inquiry respecting . . . [Joseph] Smith" and learned from "several persons in different places" that Joseph was "about 21 years [old]; that previous to his declaration of having found the plates he made no pretensions to religion."[50]
Observer and Telegraph (newspaper):
Four LDS men from New York state taught that at the time the angel appeared to Joseph Smith (22 September 1823) he "made no pretensions to religion of any kind."[52]
Palmyra Reflector (newspaper):
The editor of a Palmyra, New York newspaper claimed that he has been "credibly informed," and was "quite certain," that "the prophet . . . never made any serious pretensions to religion until his late pretended revelation"—meaning the Book of Mormon, which was made known among Palmyra's residents in the Fall of 1827.[53]
Orson Pratt:
Orson Pratt and Lyman Johnson taught on 8 April 1832 that "in 1827 a young man called Joseph Smith of the state of New York, of no denomination [i.e., not belonging to a church], but under conviction, inquired of the Lord . . . [and] an angel [appeared to him] . . . who gave information where the plates were deposited."[54] Pratt clarified in a much later statement that between 1820 and 1823 Joseph Smith "was not a member of any church."[55]
Thus, a great deal of contemporary evidence disproves the late, second hand claims.
Critical sources |
Primary Sources
|
One critical author states, "Joseph [Smith] added new elements to his later narratives that are not hinted at in his earlier ones. His first vision evolved from a forgiveness epiphany [1832 account] to a call from God the Father and Jesus Christ to restore the true order of things [1842 account]."
Taken altogether, the above information reveals that Joseph Smith considered his initial calling to have come directly from Deity in the Sacred Grove in 1820—not at some later time. The wording in the Prophet's 1832 First Vision account can be comfortably interpreted to mean that he understood this extraordinary event represented the beginning of a new gospel dispensation.
In Joseph Smith's 1832 account he plainly states that before the First Vision took place he was of the opinion that "mankind . . . had apostatized from the true and living faith, and there was no society or denomination that built upon the gospel of Jesus Christ as recorded in the New Testament." When the Prophet saw Jesus Christ face to face during the First Vision experience the Savior verified what Joseph had previously believed by saying, "the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good; no, not one. They have turned aside from the gospel and keep not my commandments" (emphasis added).
During the lifetime of Joseph Smith the word DISPENSATION was defined in a popular English dictionary in the following manner: "a system of principles and rites enjoined [or dispensed or bestowed]; as . . . the gospel dispensation; including . . . the scheme of redemption by Christ."[56] As noted above, Jesus Christ informed Joseph Smith that mankind had turned aside from the gospel and no longer kept His commandments. He then issued a directive straight to Joseph Smith by saying, "Walk in my statutes and keep my commandments" (emphasis added). This is clearly a new beginning; the Lord enjoined His ‘system of principles’ or ‘scheme of redemption’ upon Joseph Smith. This act qualifies—by definition—as a new dispensation of the gospel.
Was this early nineteenth-century dispensation of the gospel meant only for the benefit of Joseph Smith? In writing out the 1832 account the Prophet utilized some very specific wording when he said that "the world of mankind . . . . had apostatized" and he mourned for "the sins of the world." In his perspective "no society or denomination . . . built upon the gospel." And when the Lord spoke to Joseph during the vision He emphasized that this situation was on a universal scale saying, "the world lieth in sin at this time and none doeth good; no, not one." Thus, the 1832 account definitely describes a universal apostasy—and it makes no sense that the Savior would inaugurate a dispensation of His gospel only for the sake of one individual when innumerable humans were in need of salvation.
An entry found in the Encyclopedia of Mormonism agrees with the quotations provided above. It states with regard to the First Vision: "The Lord spoke face-to-face with Joseph and called him to service."[68]
Critical sources |
|
In light of the statements produced by Joseph Smith before he wrote the 1832 quotation of Jesus Christ in the Sacred Grove, it is not possible to uphold the claim that the Lord told the Prophet on that occasion that a Christian of any denomination automatically qualified for eternal life (in the LDS understanding of the term).
While it is true that the Lord is quoted in the 1832 First Vision account as saying "all those who believe on my name may have eternal life" it can be seen in an earlier revelation dated 7 March 1831 that those who "believe on [Christ's] name" must also "come unto [Him]" in order to "have everlasting life" (D&C 45꞉5).
The Lord does not state in the 1832 narrative that eternal life is available to members of every Christian church. Rather, He declares unambiguously in that account that "none" of the existing Christian denominations of the time were keeping His commandments; they had all turned aside from His gospel. From this piece of information alone, it is clear that eternal life could not be made available to them; they were categorized by the Lord as being in a state of "sin" (cf. Romans 5꞉21; Romans 6꞉22-23). In the 1832 text Jesus Christ says to Joseph Smith - "keep my commandments," and in connection with this it can be seen in a revelation dated March 1829 that the Lord informed the Prophet that he could only be granted "eternal life" if he was "firm in keeping the commandments" that Christ gave unto him (D&C 5꞉21-22; cf. D&C 14꞉7; D&C 18꞉8; D&C 30꞉8).
On 1 November 1831 the Lord affirmed to adherents of the LDS faith that there was "only [one] true and living church upon the face of the whole earth" (D&C 1꞉30). Earlier—in May 1831—He had spoken specifically to members of "the church that profess my name" (compare with the 1832 document wording) and indicated that only the faithful members of it who endured would "inherit eternal life" (D&C 50꞉4-5). Thus, the blessing of eternal life could not be obtained without complying with certain conditions.
Before Joseph Smith penned the Lord's words that are found in the 1832 First Vision text he clearly understood that:
The implication of this last point is that only one church can perform ordinances that will be considered valid in the sight of the Lord. And so a person can only be truly obedient to all of the Lord's commandments by holding membership in His one true Church. Joseph Smith indicated in the introductory remarks of the 1832 history that he had received priesthood authority, from a heavenly source, which enabled him to "administer . . . the commandments . . . and the ordinances".
Critical sources |
|
One discrepancy between the 1832 First Vision account and the official 1838 recital is that it portrays Jesus Christ as prophesying that He will return to earth quickly to destroy wicked mortals. The 1838 story makes no mention of the impending doom of this planet's depraved inhabitants.
The claim that there is a discrepancy between the 1832 and 1838 First Vision accounts on the point of the Second Coming and destruction of the wicked appears to be a desperate attempt at sowing discord. It is a charge without much substance. The Prophet's own statement about the omission of certain items can be legitimately utilized to account for several differences in the two documents.
This criticism loses its negative effect when it is weighed in the balance against the content of the relevant historical documents. In the 1832 account the Lord says:
mine anger is kindling against the inhabitants of the earth to visit them ac[c]ording to th[e]ir ungodliness and to bring to pass that which <hath> been spoken by the mouth of the prophets and Ap[o]stles behold and lo I come quickly as it [is] written of me in the cloud <clothed> in the glory of my Father.
There is, indeed, no reference to this specific prophecy in the First Vision portion of the 1838 document. However, Joseph Smith clearly states in that very narrative that Jesus Christ told him "many other things" during the First Vision that he decided not to write down at that time! Thus, an argument from silence (on the part of the critics) is utterly unconvincing. A close look at the remainder of the 1838 historical text reveals that the angel Moroni did, in fact, speak to Joseph Smith about prophecies of the Savior's return and the destruction of the wicked. The Prophet reports:
[The angel] first quoted part of the third chapter of Malachi and he quoted also the fourth or last chapter of the same prophecy though with a little variation from the way it reads in our Bibles. Instead of quoting the first verse as reads in our books he quoted it thus, 'For behold the day cometh that shall burn as an oven, and all the proud <yea> and all that do wickedly shall burn as stubble, for <they> that cometh shall burn them saith the Lord of hosts, that it shall leave them neither root nor branch.' And again he quoted the fifth verse thus, 'Behold I will reveal unto you the Priesthood by the hand of Elijah the prophet before the coming of the great and dreadful day of the Lord.' . . . . He also quoted the second chapter of Joel from the twenty eighth to the last verse. He also said that this was not yet fulfilled but was soon to be.
The 1832 and 1838 histories present the very same prophecy of the destruction of the wicked at the time of the Lord's Second Coming. The 1832 account portrays the Lord speaking it personally; the 1838 account portrays an angel relaying the words of the Lord as recorded in prophetic, biblical texts. Either way, the message is the same.
Critical sources |
|
Joseph Smith's 1832 First Vision account does not explicitly say that he was persecuted for relating his spiritual manifestation to others. Some have claimed that this stands as evidence that the Prophet's story evolved over time—probably to add a sense of drama. However, the Prophet's 1832 history of the Restoration talks about persecution in very close proximity to the First Vision recital. The persecution is situated squarely between the First Vision experience and the angel Moroni visitations. The documentary evidence presented above demonstrates conclusively that Joseph Smith did not see anything wrong with telling the basic elements of his First Vision story and either giving a passing reference to other elements or leaving them out altogether. Regardless, it was still a record of the very same experience that took place at the Smith homestead near Palmyra, New York.
Joseph Smith made some remarks in his 1832 First Vision account that have a marked degree of relevance to the argument being put forward by his critics. In relation to the period of time between the First Vision and the appearance of the Book of Mormon angel he said,
Since it is explicitly stated by Joseph Smith that nobody believed his story, it would be unreasonable to assume that all of the responses to it were friendly in nature. In fact, the Prophet says right in this text that before the Book of Mormon angel visited him his family was persecuted and afflicted for some unspecified reason(s). He did not elaborate upon the nature of the "many persecutions" that took place against his family because—as far as this particular document was concerned—he had elected not to write down "many things which transpired."
The following documentary evidence from the 1838 First Vision account strengthens the argument that the 1832 text is referring to some type of persecution that took place because of Joseph's initial spiritual experience.
This 1838 description corresponds very well with the "many persecutions and afflictions" that are mentioned in the 1832 account. It also matches closely with the 1832 statements that nobody would believe Joseph's story and he reflected upon this adverse situation in his heart.
It should be pointed out that even though the 'persecution' theme is very pronounced in the 1838 account it is a piece of the story that was not always mentioned or emphasized in subsequent retelling (both published and verbal).
This last example is especially significant because it is an obvious reference to the Methodist minister who is spoken of in the 1838 History of the Church account. The 1844 rehearsal of events is less detailed but it is, nevertheless, the same exact story. The 1844 document clearly demonstrates that Joseph Smith did not always include an equal amount of story elements in his recitals of the First Vision. Critics of this manifestation should, therefore, not expect any such thing when they scrutinize the pertinent documents. If an element of the story was not known by one particular audience it cannot be automatically assumed that it was not known by another.
Online |
|
Navigators |
Critical sources |
|
The capitalized word "Angels" in Joseph Smith's diary entry for 14 November 1835 has given rise to two distinct criticisms by detractors of the faith, and one misguided conclusion by some Latter-day Saints.
The mention of "many angels" in the November 9, 1835 diary entry is a clarifying detail. The appearance of the Father and Son are clearly referenced separately from the mention of the "many angels." Since the visit of the Father and Son are acknowledged in the diary entry for the 9th the change from "first visitation of Angels" to "the First Vision" in the History of the Church entry is not a "falsification" of information.
Joseph Smith never actually referred to what we now call the "First Vision" by that name. Instead, he referred to it as the "first visitation of angels" or the "first communication." Joseph also referred to Moroni's visit as "another vision of angels."

The account that Joseph entered in his journal on 9 November 1835 was a detailed account which clearly describes two personages, as well as "many angels." The account that Joseph wrote just five days later in his journal on 14 November 1835 was a one line summary of the event, which he described as "the first visitation of Angels." Critics of the Church seem to believe that Joseph completely changed his story from "two personages" to "Angels" over the course of only five days. The truth is that Joseph referred to all of the personages that appeared to him as "angels."
This confusion regarding "angels" versus "personages" is illustrated in a critical "Mormoninfographic".[70] We have illustrated the error by comparing Joseph's journal entries on both days.


There were at the time people who went to the wood to pray after reading the Bible, and as a result received visions and epiphanies. The Encyclopedia of Mormonism (1992; 2007) noted that "[i]nitial skepticism toward Joseph Smith's testimony was understandable because others had made similar claims to receiving revelation from God."[71] Similarly, the Church's new narrative history Saints (2018) notes that after Joseph's vision when he spoke to the reverend about his vision that "[a]t first the preacher treated his words lightly. People claimed to have heavenly visions from time to time."[72] Visionaries are not that uncommon in environments where people are routinely open to the divine. Even the famous Charles Finney had one. Finney, after retiring to the woods to pray, described the experience:
Just at this moment I again thought I heard someone approach me, and I opened my eyes to see whether it were so. But right there the revelation of my pride of heart, as the great difficulty that stood in the way, was distinctly shown to me. An overwhelming sense of my wickedness in being ashamed to have a human being see me on my knees before God, took such powerful possession of me, that I cried at the top of my voice, and exclaimed that I would not leave that place if all the men on earth and all the devils in hell surrounded me. "What!" I said, "such a degraded sinner I am, on my knees confessing my sins to the great and holy God; and ashamed to have any human being, and a sinner like myself, find me on my knees endeavoring to make my peace with my offended God!" The sin appeared awful, infinite. It broke me down before the Lord.
Just at that point this passage of Scripture seemed to drop into my mind with a flood of light: "Then shall ye go and pray unto me, and I will hearken unto you. Then shall ye seek me and find me, when ye shall search for me with all your heart." I instantly seized hold of this with my heart. I had intellectually believed the Bible before; but never had the truth been in my mind that faith was a voluntary trust instead of an intellectual state. I was as conscious as I was of my existence, of trusting at that moment in God's veracity. Somehow I knew that that was a passage of Scripture, though I do not think I had ever read it. I knew that it was God's word, and God's voice, as it were, that spoke to me. I cried to Him, "Lord, I take Thee at Thy word. Now Thou knowest that I do search for Thee with all my heart, and that I have come here to pray to Thee; and Thou hast promised to hear me."
That seemed to settle the question that I could then, that day, perform my vow. The Spirit seemed to lay stress upon that idea in the text, "When you search for me with all your heart." The question of when, that is of the present time, seemed to fall heavily into my heart. I told the Lord that I should take Him at his word; that He could not lie; and that therefore I was sure that He heard my prayer, and that He would be found of me.
He then gave my many other promises, both from the Old and the New Testament, especially some most precious promises respecting our Lord Jesus Christ. I never can, in words, make any human being understand how precious and true those promises appeared to me. I took them one after the other as infallible truth, the assertions of God who could not lie. They did not seem so much to fall into my intellect as into my heart, to be put within the grasp of the voluntary powers of my mind; and I seized hold of them, appropriated them, and fastened upon them with the grasp of a drowning man.
I continued thus to pray, and to receive and appropriate promises for a long time, I know not how long. I prayed till my mind became so full that, before I was aware of it, I was on my feet and tripping up the ascent toward the road. The question of my being converted, had not so much as arisen to my thought; but as I went up, brushing through the leaves and bushes, I recollect saying with emphasis, "If I am ever converted, I will preach the Gospel."[73]
Although Finney doesn't claim to have seen any personages, he does describe a communication with God. Joseph Smith describes his experiences in much the same way as others in his environment did.
Keep in mind that Joseph prayed to find out if his sins had been forgiven. And he discovered that they had. This pleased him greatly. Why did he pray about this matter? The reason is that joining a church at that time often required that one explain one's standing with God to a preacher. We are dealing with Protestant sects. And conservative Protestants believe that one is saved (justified) at the moment one confesses Jesus Christ as Lord and Savior. So Joseph, as he faced the competing Protestant sects, was deeply concerned about his sins. One had to demonstrate to oneself and also convince a preacher that one had been saved—that is, justified. And there were many instances in which prayers were answered by visions in which the person learned that God had forgiven their sins.
The difference between Joseph's experience and many other accounts by visionaries, is that, in addition to being told that his sins were in fact forgiven, he was also told not to join any denomination. When he told that part of his visionary experience, it got him into big trouble with preachers. It was not the vision that was a problem for preachers, but his reporting that he should not join some sect.
So the fact is, contrary to our current way of telling his story, the First Vision was not the beginning of Joseph's call as Seer, Prophet, Revelator and Translator. His vision signaled the beginning of the restoration. It did not begin the work of the restoration.It steered him away from joining one of the competing denominations. It was Joseph's subsequent encounters with Moroni that made him a Seer, and eventually the founding Prophet of a fledgling Church, and not his initial vision, which was initially for him a private event about which he was reluctant to talk, though eventually he dictated some accounts that were found and published during our lifetime. Joseph told a few people about it, word got around, and this caused him much trouble with Protestant preachers.
Joseph eventually wrote the account of that early vision late in his life because rumors about it had circulated and caused him difficulty. But neither Joseph nor any of the other early Saints offered that vision as a reason for others to become Latter-day Saints during his lifetime. It was only much later that what we now call the First Vision began to take on a special importance for the Saints. One reason is that Americans soon did not live in a visionary environment. The great Charles Dickens, writing in England, explained why. He called Joseph Smith vision an absurdity—"seeing visions in the age of railways."
Wilford Woodruff came into the Church of Jesus Christ because he had known earlier in his life someone he believed was a prophet who had alerted him to the soon to be restoration of primitive Christianity. This remarkable story, which was included in the lesson manual on President Woodruff, illustrates the visionary world in which Joseph was raised. Though there were a few—one or two—instances in which the visionary reported encounters with two heavenly messengers, it was most often God the Son who they reported appearing to them.
But there have been and still are peoples not impacted by post-enlightenment skepticism about divine things who are open to visions and other dramatic encounters with the divine, though they often do not speak in public about such things, since they tend to see them as strictly private blessings and not something about which one ought to be gossiping and boasting.
The first missionaries in the Church used The Book of Mormon, not the First Vision, as a witness that the heavens were open, and that each individual, by applying the promise in Moroni 10:3-5, can receive a direct manifestation from Heavenly Father, through the Holy Ghost, that The Book of Mormon is true. After that testimony is gained, it follows that Joseph Smith is a true prophet, as he brought The Book of Mormon forth and restored the fullness of the Gospel under the direction of the Savior.
The fledgling Church of Christ began with the Book of Mormon, the witnesses to the plates, the restoration of priesthood keys, and not directly with what we call the First Vision, though that initial experience assisted in Joseph avoiding what could be perceived as damaging sectarian contamination. The historical record shows that Joseph never gave any attention to the creeds or arguments of quarreling preachers. This was the purpose served by the First Vision.
Some Christians accept Paul's vision while rejecting that of Joseph Smith for a variety of reasons. Richard Lloyd Anderson made the following comparisons.
Many Christians who comfortably accept Paul’s vision reject Joseph Smith’s. However, they aren’t consistent in their criticisms, for most arguments against Joseph Smith’s first vision would detract from Paul’s Damascus experience with equal force.
For instance, Joseph Smith’s credibility is attacked because the earliest known description of his vision wasn’t given until a dozen years after it happened. But Paul’s earliest known description of the Damascus appearance, found in 1 Corinthians 9꞉1, was recorded about two dozen years after his experience.
Critics love to dwell on supposed inconsistencies in Joseph Smith’s spontaneous accounts of his first vision. But people normally give shorter and longer accounts of their own vivid experiences when retelling them more than once. Joseph Smith was cautious about public explanations of his sacred experiences until the Church grew strong and could properly publicize what God had given him. Thus, his most detailed first vision account came after several others—when he began his formal history.
This, too, parallels Paul’s experience. His most detailed account of the vision on the road to Damascus is the last of several recorded. (See Acts 26:9–20.) And this is the only known instance in which he related the detail about the glorified Savior prophesying Paul’s work among the Gentiles. (See Acts 26:16–18.) Why would Paul include this previously unmentioned detail only on that occasion? Probably because he was speaking to a Gentile audience, rather than to a group of Jewish Christians. Both Paul and Joseph Smith had reasons for delaying full details of their visions until the proper time and place.[74]
Joseph Smith left several accounts of his First Vision. None of these accounts is identical with any other. As the main page discusses, some critics wish to argue that Joseph's vision accounts are mutually contradictory, and thus that there was no vision.
Latter-day Saints often point out that the Bible's accounts of Paul's vision on the road to Damascus appear to be contradictory. Yet, the Church's sectarian critics accept Paul's account as true despite the Bible containing apparently frank contradictions in its accounts. While accepting or explaining away these discrepancies, the critics nevertheless refuse to give Joseph Smith the same latitude. Members of the Church have long pointed out that this is a clear double standard, designed to bias the audience against Joseph from the beginning.
Perhaps because of the force of this argument, some critics have begun to argue that no contradiction exists between the versions of Paul's vision.
Author Richard Abanes wrote that contradictions in the stories of Paul's vision were
long ago resolved by scholars analyzing the Greek texts. The discrepancies in Paul's account involve modern ignorance of the Greek wording used.[75]
In support of this claim, Abanes cites W.E. Vine, Vine's Expository Dictionary of New Testament Words p. 544.
Despite Abanes' claim, Greek scholarship has not resolved this issue. In fact, his use of the scholarship is dated, he ignores contrary views, and does not seem to realize that the Bible text itself (including the Acts of the Apostles) violates his supposed 'rule' more often than it keeps it.
The two verses usually at issue are Acts 9꞉7 and Acts 22꞉9. For example, one Wikipedia editor claims that
"There is no conflict in the three accounts of Paul's vision if you read Acts 22:9 in any version other than the KJV. For instance, in the New American Standard Bible and the New International version, it says that Paul's companions did not "understand the voice"—that is hear what was uttered with understanding."[76]
| Bible version | Acts 9:7 | Acts 22:9 | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Summary |
Heard voice, saw no one? |
Saw light, heard no voice? |
|
| KJV |
And the men which journeyed with him stood speechless, hearing a voice, but seeing no man. |
And they that were with me saw indeed the light, and were afraid; but they heard not the voice of him that spake to me. |
|
The work cited by Abanes is not a recent work of Greek scholarship—it was first published in 1940.[77] In the reference for ακούω, we read:
Thus, by this source, Abanes hopes to argue that there can be "no idea of any contradiction":
| Factor | Acts 9:7 | Acts 22:9 | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case |
partitive genitive |
accusative |
|
| Meaning |
One hears the sound |
One hears the message |
—|- |
We have seen Abanes appeal to a source that was more than sixty years old at the time of his writing. Have modern Greek scholars anything to add to our discussion?
Daniel Wallace (a non-LDS, conservative Christian scholar) wrote of this same issue:
...There seems to be a contradiction between this account [Acts 9:7] of Paul's conversion and his account of it in Acts 22, for there he says, "those who were with me..did not hear the voice..." However, in Acts 22:9 the verb ακούω takes an accusative direct object. On these two passages, Robertson states: '...it is perfectly proper to appeal to the distinction in the cases in the apparent contradiction....The accusative case (case of extent) accents the intellectual apprehension of the sound, while the genitive (specifying case) calls attention to the sound of the voice without accenting the sense.'...
The NIV [a conservative Bible translation, the New International Version] seems to follow this line of reasoning....[thus the differences in case] can be appealed to to harmonize these two accounts....(italics in original)[78]
Thus, Wallace is here dealing with the exact verses under discussion, and notes the exact argument which Abanes makes. Does he agree? Let us see:
On the other hand, it is doubtful that this is where the difference lay between the two cases used with ακούω in Hellenistic Greek: the N[ew] T[estament] (including the more literary writers) is filled with examples of ακούω + genitive indicating understanding[79]....as well as instances of ακούω + accusative where little or no comprehension takes place[80]}....The exceptions, in fact, are seemingly more numerous than the rule!
Thus, regardless of how one works through the accounts of Paul's conversion, an appeal to different cases probably ought not form any part of the solution (italics and bold italics in original).[81]
Thus, the New Testament itself does not agree with Abanes' reading. Far from supporting him, Greek scholarship argues against his solution—the Bible has more examples where his supposed "rule" is broken than when it is followed. (Even Acts itself contains three counterexamples!)
It would seem that this approach has been developed by those who wish to maintain the idea of biblical inerrancy in the face of the Greek evidence.
Critical sources |
|
Wiki links |
|
Online |
|
Video |
|
Navigators |
Author's source(s)
Matthew 16:18
Response
Author's source(s)
Hebrews 3:1; 4:14-16; 5:1-9; 6:20; 7:11-28.
Response
Author's source(s)
Doctrine and Covenants 115:4.
Response
Author's source(s)
Doctrine and Covenants 84:3-5
Response
The author states that Joseph Smith predicted that the Lord would come within “fifty-six years” and that this “prophecy never came true either.”
Author's sources: Joseph Smith, ‘’History of the Church’’, vol. 2 (Salt Lake Cithy: Deseret Book Co., 1978), 182.
Question: Did Joseph Smith prophesy that Jesus Christ would return in 1890?
Template:IndexClaimItemShort Question: Did Joseph Smith marry Fanny Alger as his first plural wife in 1833? Question: Did some of Joseph Smith's associates believe that Joseph Smith had an affair with Fanny Alger?
Template:IndexClaimItemShort Question: What was the Council of Fifty? Question: Was Joseph Smith anointed to be "King over the earth" by the Council of Fifty?

FAIR is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing well-documented answers to criticisms of the doctrine, practice, and history of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
We are a volunteer organization. We invite you to give back.
Donate Now